According to this documentation published more than a decade ago, “the simplest type of mathematical program is a linear program. For your mathematical program to be a linear program you need the following conditions to be true:
• The decision variables must be real variables;
• The objective must be a linear expression;
• The constraints must be linear expressions.
Linear expressions are any expression of the form a1x1 + a2x2 + a3x3 + …anxn{<=, =, >=}b
where the ai and b are known constants and xi are variables. The process of solving a linear program is called linear programing. Linear programing is done via the Revised Simplex Method (also known as the Primal Simplex Method), the Dual Simplex Method or an Interior Point Method.
PulP call any of numerous external LP solvers (CBC, GLPK, CPLEX, Gurobi etc) to solve LP model and then use python commands to manipulate and display the solution.
Case Study 1 – Scheduling Problem provided by Ritvikmath at his github. Hypothetically there is a small workshop composed of n workers, and take shift to conduct tasks. There are several constraints:
- each day there are 2 persons on duty
- work is distributed evenly
- time-off requests respected
So to put above constraints into codes:
from pulp import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from time import time
#constraint1
def add_enough_workers_constraint(prob: pulp.LpProblem, p_vars: list, num_employees: int, num_days: int, num_shifts_per_day: int):
#for each day...
for d in range(num_days):
#make sure that enough people are working
prob += sum([p_vars[i][d] for i in range(num_employees)]) == num_shifts_per_day
#constraint2
def add_equal_work_constraint(prob: pulp.LpProblem, p_vars: list, num_employees: int, num_days: int, num_shifts_per_day: int):
#get the upper and lower limits of number of days each employee will work
lower_days_worked = int(num_shifts_per_day*num_days/num_employees)
upper_days_worked = lower_days_worked + 1
#for each employee...
for n in range(num_employees):
#make sure that they are working AT MOST upper_days_worked
prob += sum(p_vars[n]) <= upper_days_worked
#make sure that they are working AT LEAST lower_days_worked
prob += sum(p_vars[n]) >= lower_days_worked
#constraint3
def add_time_off_constraint(prob: pulp.LpProblem, p_vars: list, time_off_requests: list, num_employees: int, num_days: int):
#for each time off request...
for employee, day in time_off_requests:
#add constraint that this person will not work on this day
prob += p_vars[employee][day] == 0
Note the special features in PuLP is to define prob is Lp Problem or other problem, then p_vars as list, in this case list composed of i(employees) and d(days), lastly, note that plus equal sign after prob to be an operation such as sum of some items meets certain constraints.
Then set objective function
#objective function
def get_number_matching_shifts(prob: pulp.LpProblem, p_vars: list, shift_preferences: list, num_employees: int, num_days: int):
#create initial preference list, all 0
preference_list = [0 for _ in range(num_employees*num_days)]
#for each shift preference...
obj = 0
for employee, day in shift_preferences:
#add this to optimization problem
obj += p_vars[employee][day]
prob += obj
Finally wrap up in one function and run, spit out the diagram
#drive code
def get_shifts(num_days: int, num_employees: int, num_shifts_per_day: int, time_off_requests: list, shift_preferences: list):
#init problem and define all vars
prob = LpProblem("shifts", LpMaximize)
p_vars = [[] for _ in range(num_employees)]
leading_zeros_employees = '0'*int(np.log10(num_employees-1))
leading_zeros_days = '0'*int(np.log10(num_days-1))
for n in range(num_employees):
for d in range(num_days):
var_name = f'P_{(leading_zeros_employees+str(n))[-len(leading_zeros_employees)-1:]}_{(leading_zeros_days+str(d))[-len(leading_zeros_days)-1:]}'
v = LpVariable(var_name, 0, 1, LpInteger)
p_vars[n].append(v)
get_number_matching_shifts(prob, p_vars, shift_preferences, num_employees, num_days)
add_enough_workers_constraint(prob, p_vars, num_employees, num_days, num_shifts_per_day)
add_equal_work_constraint(prob, p_vars, num_employees, num_days, num_shifts_per_day)
add_time_off_constraint(prob, p_vars, time_off_requests, num_employees, num_days)
start = time()
status = prob.solve()
end = time()
seconds = end - start
print('Status:', 'success' if status==1 else 'failure')
print('Seconds:' if seconds > 1 else 'Milliseconds:', round(seconds,2) if seconds > 1 else int(seconds*1000))
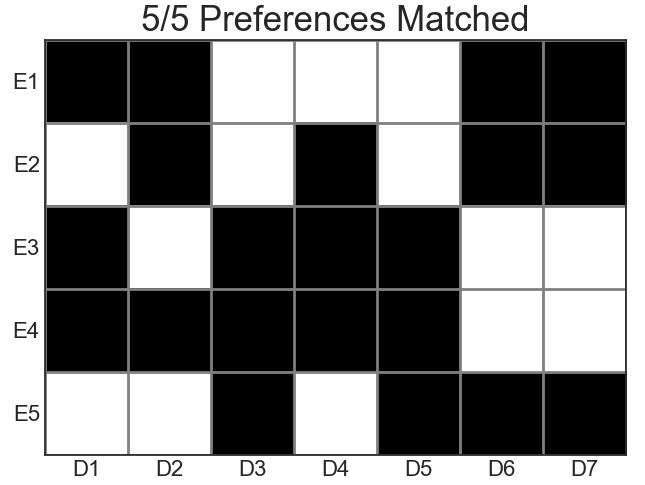
shifts = np.array([int(v.varValue) for v in prob.variables()]).reshape(num_employees, num_days)
plt.figure()
plt.figure(figsize=(num_employees*1.5, num_days*1.5))
im = plt.imshow(shifts, aspect='equal', cmap='gray')
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(0, num_days, 1))
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(0, num_employees, 1))
# Labels for major ticks
ax.set_xticklabels([f"D{i}" for i in range(1,num_days+1)], fontsize=16)
ax.set_yticklabels([f"E{i}" for i in range(1,num_employees+1)], fontsize=16)
# Minor ticks
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(-.5, num_days, 1), minor=True)
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(-.5, num_employees, 1), minor=True)
# Gridlines based on minor ticks
ax.grid(which='minor', color='gray', linestyle='-', linewidth=2)
num_prefs_matched = int(prob.objective.value())
plt.title(f'{num_prefs_matched}/{len(shift_preferences)} Preferences Matched', fontsize=25)
print('===============================')
for i, time_off_request in enumerate(time_off_requests):
print(f"E{time_off_request[0]+1} cannot work on D{time_off_request[1]+1}")
print('===============================')
for i, shift_pref in enumerate(shift_preferences):
print(f"E{shift_pref[0]+1} prefers working on D{shift_pref[1]+1}")
print('===============================')
plt.show()
return prob, shifts
#play around with these
num_days = 7
num_employees = 5
num_shifts_per_day = 2
time_off_requests = [
[0,0],
[0,1],
[2,0],
[3,0],
[4,5]
]
shift_preferences = [
[0,2],
[0,4],
[1,4],
[2,1],
[4,0]
]
prob, shifts = get_shifts(num_days, num_employees, num_shifts_per_day, time_off_requests, shift_preferences)