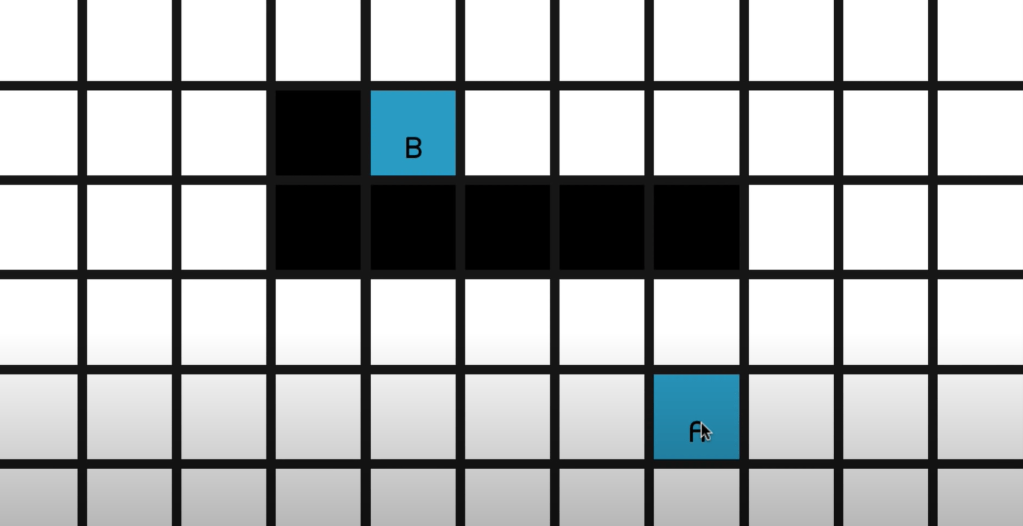
Sebastian is brilliant to explain this A* algorithm far better than academic which takes hours. The problem in simple form is like below, you need to find the optimal path from A to B. The natural resort is to use A* search algorithm.
What is A* algorithm, according to wiki, “A* (pronounced “A-star”) is a graph traversal and path searchalgorithm, which is often used in many fields of computer science due to its completeness, optimality, and optimal efficiency.[1] One major practical drawback is its {\displaystyle O(b^{d})}
Here is the way it works: for each node starting from A, calculating all its surrounding nodes with G cost, H cost and F cost. Then pick the ones that have the lowest F cost.
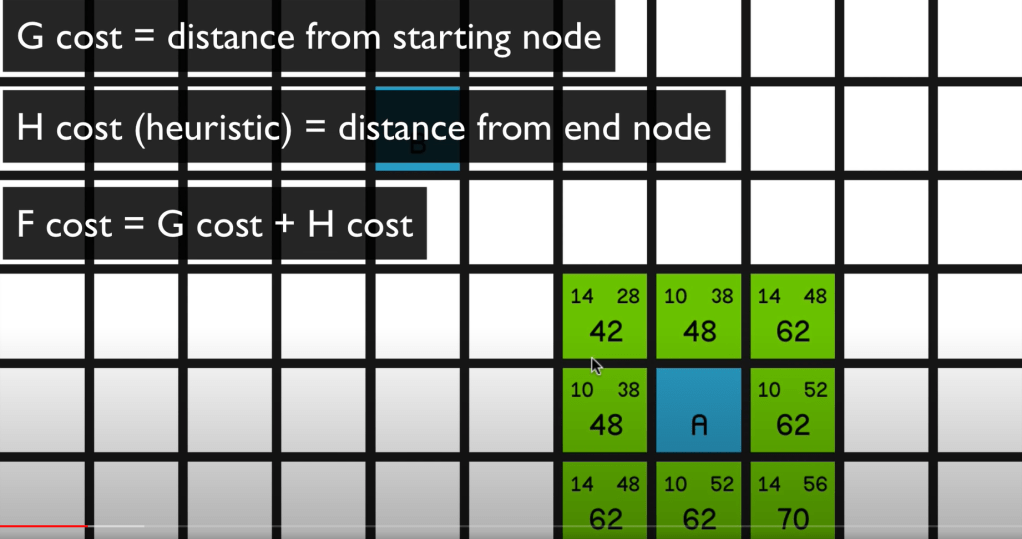
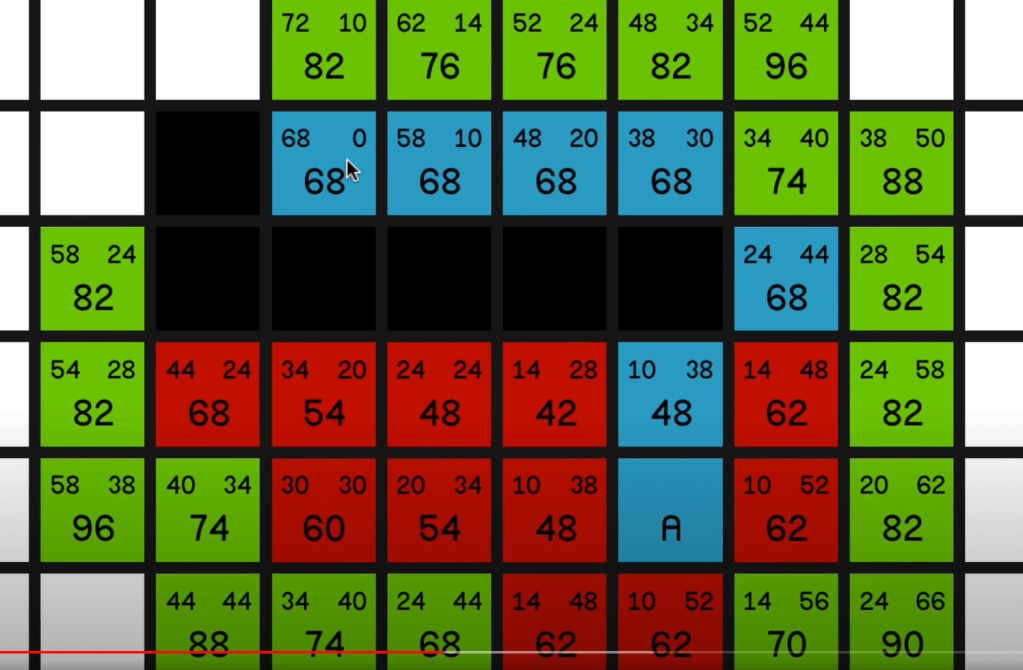
However what if there are obstacles like the black blocks in below graph, we need to continue exploring like we play the mining game of Microsoft, until we obtain the optimal path as shown in blue color. Note the value of G, H, and F cost keep updating along the way.
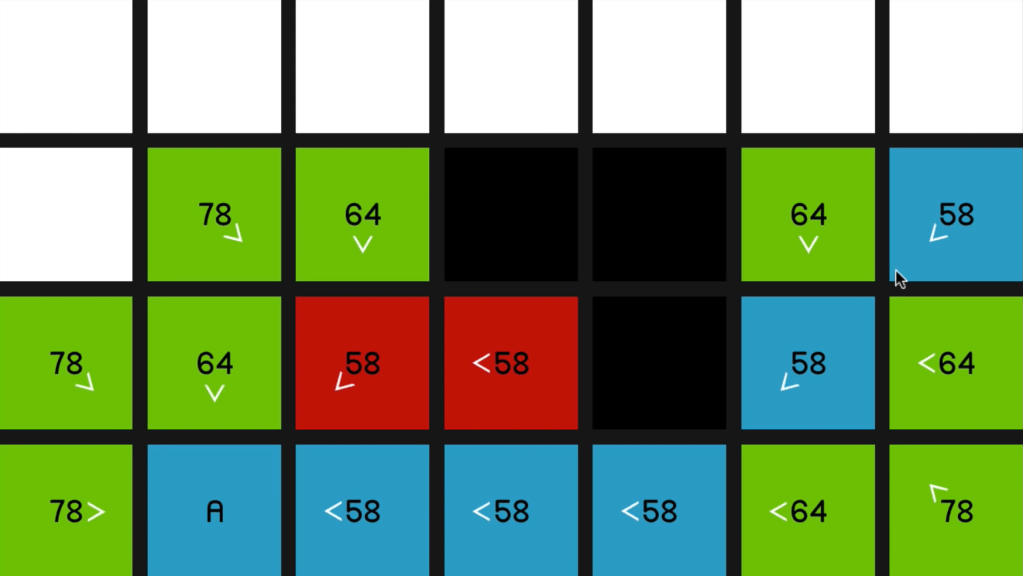
Next shows a shorthand to show the F cost value and figure out the path too.
To realize above the pseudocodes by Sebastian is
# A* Search Algorithm path finding pseudocodes
OPEN //the set of nodes to be evaluated
CLOSED //the set of nodes already evaluated
add the start node to OPEN
loop
current = node in OPEN with the lowest f_cost
remove current from OPEN
add current to CLOSED
if current is the target node //path has been found
return
foreach neighbour of the current node
if neighbour is not traversable or neighbour is in CLOSED
skip to the next neighbour
if new path to neighbour is shorter OR neighbour is not in OPEN
set f_cost of neighbour
set parent of neighbour to current
if neighbour is not in OPEN
add neighbour to OPEN