Touch on several important concepts: Kernel, Order of element
First kernel. In linear algebra, we got to know that vectors in kernel or null space of sent to null via a linear transformation. In Linear Algebra_3 blog,
“So what is the concept of null space, according to wiki, it’s also called kernel, “given a linear map L : V → W between two vector spaces V and W, the kernel of L is the vector space of all elements v of V such that L(v) = 0, where 0 denotes the zero vector in W“, illustrated by the graph below:

Here are some more simple but edgy cases of matrix’s null space
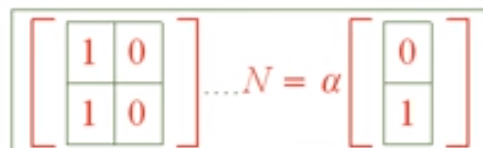
Now escalated to group theory kernel is being understood with a new perspective.
Even from above LA knowledge we know kernel is the property of the Linear Transformation not the property to the vectors. Now take the view form group theory, which is consistent to above definition.
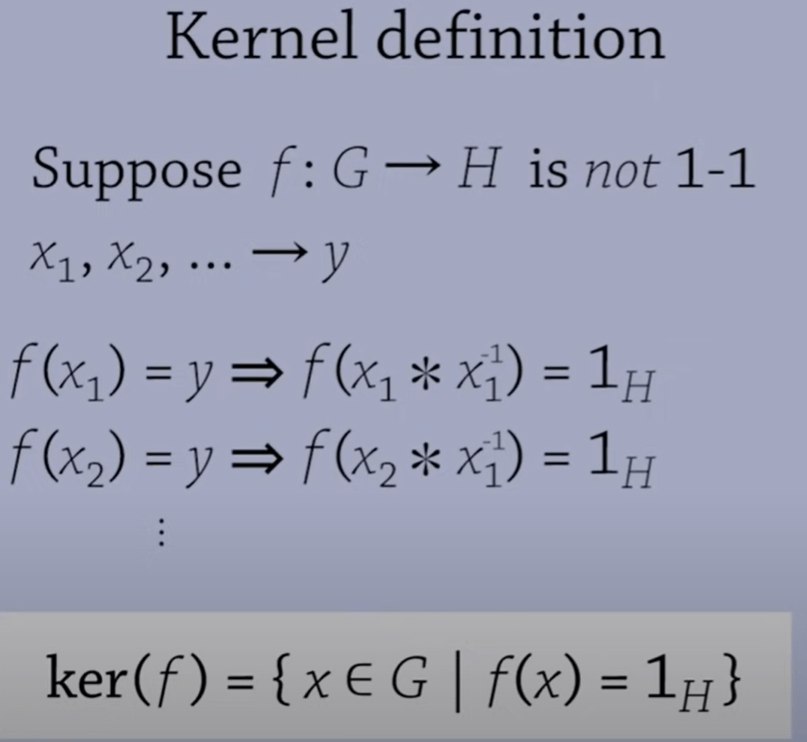
The kernel is a property of homomorphism that sends multiple element in G to identity in H. Wait, this is odd, every element multiplying/operating its inverse is sent to an identity in H. It could be more to one injection. But if the kernel only contains the identity then the morph is one to one.
Kernel is always a subset of G, but it also always is a subgroup of G (to be proved)
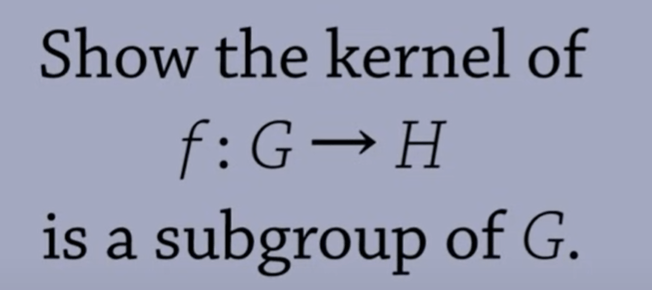
Second, order of element. The definition of order of element in a group is the smallest integer that raised by the element to be equal to e, identity.

For example, the group of real number under closure of x, the identity is 1. The element 1’s order is 1 because 1^ 1 = 1, the element -1 order is 2 because (-1)^2 = 1. all other elements has no such n to be raised to equal to 1, hence they have infinite order.
Now if we look at the group of complex number (excluding 0), there are infinite number of elements for example z, that satisfy z^n = 1, z is roots of unity. i is one of root unity and order of i element is 4.

One more example, most exciting example of matrix whose determinant is not zero:

more particular example of the following rotation matrix:
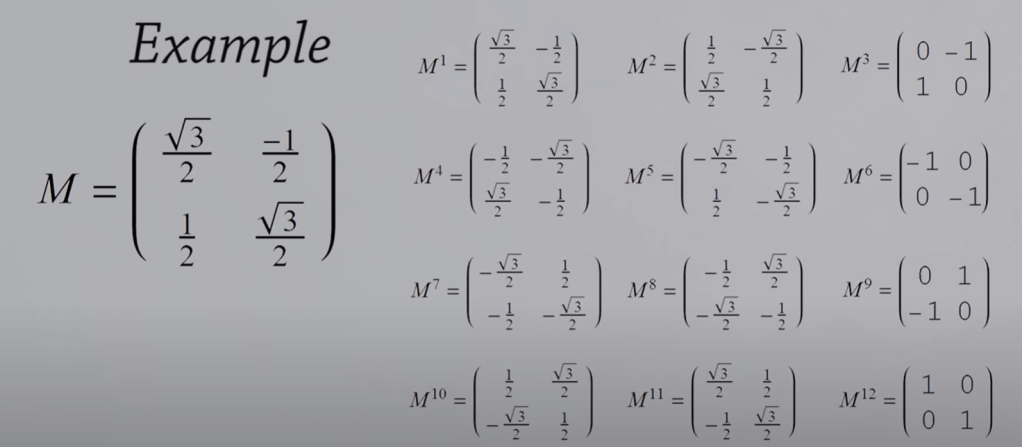
the order of this element is 12, |M| = 12