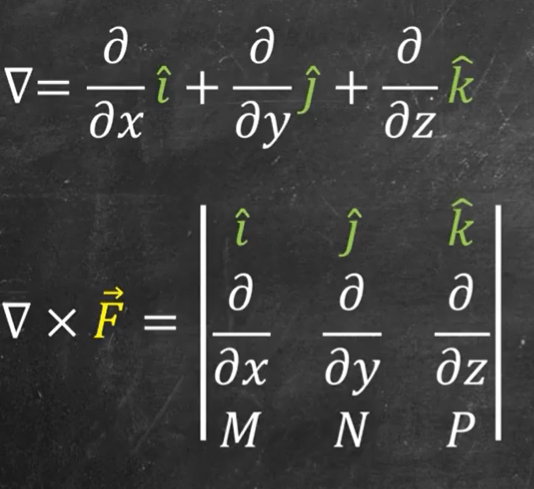With the foundation constructed in last blog Multivariable Calculus_6, we now dive into implicit surface which is hovering above an 2-D plane underneath, we claim these conditions:

Then the surface area can be computed as
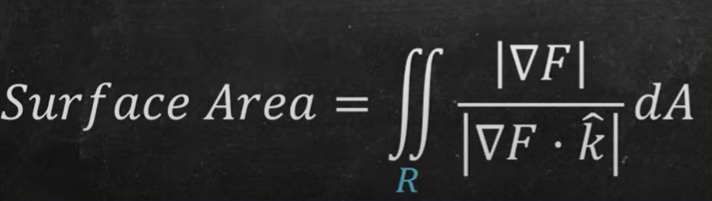
It can be generalized to other axis if we replace the k hat to a generic symbol p hat. So if we have an explicit plane as

The details with an example can be viewed at this clip.
Next upgrading to higher dimensions, from 2D to 3D, the formulas are similar:
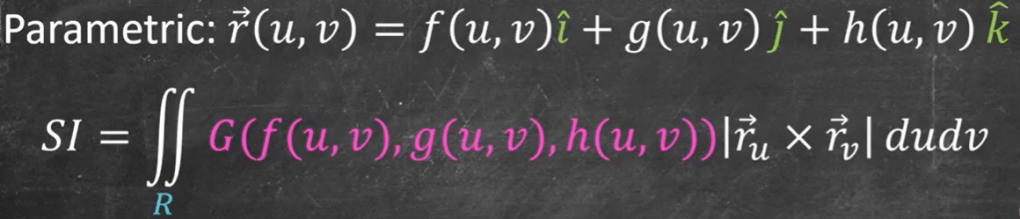
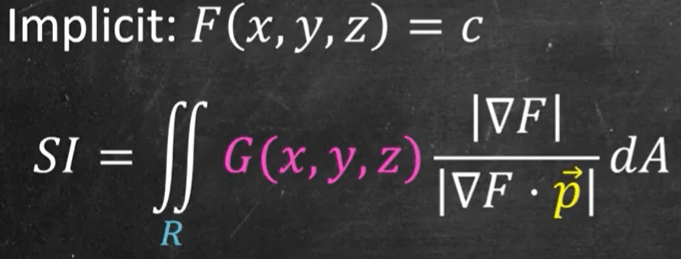

Deduce the following formulas and followed up with some examples.
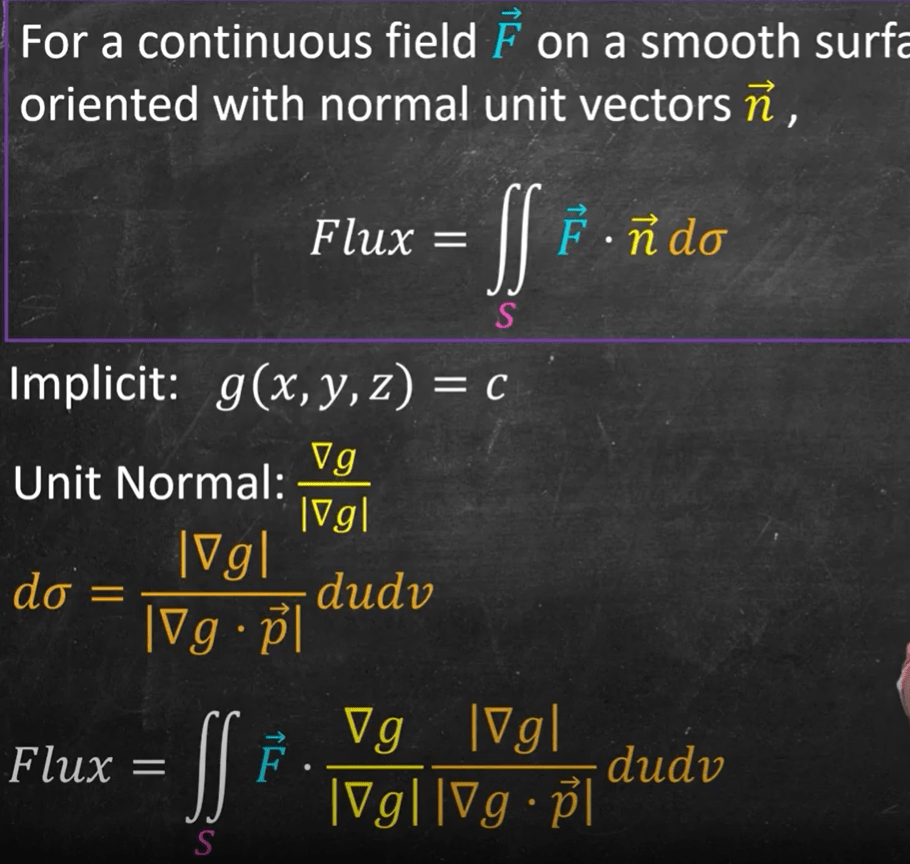
Curl in 3D:
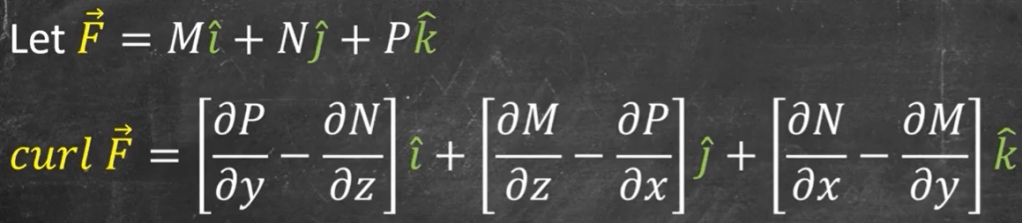
Here he gives a great definition of “operator”, which is also a function that takes in other function and spit out new function such as
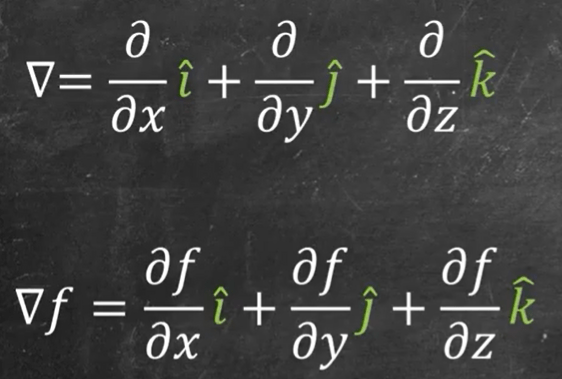
the delta here is the operator. We also heard of Laplacian operator like gradient of gradient function.
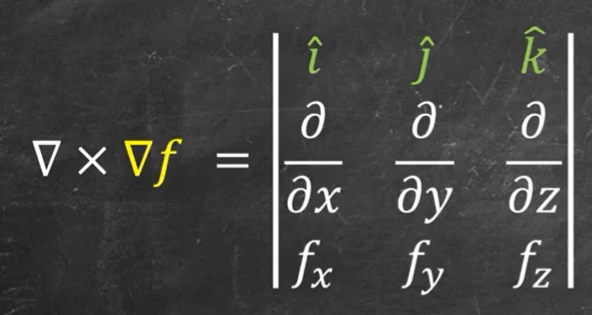

Another operator is like this