In adversarial games such as chess, a systematic approach is to apply minimax and alpha-beta pruning, with which, the machine – deep blue – can beat the human champion.
To illustrate this approach, let’s assume from a starting point, there are only two choices, then we can draw an exhaustive tree diagram like below:

Another case taught in computer science is the British Museum Searching.

The machine way, or brute force way sure works but in a very time-consuming fashion. Hence A* searching is applied to speed up.
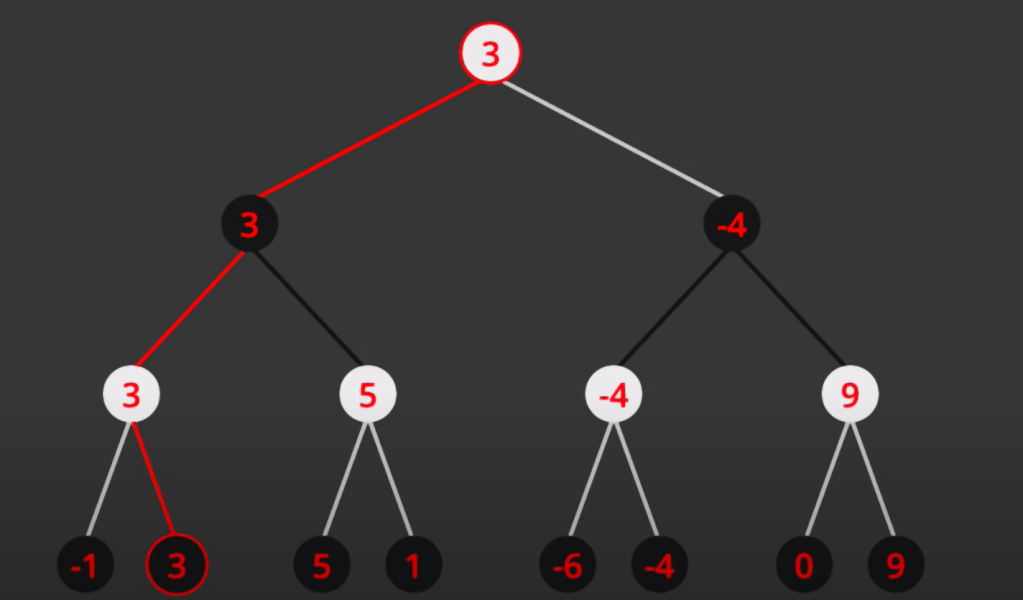
In both cases, the tree structure is drawn to help think and solve such kind of problems. If you have a comprehensive static values unfolded like below, one can easily pick up the optimal path for white players as highlighted in red color below:
Now let’s write a snippet to realize this approach referencing Sebastian Lague.
# it's recursive! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l-hh51ncgDI
function minimax(position, depth, maximizingPlayer)
if depth == 0 or game over in position
return static evaluation of position
if maximizingPlayer
maxEval = -infinity
for each child of position
eval = minimax(child, depth - 1, false)
maxEval = max(maxEval, eval)
return maxEval
else
minEval = +infinity
for each child of position
eval = minimax(child, depth - 1, true)
minEval = min(minEval, eval)
return minEval
// initial call
minimax(currentPosition, 3, true) Next, knowing the speed is slow if exhaustively going through all nodes, we will try to make it faster. Simple logic could be applied so we don’t waste time pruning those we can spot earlier. hence, the codes are updated adding alpha beta parameters:
# optimized by alpha-beta approach
function minimax(position, depth, alpha, beta, maximizingPlayer)
if depth == 0 or game over in position
return static evaluation of position
if maximizingPlayer
maxEval = -infinity
for each child of position
eval = minimax(child, depth - 1, alpha, beta false)
maxEval = max(maxEval, eval)
alpha = max(alpha, eval)
if beta <= alpha
break
return maxEval
else
minEval = +infinity
for each child of position
eval = minimax(child, depth - 1, alpha, beta true)
minEval = min(minEval, eval)
beta = min(beta, eval)
if beta <= alpha
break
return minEval
// initial call
minimax(currentPosition, 3, -∞, +∞, true)