Discrete Mathematics contains a wide array of topics such as computer science(sorting), information theory(coding theory), logic(study of the principles of valid reasoning and inference), set theory, combinatorics(study in which discrete structures can be combined), graph theory, probability number theory, algebraic structures and calculus, geometry, topology.
First, the concept of preposition which is a statement of true of false, then there is unary and binary operator on one preposition. Unary can be negate while binary could involve two prepositions P & Q, the combination itself is a preposition. “P –> Q” means if P then Q is an implication of conditional statement.
There are multiple equivalent ways to express this implication pair:

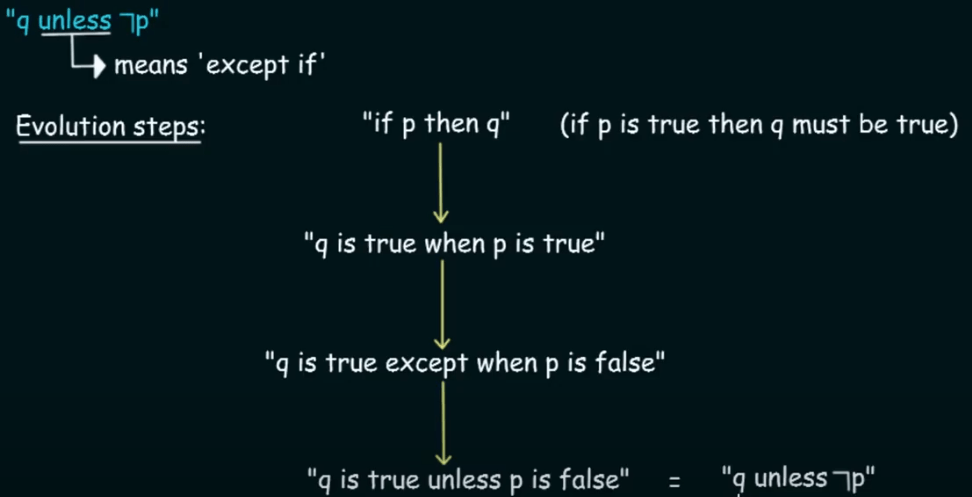
converse contrapositive and inverse

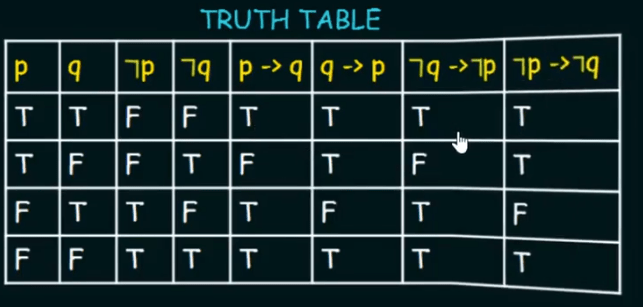
biconditional operator: p <–> q same as p iff q means p if and only if q.
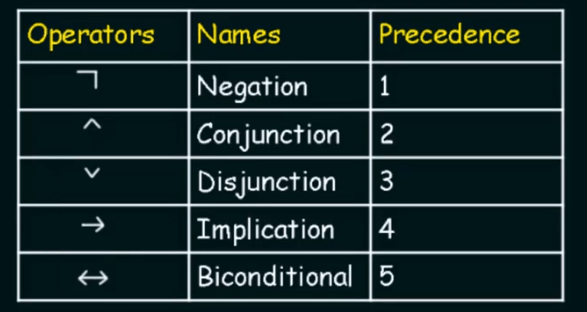
Here is the precedence table of logical operators:
What’s the purpose of learning this logical operators, here is the use case – translate esoteric English(other languages too) expressions into meaning.

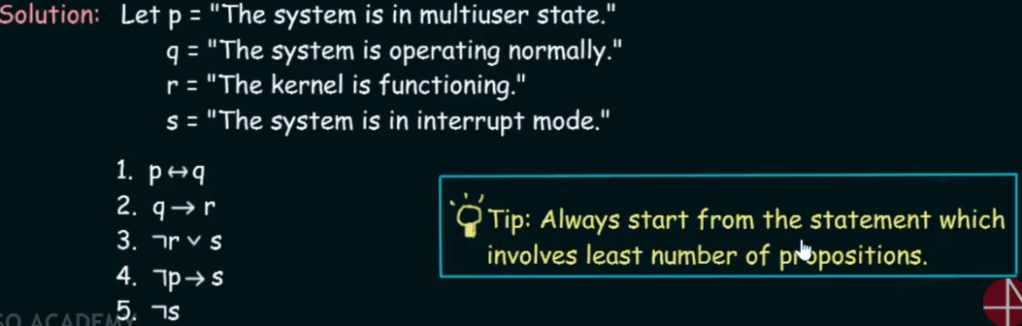
So system specifications consistent means all statements are true.