Graph torus by parametrical surface concept (picked up from 3b1b in khan academy)

Jacobian matrix. it’s critical in dealing with non-linear multivariable problem. The core of the idea is linearization of non-linear equations by fixating on a point, then approximate the micro level transformation to be linear by building up the partial derivative matrix of the function.
Laplacian Computation, for example, to compute the following function to get divergence, which is the expressed as triangle f = upside down triangle dot another triangle(gradient) f. The output is a scaler value, if positive, it’s diverging, vice versa.


Curl of vector field. analogous to the idea of divergence returns a scaler value to indicate if the fluid flow is positive, negative or zero curl.

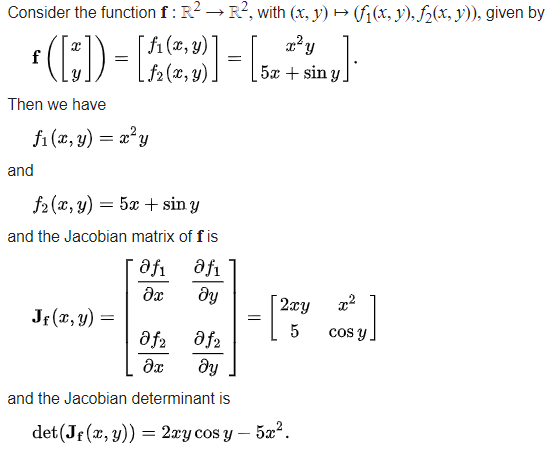
Lagrangian multiple is applied in optimization problems such as

Lagrangian is basically just the same concept of Lagrangian multiple, but repackaged in one equation.
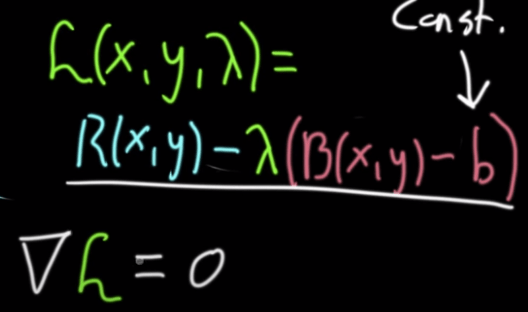
Rank of matrix, ranks are the true dimensions or features/columns that are not dependent to each other.
Go over the computation of ODE again, make sure grasp it to the level of proficiency.

Another example with forced damping, not sure how the A is deduced? theta is pie, sin(pie) = cos(pie), hence -sin(pie) –> –1 = 1???
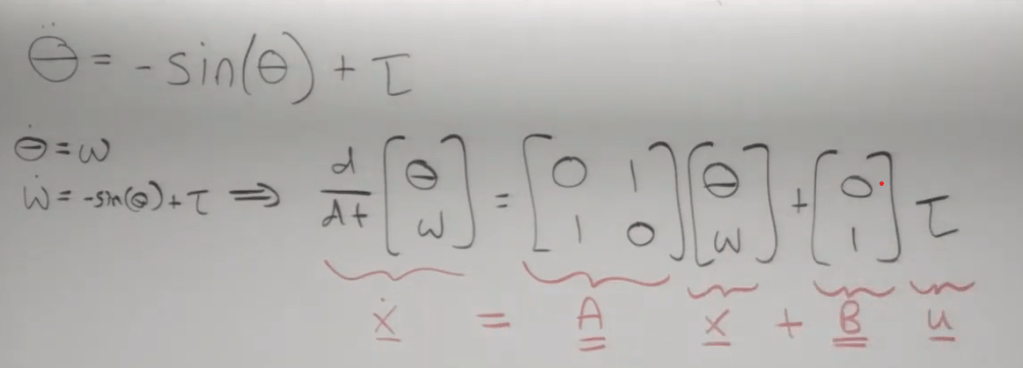
Convolution Integral, used in inhomogenous systems where a damping force is added on the right side of the ODE, for example
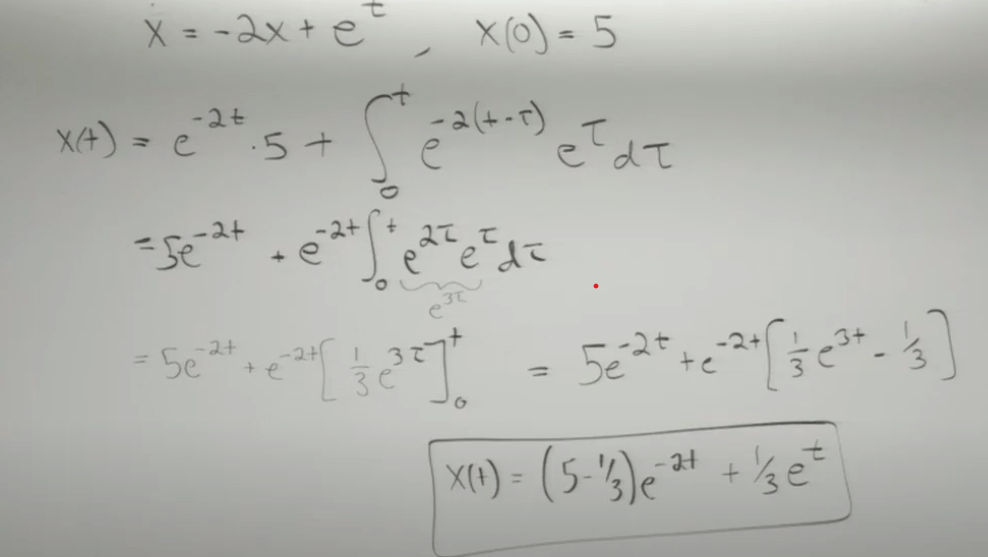
general solution versus particular solution to inhomogeneous equation.
Why Matrix, use Matrix to lower the higher order ODE all into first order ODEs, and easy to solve.
What is “singular” – a matrix/function is singular, means the determinant is zero. Some vector x after multiplication goes to/maps to/collapse to zero, equally, lost a degree of freedom, from higher dimensional space Rm to R(m-1).
“a subspace of a vector space consisting of vectors that under a given linear transformation are mapped onto zero” – formal definition
inverse matrix computation:
