The key question to ask is how to realize computer graphics? Starting from the very basic unit – primitive and from the very basic math/geometry concepts. From Keenan Crane’s course page and NeHe’s open course on OpenGL, a great deal about CG can be learned.
The course by Prof. Crane’s is broken down to: Drawing a Triangle, Spatial Transformation, 3D Rotations and Complex Transformations, Perspective Projection and Texture Mapping, Depth and Transparency, Meshes and Manifolds, Digital Geometry Processing, Geometric Queries, Spatial Data Structures, Color, Radiometry, Rendering Equation, Numerical Integration, Monte Carlo Rendering, Variance Reduction, Animation, Dynamics and Time integration, Optimization, Physically-based Animation and PDEs.
No matter how complex the final products are, CG always can start from the simplest form such as
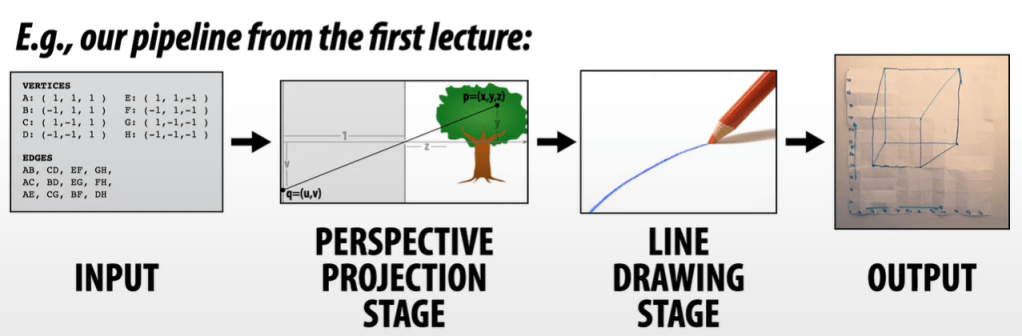
CG is about how to build up the intermediate staging step, which is rasterization pipeline. The math is detailed our in lectures on youtube, while their assignments are also splendid resources to learn.
| Assignment 1: DrawSVG | Assignment 2: MeshEdit |
| Assignment 3: PathTracer | Assignment 4: Animation |
For example in the DrawSVG assignment, there are the following tasks:
- Task 1 (Hardware Renderer): 5
- Task 2 (Drawing Lines): 5
- Task 3 (Drawing Triangles): 15
- Task 4 (Supersampling): 15
- Task 5 (Transforms): 10
- Task 6 (Scaled Images): 15
- Task 7 (Trilinear Filtering): 15
- Task 8 (Alpha Compositing): 5
- Task 9 (Draw Something!): 5
A copy of answer is provided in github page:
#include "software_renderer.h"
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include "triangulation.h"
using namespace std;
namespace CMU462 {
// Implements SoftwareRenderer //
void SoftwareRendererImp::draw_svg( SVG& svg ) {
// set top level transformation
transformation = svg_2_screen;
// draw all elements
for ( size_t i = 0; i < svg.elements.size(); ++i ) {
draw_element(svg.elements[i]);
}
// draw canvas outline
Vector2D a = transform(Vector2D( 0 , 0 )); a.x--; a.y--;
Vector2D b = transform(Vector2D(svg.width, 0 )); b.x++; b.y--;
Vector2D c = transform(Vector2D( 0 ,svg.height)); c.x--; c.y++;
Vector2D d = transform(Vector2D(svg.width,svg.height)); d.x++; d.y++;
rasterize_line(a.x, a.y, b.x, b.y, Color::Black);
rasterize_line(a.x, a.y, c.x, c.y, Color::Black);
rasterize_line(d.x, d.y, b.x, b.y, Color::Black);
rasterize_line(d.x, d.y, c.x, c.y, Color::Black);
// resolve and send to render target
resolve();
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::set_sample_rate( size_t sample_rate ) {
// Task 4:
// You may want to modify this for supersampling support
this->sample_rate = sample_rate;
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::set_render_target( unsigned char* render_target,
size_t width, size_t height ) {
// Task 4:
// You may want to modify this for supersampling support
this->render_target = render_target;
this->target_w = width;
this->target_h = height;
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::draw_element( SVGElement* element ) {
// Task 5 (part 1):
// Modify this to implement the transformation stack
switch(element->type) {
case POINT:
draw_point(static_cast<Point&>(*element));
break;
case LINE:
draw_line(static_cast<Line&>(*element));
break;
case POLYLINE:
draw_polyline(static_cast<Polyline&>(*element));
break;
case RECT:
draw_rect(static_cast<Rect&>(*element));
break;
case POLYGON:
draw_polygon(static_cast<Polygon&>(*element));
break;
case ELLIPSE:
draw_ellipse(static_cast<Ellipse&>(*element));
break;
case IMAGE:
draw_image(static_cast<Image&>(*element));
break;
case GROUP:
draw_group(static_cast<Group&>(*element));
break;
default:
break;
}
}
// Primitive Drawing //
void SoftwareRendererImp::draw_point( Point& point ) {
Vector2D p = transform(point.position);
rasterize_point( p.x, p.y, point.style.fillColor );
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::draw_line( Line& line ) {
Vector2D p0 = transform(line.from);
Vector2D p1 = transform(line.to);
rasterize_line( p0.x, p0.y, p1.x, p1.y, line.style.strokeColor );
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::draw_polyline( Polyline& polyline ) {
Color c = polyline.style.strokeColor;
if( c.a != 0 ) {
int nPoints = polyline.points.size();
for( int i = 0; i < nPoints - 1; i++ ) {
Vector2D p0 = transform(polyline.points[(i+0) % nPoints]);
Vector2D p1 = transform(polyline.points[(i+1) % nPoints]);
rasterize_line( p0.x, p0.y, p1.x, p1.y, c );
}
}
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::draw_rect( Rect& rect ) {
Color c;
// draw as two triangles
float x = rect.position.x;
float y = rect.position.y;
float w = rect.dimension.x;
float h = rect.dimension.y;
Vector2D p0 = transform(Vector2D( x , y ));
Vector2D p1 = transform(Vector2D( x + w , y ));
Vector2D p2 = transform(Vector2D( x , y + h ));
Vector2D p3 = transform(Vector2D( x + w , y + h ));
// draw fill
c = rect.style.fillColor;
if (c.a != 0 ) {
rasterize_triangle( p0.x, p0.y, p1.x, p1.y, p2.x, p2.y, c );
rasterize_triangle( p2.x, p2.y, p1.x, p1.y, p3.x, p3.y, c );
}
// draw outline
c = rect.style.strokeColor;
if( c.a != 0 ) {
rasterize_line( p0.x, p0.y, p1.x, p1.y, c );
rasterize_line( p1.x, p1.y, p3.x, p3.y, c );
rasterize_line( p3.x, p3.y, p2.x, p2.y, c );
rasterize_line( p2.x, p2.y, p0.x, p0.y, c );
}
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::draw_polygon( Polygon& polygon ) {
Color c;
// draw fill
c = polygon.style.fillColor;
if( c.a != 0 ) {
// triangulate
vector<Vector2D> triangles;
triangulate( polygon, triangles );
// draw as triangles
for (size_t i = 0; i < triangles.size(); i += 3) {
Vector2D p0 = transform(triangles[i + 0]);
Vector2D p1 = transform(triangles[i + 1]);
Vector2D p2 = transform(triangles[i + 2]);
rasterize_triangle( p0.x, p0.y, p1.x, p1.y, p2.x, p2.y, c );
}
}
// draw outline
c = polygon.style.strokeColor;
if( c.a != 0 ) {
int nPoints = polygon.points.size();
for( int i = 0; i < nPoints; i++ ) {
Vector2D p0 = transform(polygon.points[(i+0) % nPoints]);
Vector2D p1 = transform(polygon.points[(i+1) % nPoints]);
rasterize_line( p0.x, p0.y, p1.x, p1.y, c );
}
}
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::draw_ellipse( Ellipse& ellipse ) {
// Extra credit
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::draw_image( Image& image ) {
Vector2D p0 = transform(image.position);
Vector2D p1 = transform(image.position + image.dimension);
rasterize_image( p0.x, p0.y, p1.x, p1.y, image.tex );
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::draw_group( Group& group ) {
for ( size_t i = 0; i < group.elements.size(); ++i ) {
draw_element(group.elements[i]);
}
}
// Rasterization //
// The input arguments in the rasterization functions
// below are all defined in screen space coordinates
void SoftwareRendererImp::rasterize_point( float x, float y, Color color ) {
// fill in the nearest pixel
int sx = (int) floor(x);
int sy = (int) floor(y);
// check bounds
if ( sx < 0 || sx >= target_w ) return;
if ( sy < 0 || sy >= target_h ) return;
// fill sample - NOT doing alpha blending!
render_target[4 * (sx + sy * target_w) ] = (uint8_t) (color.r * 255);
render_target[4 * (sx + sy * target_w) + 1] = (uint8_t) (color.g * 255);
render_target[4 * (sx + sy * target_w) + 2] = (uint8_t) (color.b * 255);
render_target[4 * (sx + sy * target_w) + 3] = (uint8_t) (color.a * 255);
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::rasterize_line( float x0, float y0,
float x1, float y1,
Color color) {
// Task 2:
// Implement line rasterization
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::rasterize_triangle( float x0, float y0,
float x1, float y1,
float x2, float y2,
Color color ) {
// Task 3:
// Implement triangle rasterization
}
void SoftwareRendererImp::rasterize_image( float x0, float y0,
float x1, float y1,
Texture& tex ) {
// Task 6:
// Implement image rasterization
}
// resolve samples to render target
void SoftwareRendererImp::resolve( void ) {
// Task 4:
// Implement supersampling
// You may also need to modify other functions marked with "Task 4".
return;
}
} // namespace CMU462
There is a bonus link by NeHe who taught OpenGL in such details just because when he tried to learn, there was no resource at all. Such a hero. BTW, OpenGL or open graphic library provide a suite of basic graphics. Here are his outline, not complete list:
set up an openGL window
first polygon
adding color
rotation
3D shapes
texture mapping
soil library
texture filters, lighting and keyboard control
blending
moving bitmaps in 3D space
loading and moving through a 3D world
flag effect
display lists
bitmap fonts
outline fonts
texture mapped outline fonts
cool looking fog
2D texture font
quadrics
particle engine using triangle strips
masking
lines antialiasing, timing, ortho view and simple sounds
bump-mapping multi-texturing and extensions
sphere mapping quadrics in OpenGL
tokens extensions, scissor testing and TGA loading
morphing and loading objects from a file
clipping and reflections using the stencil buffer
shadows
bezier patches fullscreen fix
blitter function raw texture loading
collision detection
model loading
picking alpha blending alpha testing sorting
loading compressed and uncompressed TGA’s
Beautiful landscapes by means of height mapping
playing AVI files in openGL