In processing texts I inevitably reached to the point where I need to decide whether to choose RF or LSTM RNN algorithm for my project.
After reading a plethora of articles, blogs in conjunction with experimental runs, I come to a clear approach-RF.
Here I summarized above work:
In 2019, FREDRIK ANKARÄNG and FABIAN WALDNER published this paper – Evaluating Random Forest and a Long Short-Term Memory in Classifying a Given Sentence as a Question or Non-Question.
RF is an ensemble learning method for classification task, originally proposed by Ho[T. Ho, “Random decision forests,” Document Analysis and Recognition, International Conference on, vol. 1, pp. 278 – 282 vol.1, 09 1995]. It addresses issue of overfit for many decision tree based models. RF uses bagging to create an average. Instead of splitting each node using the best split among all variables, RF splits each node using the best among a subset of predictors randomly chosen at that node.
About the data, which provides perspective for my research, is “Data: The data used in the study was provided by the Swedish insurance firm Hedvig and was taken from their customer service chat. It contained approximately 400,000 chat messages. The data mainly contained conversations between the users and customer service employees, as well as some automatically generated messages by the company’s chatbot”, after cleansing, the resulting data set contained 13,758 sentences for classification.
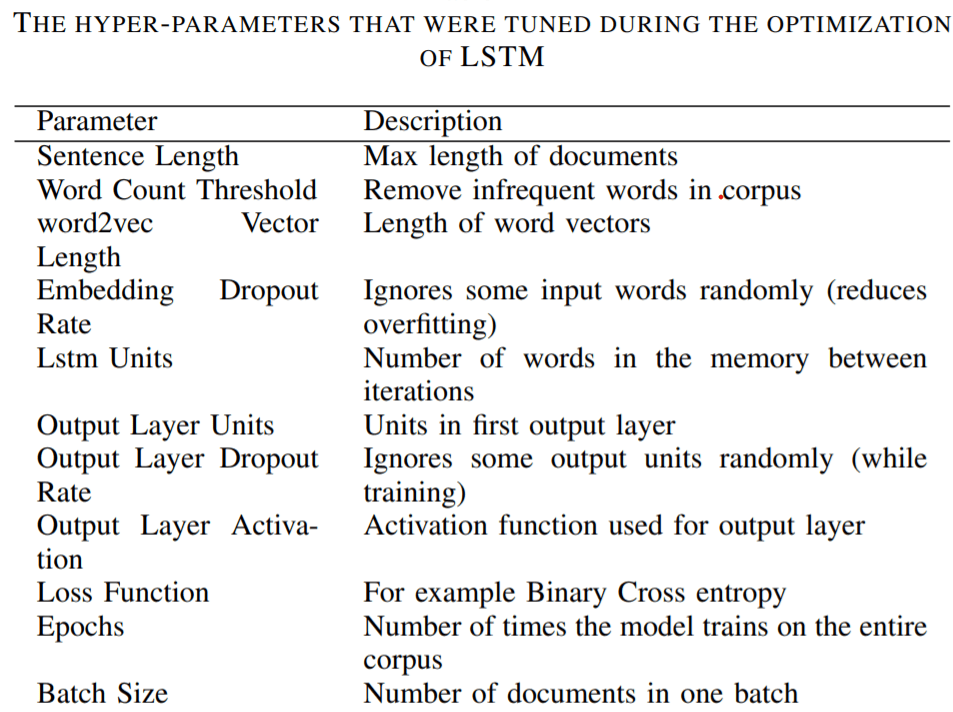
About the model, “Models: The models that were evaluated was a Random Forest and a Long Short-Term Memory neural network. The RF model used a Bag-of-Words representation of the documents. While the Bag-of-Words ignores the order of words as they appear in a document, the RF did consider n-grams of words as a feature. Hence, the RF did take the order of n-words into account. The LSTM utilized word embeddings. These were pre-trained Word2Vec vectors based on the Swedish Wikipedia2, trained with the skip-gram method. The vectors had a dimensionality of 300.”
Next important part of this research is to finetune the parameters of the two models respectively:

There is another paper SENTIMENT ANALYSIS USING RANDOM FOREST ALGORITHM-ONLINE SOCIAL MEDIA BASED published by an Indonesian student Bahrawi. The data was originally posted by Crowdflower last February and includes tweets about 6 major US airlines. Additionally, Crowdflower had their workers extract the sentiment from the tweet as well as what the passenger was disappointed about if the tweet was negative. As the original source says, a sentiment analysis job about the problems of each major U.S. airline. Twitter data was scraped from February of 2015. There are 14,640 tweets with 15 attributes.
In a blog authored by James Montantes, a deep comparison between RF and RNN is conducted.as the title explicitly declares there are three reasons he prefers RF instead of RNN, less computationally expensive and does not require a GPU to finish training and can give you a different interpretation of a decision tree but with better performance.