Word embeddings: an embedding is a dense vector of floating point values, which are trainable parameters. The more data amount, the higher dimensions/parameters. Conveniently, we can use pre-trained word embeddings downloaded from an external source (for example https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/glove/).
Word2vec is not a singular algorithm, rather, it is a family of model architectures and optimizations used to learn word embeddings from large datasets.
To be more specific, how are word embeddings created? What if you have to create word embeddings from scratch. This author gives a good answer in his blog, the diagram of steps to take for Word2vec is:
Read the text -> Preprocess text -> Create (x, y) data points -> Create one hot encoded (X, Y) matrices -> train a neural network -> extract the weights from the input layer.
Note, the X matrix will be created using the focus words and the Y matrix will be created using the context words. The next step is to choose the embedding dimension. I will choose the dimension to be equal to 2 in order to later plot the words and see whether similar words form clusters. The hidden layer dimension is the size of our word embedding in below neural network architecture. The output layers activation function is softmax. The activation function of the hidden layer is linear.
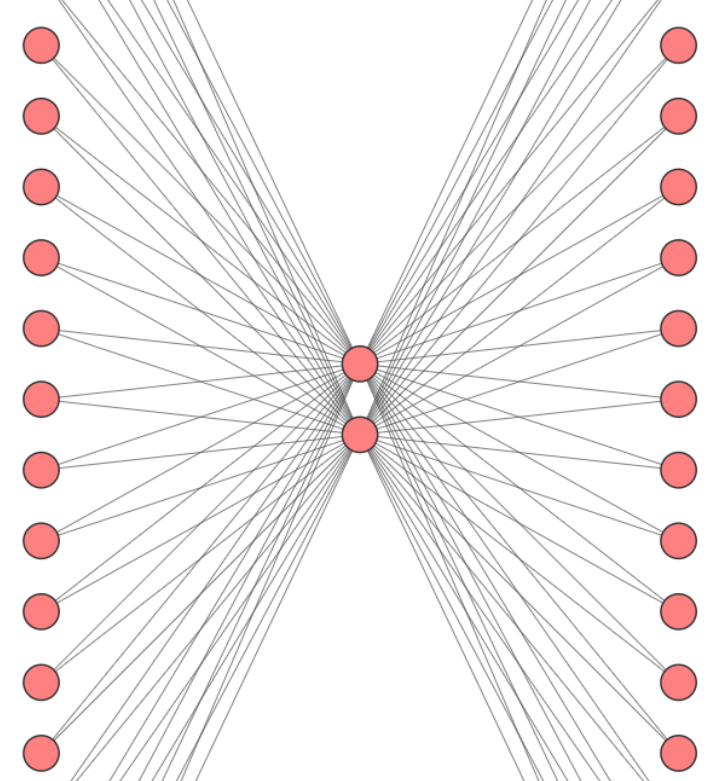
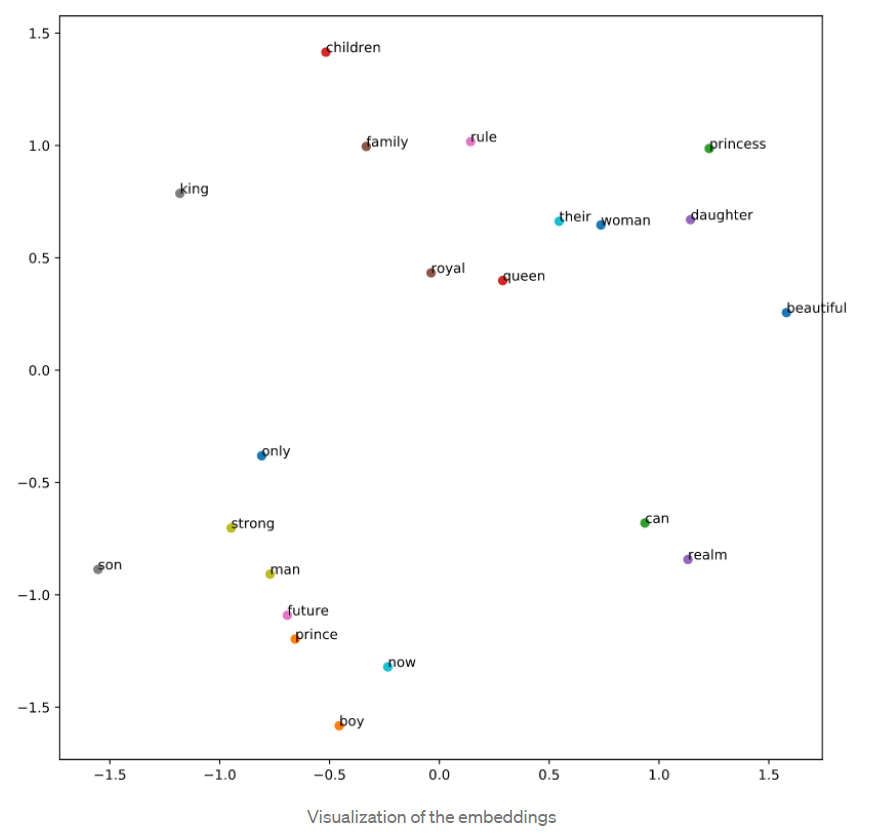
The weight of the two neurons are the parameters/dimensions of the embeddings, the sample words look like below after applying snippet of Neural Network computation
As is well known there are bag of words (BOG) and skip-gram two approaches in applying Word2vec. BOW model leverage the neighboring context without considering the sequence of words, while n-gram allow tokens to be skipped, so the context of word can be represented through a set of skip-gram pairs. Goal of skip-gram method is to maximize the probability of predicting context words given the target word. For a sequence of words w1, w2, … wT, the objective can be written as the average log probability
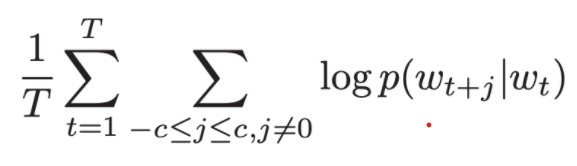
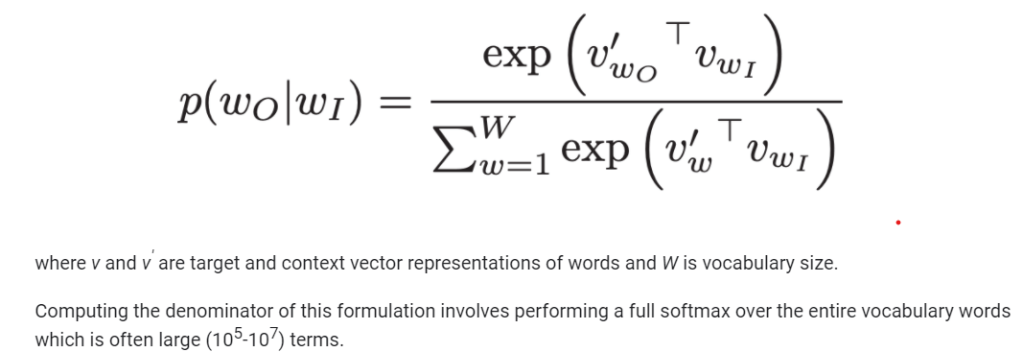
And the softmax probability is shown as
In practice, pre-trained word embeddings are used with typical word embedding dimensions being either 100, 200 or 300. The author personally use the embeddings stored here: \https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/glove/.
This is a massive quantity for computation, so Noise Contrastive Estimation loss function is an efficient approximation for a full softmax, of which the simplified form is “negative sampling”.
Next apply this RNN method for text classification, illustrated by Tensorflow official page, using IMDB large movie review dataset to conduct sentiment analysis.
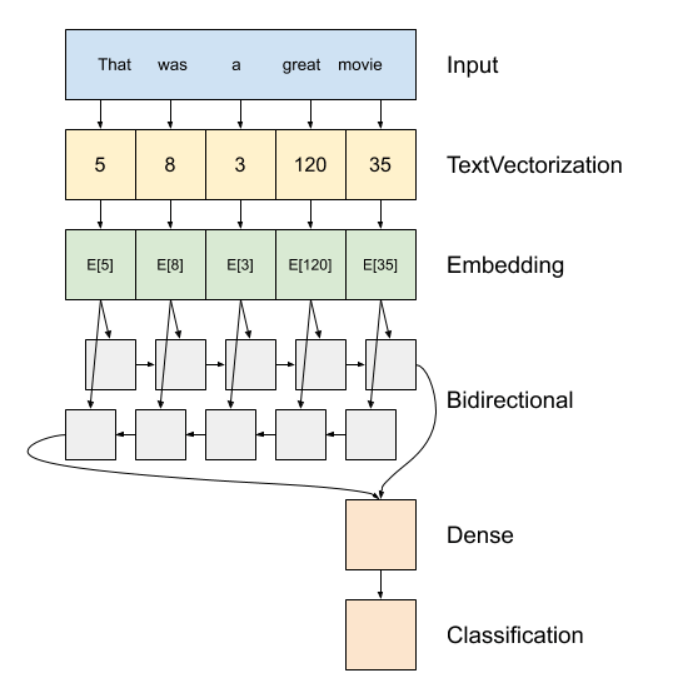
The first three steps: input texts, textvectorization and embedding are detailed already, next, RNNs pass the outputs form previous timestep as input to feed into the next timestep. The tf.keras.layers. Bidirectional wrapper propagate the input forward and backwards and then concatenates the final output.
sample_text = ('The movie was not good. The animation and the graphics '
'were terrible. I would not recommend this movie.')
predictions = model.predict(np.array([sample_text]))
print(predictions)
[[-1.7091906]]