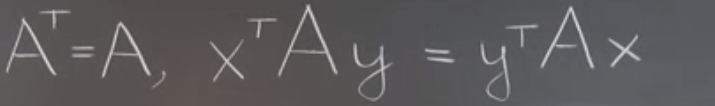Borrowed from algebra it becomes a genius work to weld matrix and algebra together. For the below linear system expression originally for polynomials, writing it to the form of Ax = b will be an incredible convenient algebraical way to solve math problems!
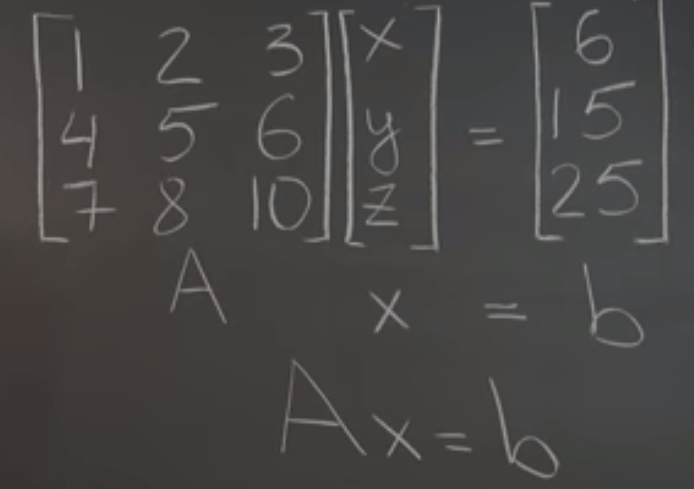
First, to lay out the matrix multiplication rules. it follows the same vein as previous linear combination and decomposition practices:

With a little bit more play around we came to realization that the matrix multiplication is basically actions exerted onto the matrix right side to the left side. For example, the single matrix/vector 1, 1, 1 here just pick each column in the left matrix and add up.
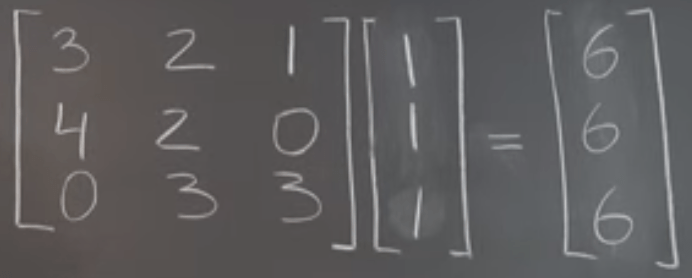
Then expand the right side vector to real matrix,

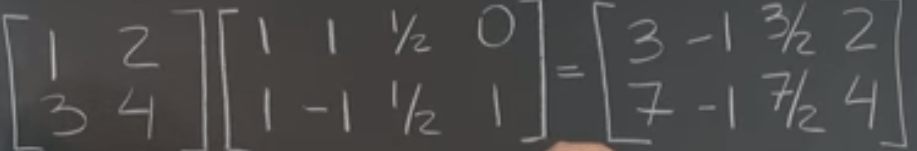
Another case
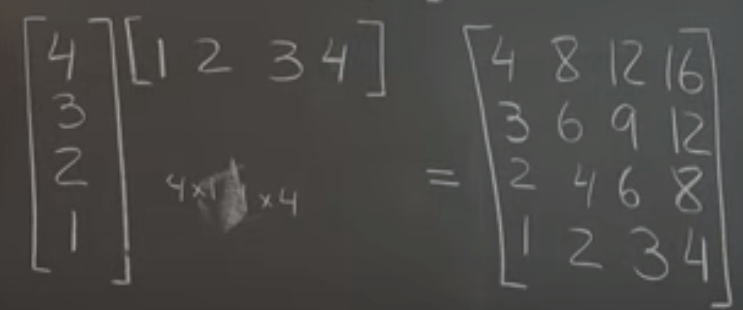
In actual computation, use the simple rule – row time column sequentially. You can picturing to pivot the column to row and line in the bottom of the left matrix. It’s consistent to column picking method. Note for particular position say column2, row3 in the final product, one just needs to pick the corresponding row3 in the left matrix and column 2 in right matrix and then pivot column2 to line up, adding each vertical product. This operation is given the name dot product.
Second, to study the null space features in matrix production. The Null Space of the Product AB is “equivalent” to the null space of the right matrix B as shown below, but in strict math language: we call Nb is subspace of NC. It’s a subspace not an equivalent because matrix A could be zero. What’s more important is to be able to infer this conclusion purely algebraically: CNb = ABNb = 0, hence Nb is subspace of Nc. Column space, Rc is the subspace of RA.
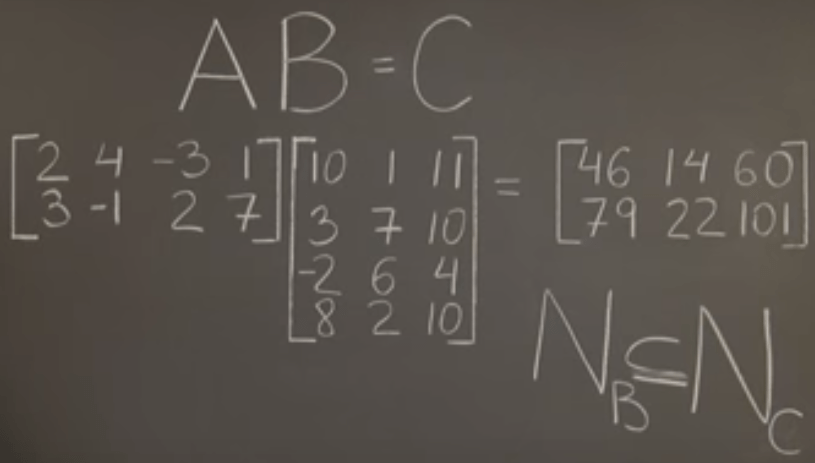
So to express null space, other than the traditional way below
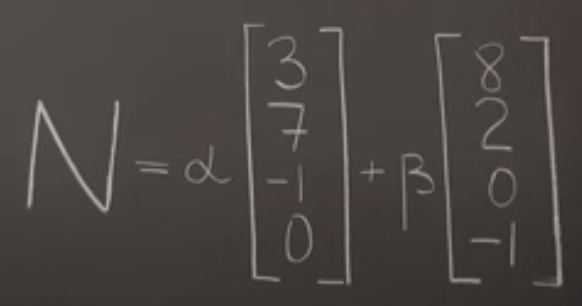
The new form is
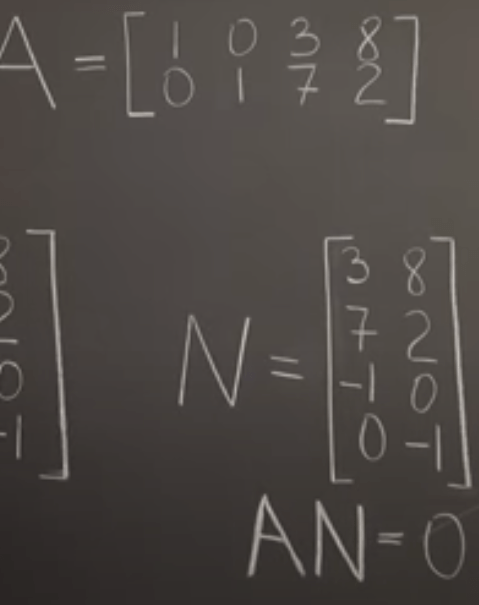
The optimal form is
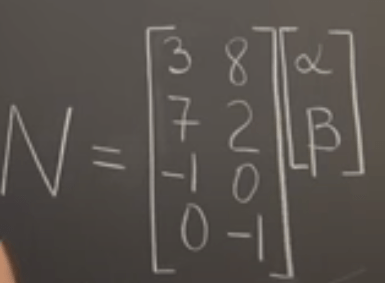
Second, go deeper to multiply three matrices, it’s the common forms we see all the time:

Identity Matrix: on the right side, normal position, it’s a column picker, if you put it on the left side, it’s a row picker.
Inverse Matrix: AB = BA, that’s a distinctive feature of inverse matrix. But not every matrix has an inverse. For example a three-three matrix composed of 123456789 to reach identity matrix is not possible.

how to calculate inverse matrix? There is an inverse matrix algorithm, that list the identity to the right side of the matrix, and then conduct the Gaussian Elimination. Why it works? Gr. Grinfeld has several explanations after learning elementary matrices:

how to calculate the inverse of matrix product?

Matrix multiplication can denote rotation:
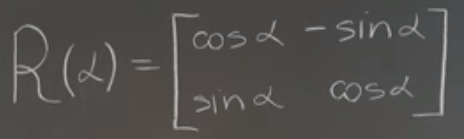

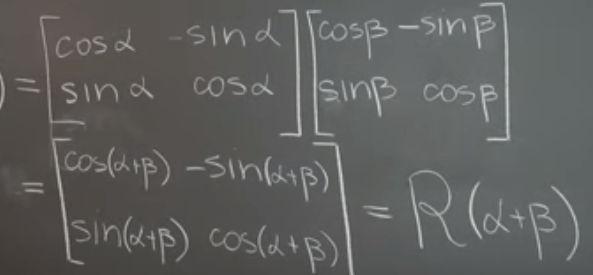
Matrix Transpose: transpose of product is the transpose of individual matrix in reverse order:


Symmetric Matrices: The product A ᵀA is Always a Symmetric Matrix. It’s insightful by simply looking at how they unfold. or it can be proved by

The Combination xᵀAy:

If the A is a symmetric matrix, x and y can switch positions.