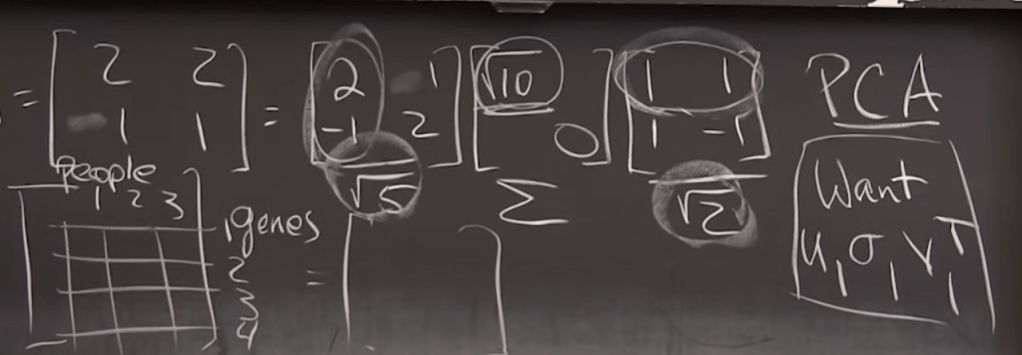SVD is such an important concept and technique in all walks of life especially in data science, we need to grasp to a deep level.
Professor J. Nathan Kutz might be the best one who explains SVD and relation to eigen vector eigen value so well.
It all starts from a fundamental understanding of what a matrix A does in the equation of Av. It rotate and stretch/squash the vector/function v. Using a simple example:

It rotates to the y vector in graph, and we can decompose to the theta rotation part and alpha stretching part:

Extending to two-dimensions – a sphere composed to two orthnormal unit vectors v1 and v2, being rotated and stretched a hyper ellipse:

Extending to multiple vectors(n-dim sphere): note this n by n dimension of vectors V is a hard-to-understand part. To put in another way, the question is why v is a n by n dimensions. V is the underlying a group of orthonormal vectors that will be transformed by the matrix A as well as defined in forming/collecting matrix A, which is the columns/features. Because there are n features when the experiment designer decides to collect, the row number of V is n, on the other hand, each row is supposed to be a set of scalars with the number of scalars equivalent to dimensions, so n again. sf
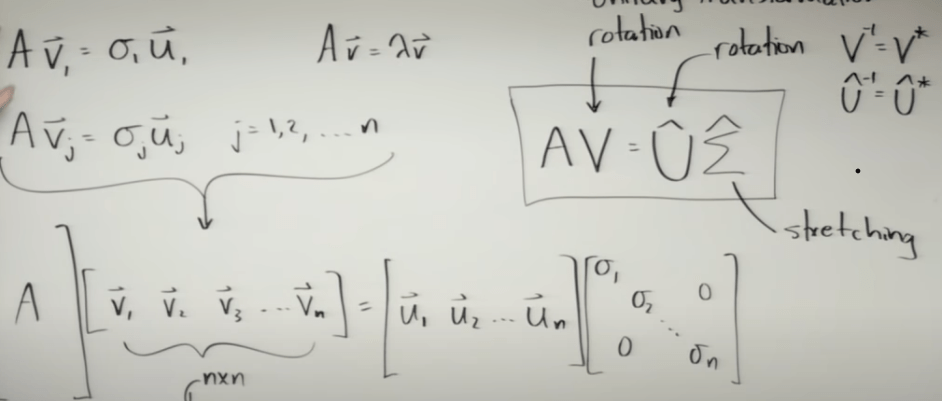
The form AV = Usigma is just a simplistic form of the same matrix idea above. Conceptually understanding v1…vn are orthonormal vectors, it’s easy to know the mxn of A, nxn of V, same, nxn of U hat and there are n sigmas.
After reviewing Dr.Strang’s course 18.065, it’s further clarified that U and V are eigenvectors of ATA and AAT respectively.

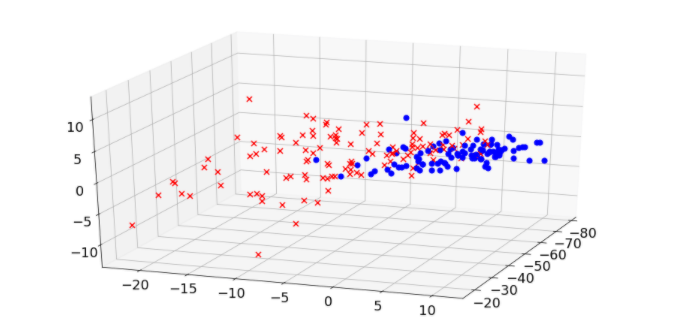
That’s how in ovarian cancer sample, once found pca, we can compute backward the diagnorsis/predicated value, then compare to the actual diagnosis by the graph below

Moreover, it’s worthy to stress the dimensions of A Uhat,sigma and V.T hat.
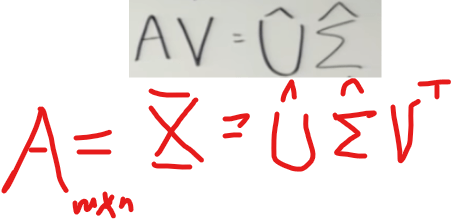
Next, how to compute SVD? Cleverly convert to eigen vector and eigen value computation as follows. Note the concept of unitary vector’s inverse is equivalent to it’s conjugate is applied here.
Next, how to compute SVD? Cleverly convert to eigen vector and eigen value computation as follows. Note the concept of unitary vector’s inverse is equivalent to it’s conjugate is applied here.
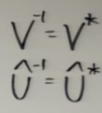
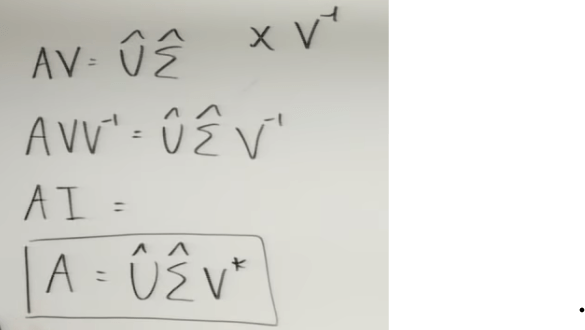

If we time transposed A on both sides of the equation,

It becomes an eigen problem that can be computed for both sigma (square of sigma is lambda) and unitary vector set V. Transpose A on another direction, we get unitary vector set of U:
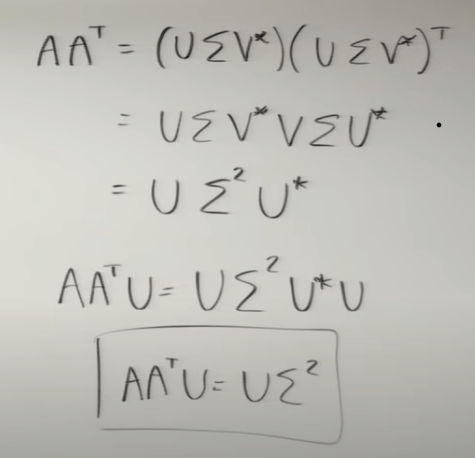
AtA is the the covariance matrix. The mathematical meaning of covariance or AtA is how similar the variances/change of features/dimensions are.
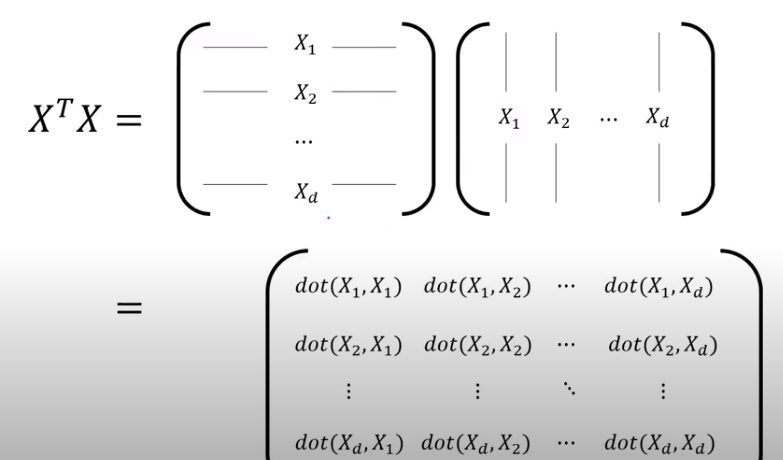
The result is a d by d symmetrical matrix. It is a pivoting and stretching (linear transforming) of original mxd matrix.
Enhancing this knowledge (because it’s so important) by Prof. Gilbert Strang on Dec 19th, 2022 by an example: