Lots of math problem in real world is hard to solve, an approach to tackle is called perturbation theory. What is perturbation theory, basically, we split the Hamiltonian into a piece we know how to solve (the “reference” or “unperturbed” Hamiltonian) and a piece we don’t know how to solve (the “perturbation”). As long as the perturbation is small compared to the unperturbed Hamiltonian, perturbation theory tells us how to correct the solutions to the unperturbed problem to approximately account for the influence of the perturbation.

When epsilon is zero, it is reduced to an unperturbed problem.
For example solve a hard problem X^5 + X = 1

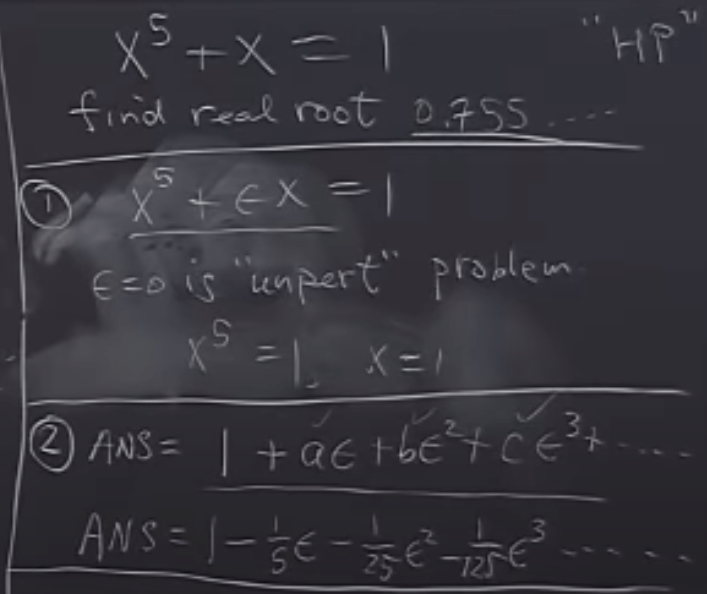
The essence of solving this kind of hard problem is not to get the equal output (f = g), but a asymptotic output (f ~ g).
Then jump to the Riccati Equation,
Riccati equation in the narrowest sense is any first-order ordinary differential equation that is quadratic in the unknown function. In other words, it is an equation of the form
