What is HTTPS, it’s composed of HTTP and S part. HTTP, in whole is The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) for content to be transferred via internet. However it’s not safe, so Secure Socket Layer (SSL) layered on top of HTTP, creating HTTPS. By default HTTP use port 80 and HTTPS uses 443. Here are commonly used ports:

Note we also saw 8888, for example one can type “telnet etna.informatik.privat 8888” to connect to a private localhost.
TLS is composed of several sub-protocols such as record protocol, handshake protocol, warning protocol, change cipher specification protocol, extended protocol, etc. It uses a number of cutting-edge cryptographic technologies such as symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption, and identity authentication. The browser and the server need to select a set of appropriate encryption algorithms to achieve secure communication when using TLS to establish a connection. The combination of these algorithms is called a “cipher suite” also called an encryption suite.
There are symmetric and asymmetric encryption. The design of asymmetric encryption algorithms is much more difficult than symmetric algorithms. There are only a few in TLS, such as DH, DSA, RSA, ECC, etc. RSA is probably the most famous of them. It can almost be said to be synonymous with asymmetric encryption. Its security is based on the mathematical problem of “integer factorization”. It uses the product of two very large prime numbers as the material for generating the key. It is very difficult to calculate the private key. 10 years ago, the recommended length of RSA keys was 1024, but with the improvement of computer computing power, 1024 is now insecure, and it is generally believed that at least 2048 bits are required. ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) is a “rising star” in asymmetric encryption. It is based on the mathematical problem of “elliptic curve discrete logarithm”. It uses specific curve equations and base points to generate public and private keys. The sub-algorithm ECDHE is used for key exchange. , ECDSA is used for digital signatures.
Another import terminology is digest algorithm or Hash Algorithm. The abstract algorithm actually maps the data from a “large space” to a “small space”, so there is the possibility of “collision” (collision, also called collision), just like fingerprints in reality, there may be two copies Different original texts correspond to the same abstract. A good digest algorithm must be able to “resist conflict” and make this possibility as small as possible. Because the digest algorithm has “one-way” and “avalanche effect” on the input, small differences in the input will cause drastic changes in the output, so it is also used by TLS to generate pseudo random function (PRF).
It’s worth knowing what Hash Message Authentication Code (HMAC) is.
The principle of digital signature is actually very simple. It is to reverse the usage of public key and private key. Previously, it was public key encryption and private key decryption. Now it is private key encryption and public key decryption.
However, because the efficiency of asymmetric encryption is too low, the private key only encrypts the digest of the original text, so the amount of calculation is much smaller, and the digital signature obtained is also very small, which is convenient for storage and transmission.
I confused Hash algo to QR codes, QR codes (Quick Response codes) are two-dimensional barcodes that store data in a grid of black and white squares. Here’s how they are created:
1. Encode the Data 📝
First, the data (text, URL, number, etc.) is converted into a binary format.
Each character is represented in binary according to an encoding standard:
Kanji Mode → Optimized for Japanese characters.
Numeric Mode → Stores only numbers (compressed for efficiency).
Alphanumeric Mode → Stores letters, numbers, and a few symbols.
Byte Mode → Stores binary data, including special characters.
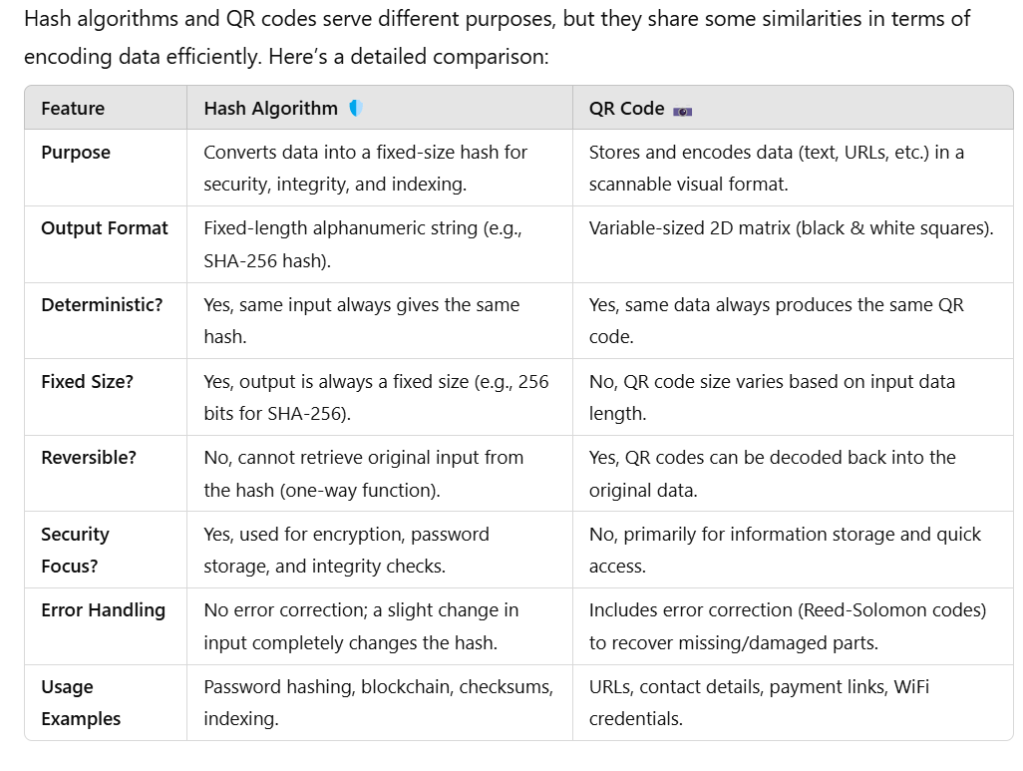
A hash function is like a fingerprint: You can verify identity but can’t reconstruct the person from their fingerprint.A QR code is like a barcode: You can scan it and retrieve the exact stored data.