There are some NP problems (nondeterministic problems) that we will apply SA (simulated annealing) algorithms, Genetic Algorithms etc. to solve. The key is to overcome being stuck in a local area. Simulated Annealing allows several testing leaps in the beginning so the probability of reaching a global minimum or maximum is high.
Whether to continue exploring, SA needs to compute a probability score, from equation below, one can see a higher temperature or smaller loss will cause higher probability.
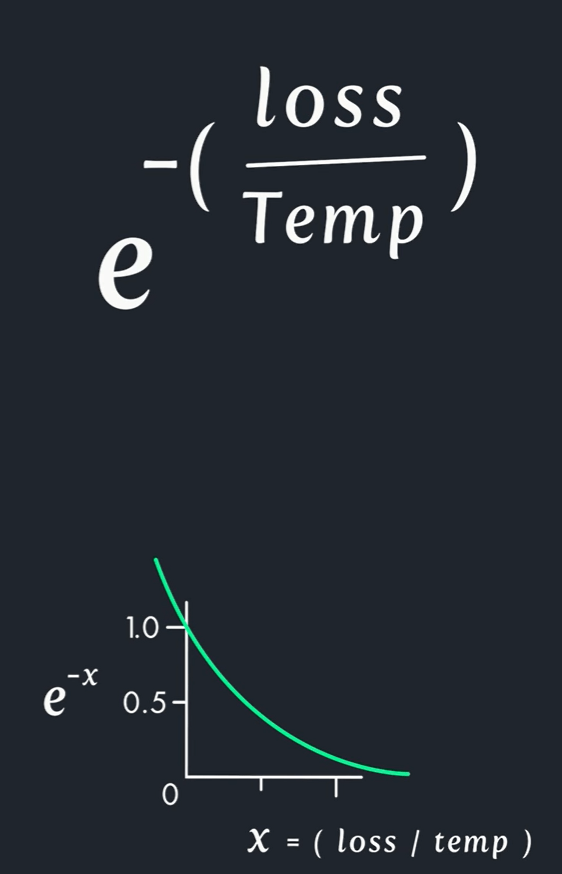


The python codes as
# Simulated Annealing
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def h(x):
if x < -1 or x > 1:
y = 0
else:
y = (np.cos(50*x) + np.sin(20*x))
return y
hv = np.vectorize(h)
X = np.linspace(-1, 2, num=1000)
plt.plot(X, hv(X))
plt.show()
# simple greedy search will stop at a local minmum or maxmum
def simple_greedy_search(func, start=0, N=100):
x = start
history = []
for i in range(N):
history.append(x) # keep track of steps
u = 0.001 #np.random.rand() #some noise
xleft, xright = x-u, x+u #look around the neighborhood
yleft, yright = func(xleft), func(xright)
if yleft > yright:
x = xleft
else:
x = xright
return x, history
x0, history = simple_greedy_search(hv, start=-0.02, N=100)
# here is the simulated annealing algorithm
def SA(search_space, func, T):
scale = np.sqrt(T)
start = np.random.choice(search_space)
x = start * 1
cur = func(x)
history = [x]
for i in range(1000):
prop = x + np.random.normal()*scale #.uniform(-1, 1, size=1) *scale
if prop > 1 or prop < 0 or np.log(np.random.rand()) * T > (func(prop) - cur):
prop = x
x = prop
cur = func(x)
T = 0.9 * T # reduce temperature by 10% each iteration
history.append(x)
return x, history
SA is so powerful that those NP problems such as TSP(traveling salesman problem), Sudoku and Rubik problems can be systematically solved by SA.
below are the python codes to use SA solving Sudoku by ChallengingLuck
# Simulated Annealing (SA) techqnique to solve Sudoku posted by challengingLuck
import random
import numpy as np
import math
from random import choice
import statistics
startingSudoku = """
024007000
600000000
003680415
431005000
500000032
790000060
209710800
040093000
310004750
"""
sudoku = np.array([[int(i) for i in line] for line in startingSudoku.split()])
def PrintSudoku(sudoku):
print("\n")
for i in range(len(sudoku)):
line = ""
if i == 3 or i == 6:
print("---------------------")
for j in range(len(sudoku[i])):
if j == 3 or j == 6:
line += "| "
line += str(sudoku[i,j])+" "
print(line)
def FixSudokuValues(fixed_sudoku):
for i in range (0,9):
for j in range (0,9):
if fixed_sudoku[i,j] != 0:
fixed_sudoku[i,j] = 1
return(fixed_sudoku)
# Cost Function
def CalculateNumberOfErrors(sudoku):
numberOfErrors = 0
for i in range (0,9):
numberOfErrors += CalculateNumberOfErrorsRowColumn(i ,i ,sudoku)
return(numberOfErrors)
def CalculateNumberOfErrorsRowColumn(row, column, sudoku):
numberOfErrors = (9 - len(np.unique(sudoku[:,column]))) + (9 - len(np.unique(sudoku[row,:])))
return(numberOfErrors)
def CreateList3x3Blocks ():
finalListOfBlocks = []
for r in range (0,9):
tmpList = []
block1 = [i + 3*((r)%3) for i in range(0,3)]
block2 = [i + 3*math.trunc((r)/3) for i in range(0,3)]
for x in block1:
for y in block2:
tmpList.append([x,y])
finalListOfBlocks.append(tmpList)
return(finalListOfBlocks)
def RandomlyFill3x3Blocks(sudoku, listOfBlocks):
for block in listOfBlocks:
for box in block:
if sudoku[box[0],box[1]] == 0:
currentBlock = sudoku[block[0][0]:(block[-1][0]+1),block[0][1]:(block[-1][1]+1)]
sudoku[box[0],box[1]] = choice([i for i in range(1,10) if i not in currentBlock])
return sudoku
def SumOfOneBlock (sudoku, oneBlock):
finalSum = 0
for box in oneBlock:
finalSum += sudoku[box[0], box[1]]
return(finalSum)
def TwoRandomBoxesWithinBlock(fixedSudoku, block):
while (1):
firstBox = random.choice(block)
secondBox = choice([box for box in block if box is not firstBox ])
if fixedSudoku[firstBox[0], firstBox[1]] != 1 and fixedSudoku[secondBox[0], secondBox[1]] != 1:
return([firstBox, secondBox])
def FlipBoxes(sudoku, boxesToFlip):
proposedSudoku = np.copy(sudoku)
placeHolder = proposedSudoku[boxesToFlip[0][0], boxesToFlip[0][1]]
proposedSudoku[boxesToFlip[0][0], boxesToFlip[0][1]] = proposedSudoku[boxesToFlip[1][0], boxesToFlip[1][1]]
proposedSudoku[boxesToFlip[1][0], boxesToFlip[1][1]] = placeHolder
return (proposedSudoku)
def ProposedState (sudoku, fixedSudoku, listOfBlocks):
randomBlock = random.choice(listOfBlocks)
if SumOfOneBlock(fixedSudoku, randomBlock) > 6:
return(sudoku, 1, 1)
boxesToFlip = TwoRandomBoxesWithinBlock(fixedSudoku, randomBlock)
proposedSudoku = FlipBoxes(sudoku, boxesToFlip)
return([proposedSudoku, boxesToFlip])
def ChooseNewState (currentSudoku, fixedSudoku, listOfBlocks, sigma):
proposal = ProposedState(currentSudoku, fixedSudoku, listOfBlocks)
newSudoku = proposal[0]
boxesToCheck = proposal[1]
currentCost = CalculateNumberOfErrorsRowColumn(boxesToCheck[0][0], boxesToCheck[0][1], currentSudoku) + CalculateNumberOfErrorsRowColumn(boxesToCheck[1][0], boxesToCheck[1][1], currentSudoku)
newCost = CalculateNumberOfErrorsRowColumn(boxesToCheck[0][0], boxesToCheck[0][1], newSudoku) + CalculateNumberOfErrorsRowColumn(boxesToCheck[1][0], boxesToCheck[1][1], newSudoku)
# currentCost = CalculateNumberOfErrors(currentSudoku)
# newCost = CalculateNumberOfErrors(newSudoku)
costDifference = newCost - currentCost
rho = math.exp(-costDifference/sigma)
if(np.random.uniform(1,0,1) < rho):
return([newSudoku, costDifference])
return([currentSudoku, 0])
def ChooseNumberOfItterations(fixed_sudoku):
numberOfItterations = 0
for i in range (0,9):
for j in range (0,9):
if fixed_sudoku[i,j] != 0:
numberOfItterations += 1
return numberOfItterations
def CalculateInitialSigma (sudoku, fixedSudoku, listOfBlocks):
listOfDifferences = []
tmpSudoku = sudoku
for i in range(1,10):
tmpSudoku = ProposedState(tmpSudoku, fixedSudoku, listOfBlocks)[0]
listOfDifferences.append(CalculateNumberOfErrors(tmpSudoku))
return (statistics.pstdev(listOfDifferences))
def solveSudoku (sudoku):
f = open("demofile2.txt", "a")
solutionFound = 0
while (solutionFound == 0):
decreaseFactor = 0.99
stuckCount = 0
fixedSudoku = np.copy(sudoku)
PrintSudoku(sudoku)
FixSudokuValues(fixedSudoku)
listOfBlocks = CreateList3x3Blocks()
tmpSudoku = RandomlyFill3x3Blocks(sudoku, listOfBlocks)
sigma = CalculateInitialSigma(sudoku, fixedSudoku, listOfBlocks)
score = CalculateNumberOfErrors(tmpSudoku)
itterations = ChooseNumberOfItterations(fixedSudoku)
if score <= 0:
solutionFound = 1
while solutionFound == 0:
previousScore = score
for i in range (0, itterations):
newState = ChooseNewState(tmpSudoku, fixedSudoku, listOfBlocks, sigma)
tmpSudoku = newState[0]
scoreDiff = newState[1]
score += scoreDiff
print(score)
f.write(str(score) + '\n')
if score <= 0:
solutionFound = 1
break
sigma *= decreaseFactor
if score <= 0:
solutionFound = 1
break
if score >= previousScore:
stuckCount += 1
else:
stuckCount = 0
if (stuckCount > 80):
sigma += 2
if(CalculateNumberOfErrors(tmpSudoku)==0):
PrintSudoku(tmpSudoku)
break
f.close()
return(tmpSudoku)
solution = solveSudoku(sudoku)
print(CalculateNumberOfErrors(solution))
PrintSudoku(solution)
By the way, there is great guy posted 10 different solving strategies. In addition, in previous blog, I also detailed the applying of Linear Programing (LP) to solve Sudoku, which doesn’t require fancy iterative algos but simple math optimization(derivative calculation).