If inverse of matrix is equal to its transpose, then it is a orthogonal matrix. Only Square matrix we talked about the concept of Determinant.
Rank of a matrix is the number of pivots of the matrix also is the dimension of the column space of matrix A.
Simplest Matrix factorization A = LU, note inverse of a 2 by 2 square matrix rule is to keep the diagonal number and switch the the sign of the right diagonal.



Note to perform A=LU, row exchange is not allowed. IF row exchanged, that is called permutation. Under this circumstance, PA = LU. Note P for identity permutation P-1 = PT.
Ax=b how to evaluate the solvability first?

Second, to find a particular solution, the simplest way is to knock out the free variables here they are x2 and x4, by setting them to be 0.
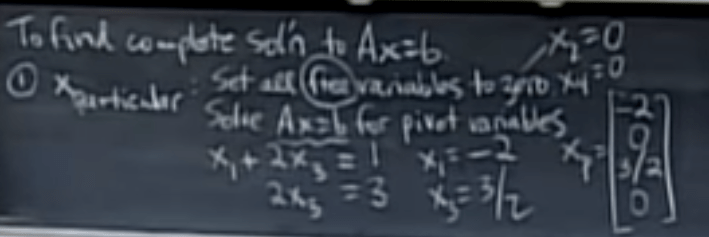
Then the full solution is to add on the null space on top of this particular solution

Summarizing the relationship of m, n, rank for a matrix’s solution

A full example to solve as practicing
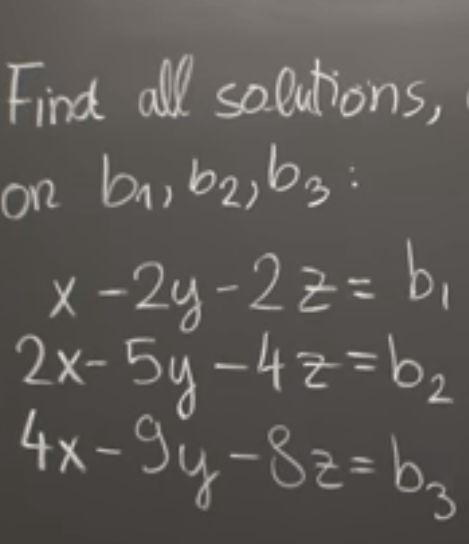

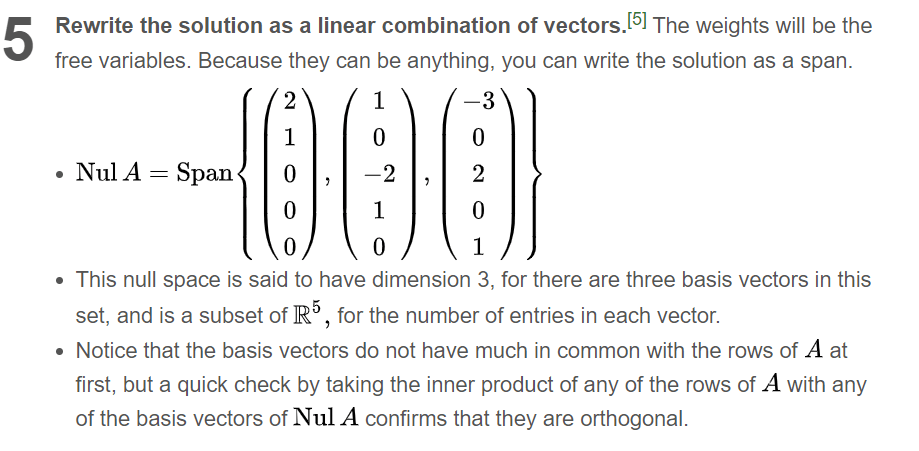
I stuck on finding the null space, so the whole process is

A quick way to find the special case Ax=0 is to set all free variable to be 1, in this example, the third one z = 1
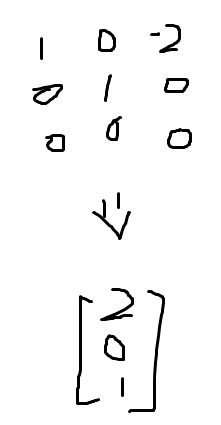
Matrix is a Transformation.
Think of Matrix composed of columns corresponding to the standard basis one by one, each column instruct how the basis is turned to:
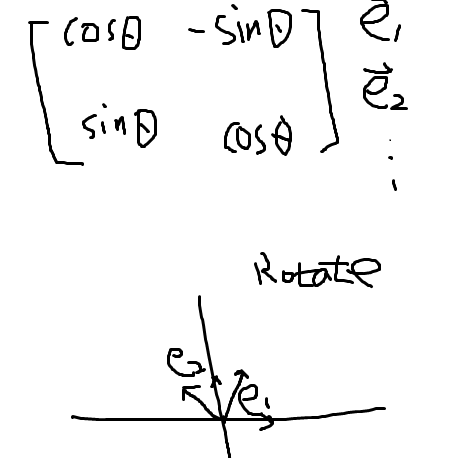
When theta is -pie/2, the rotation matrix is
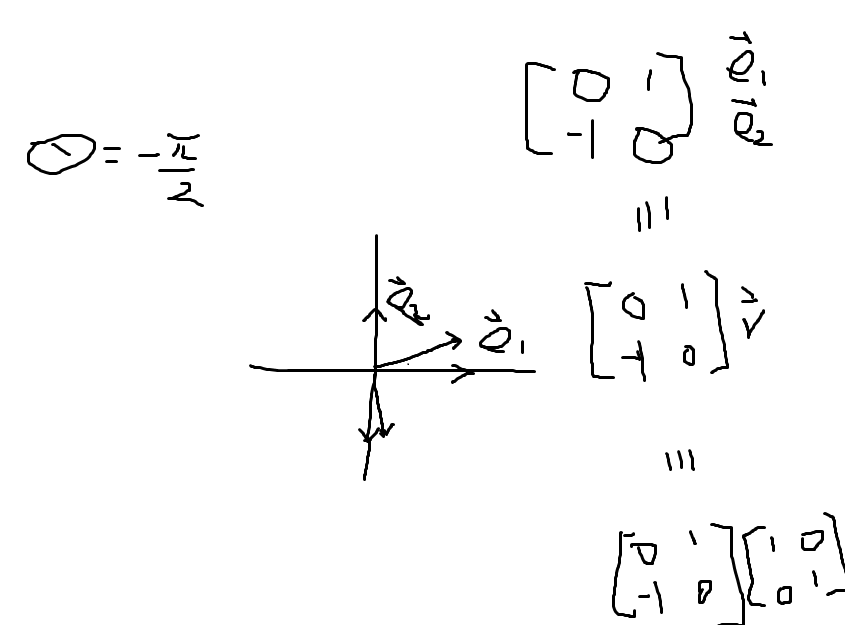
M = PDP-1
On the other hand, think of Matrix is transformation that can always be broken down to two steps: rotation and stretching. M = UE.