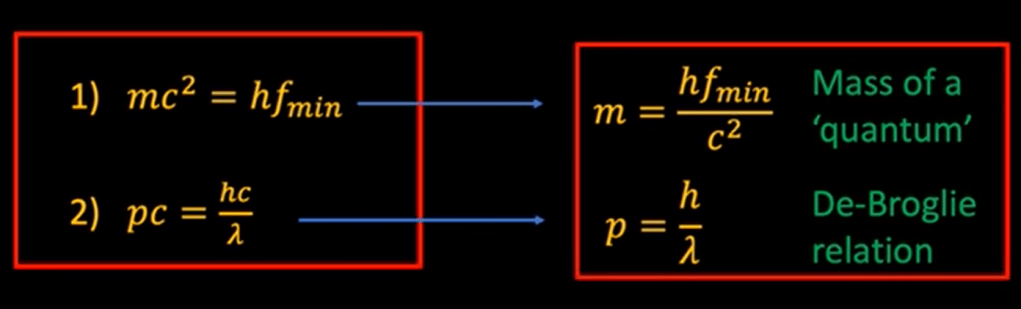
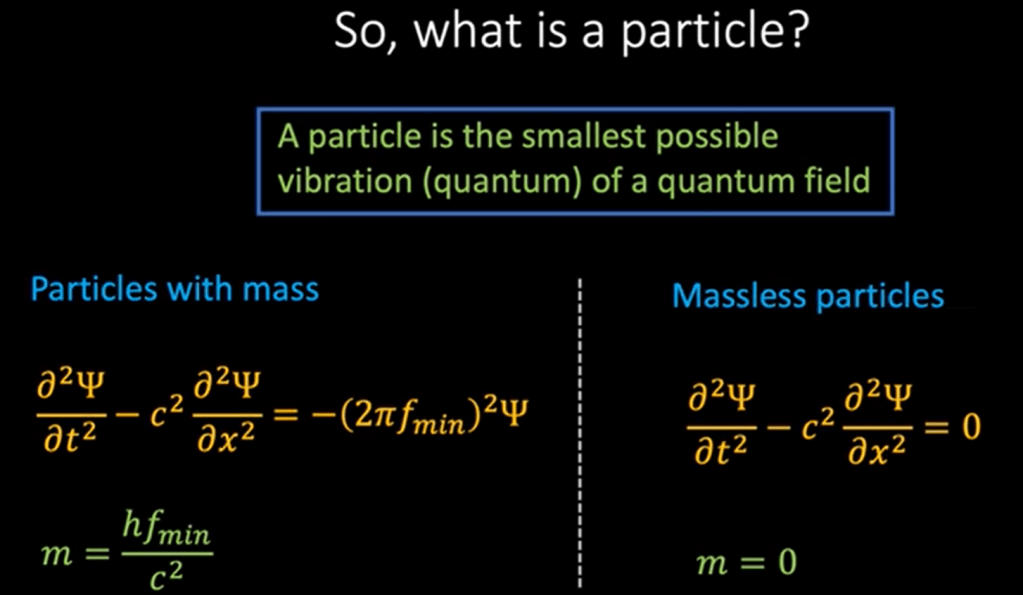So far the best I’ve learned on explaining what a particle is! It’s the smallest vibration of a quantum field.
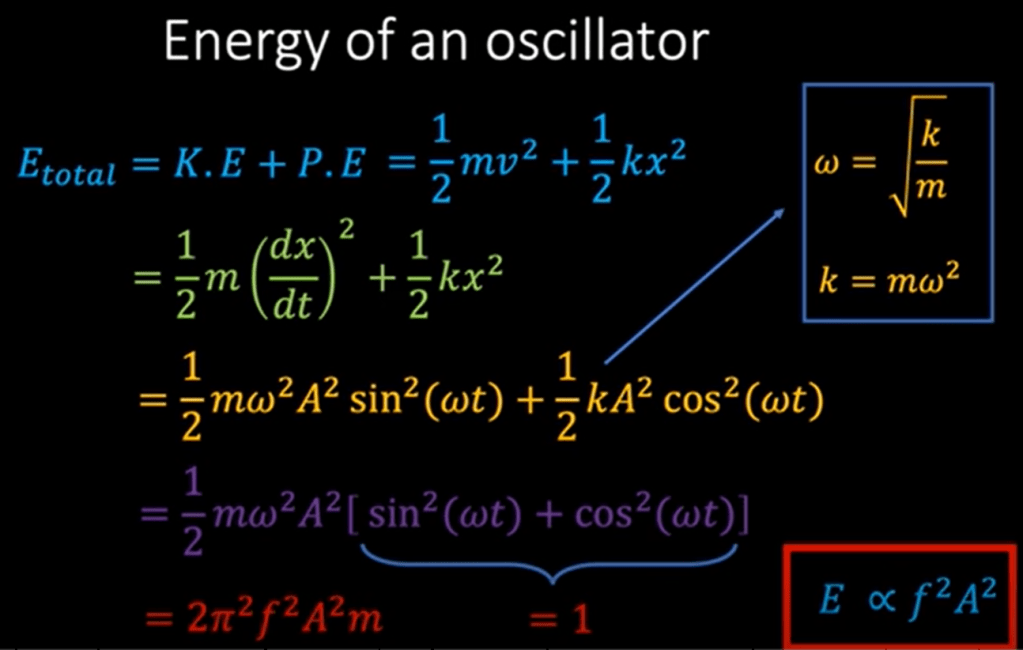
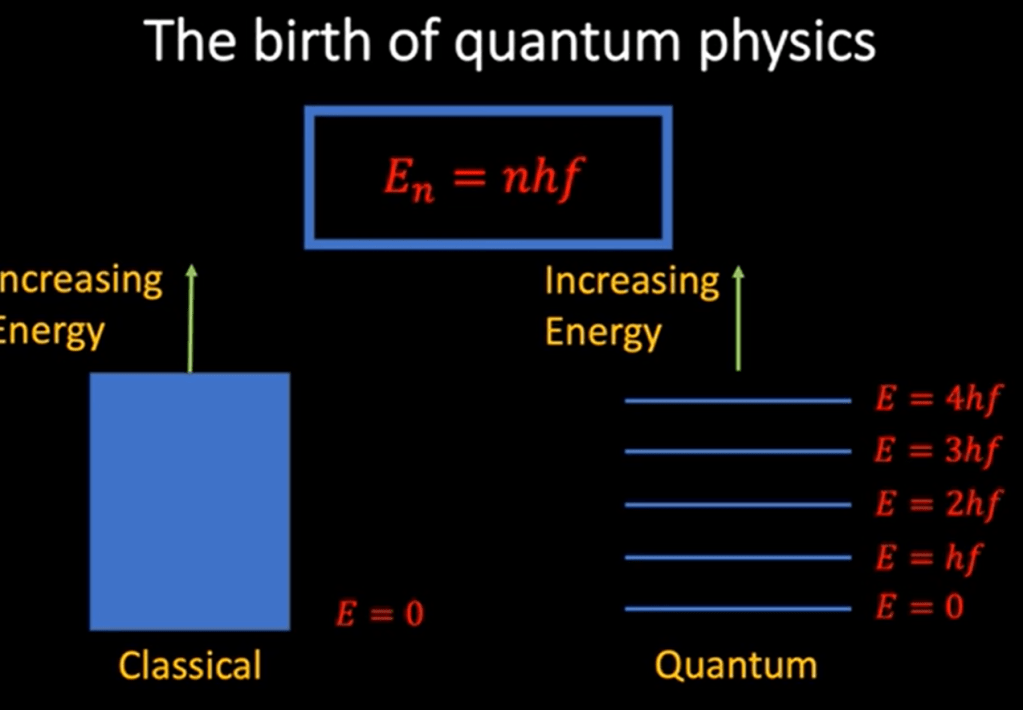
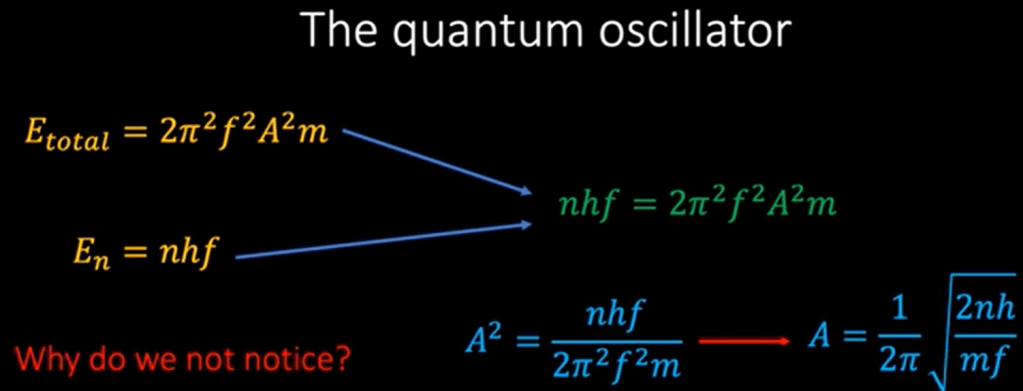

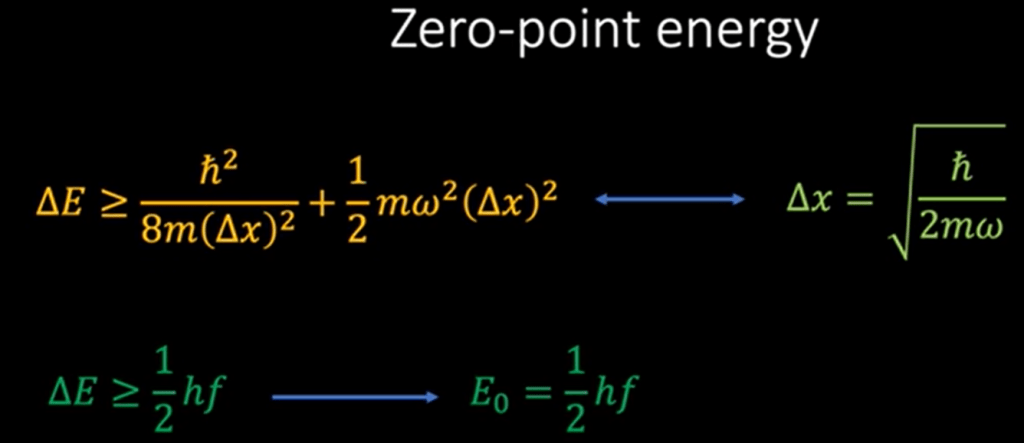
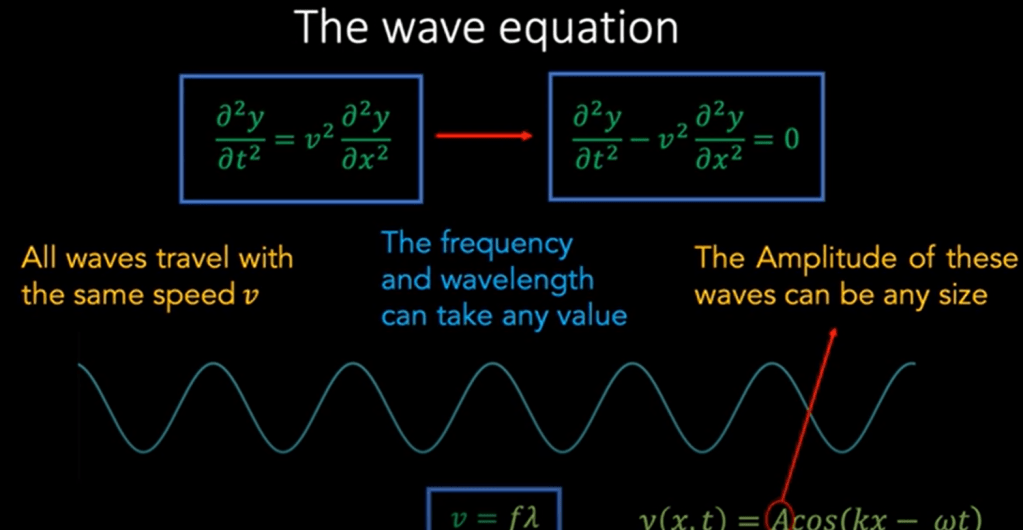
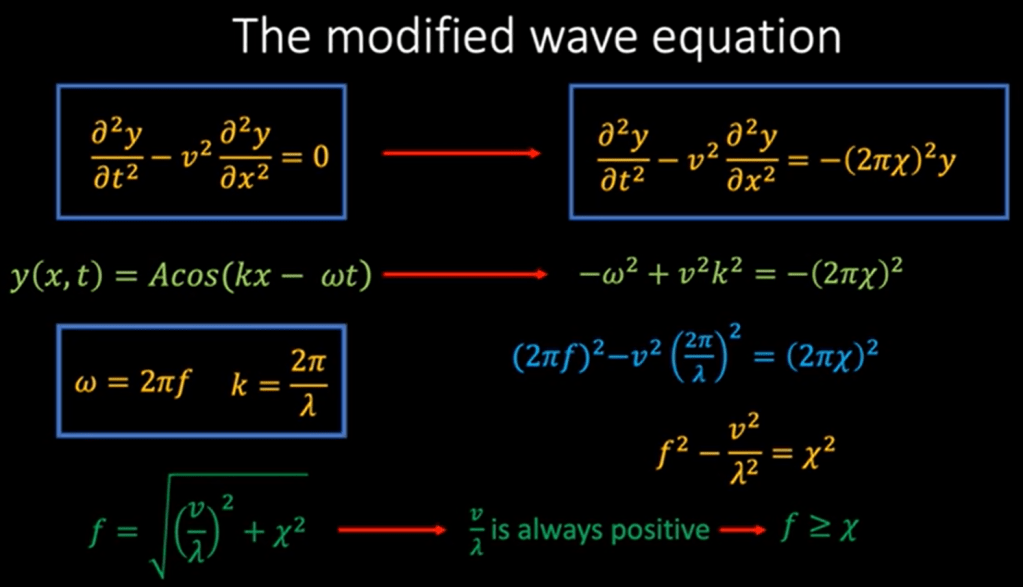
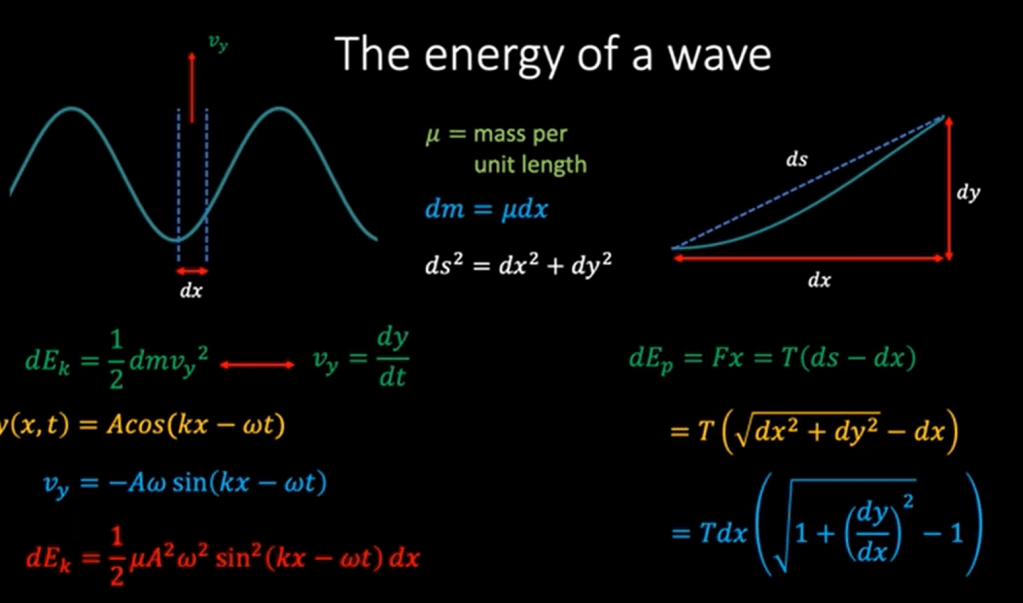
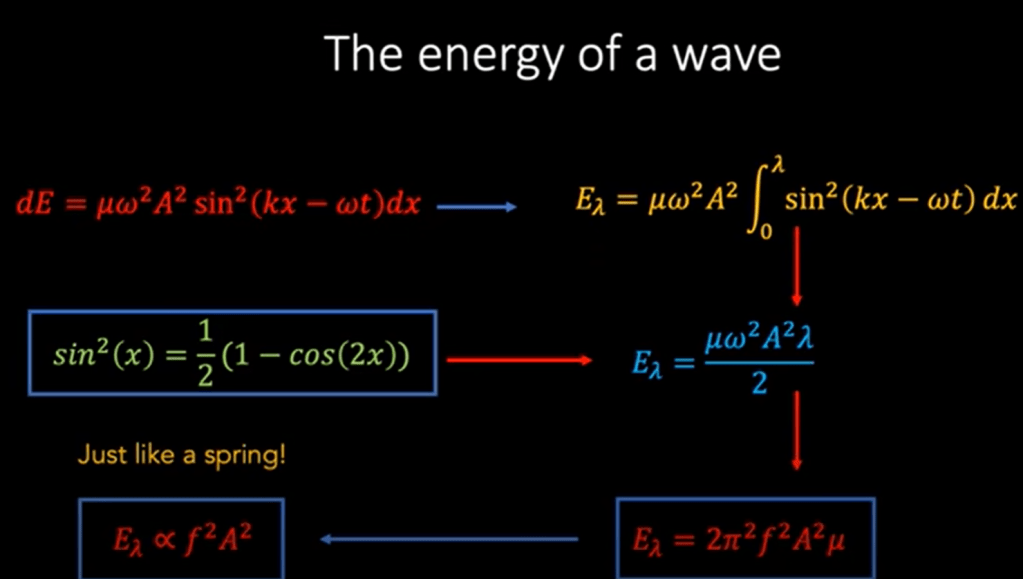
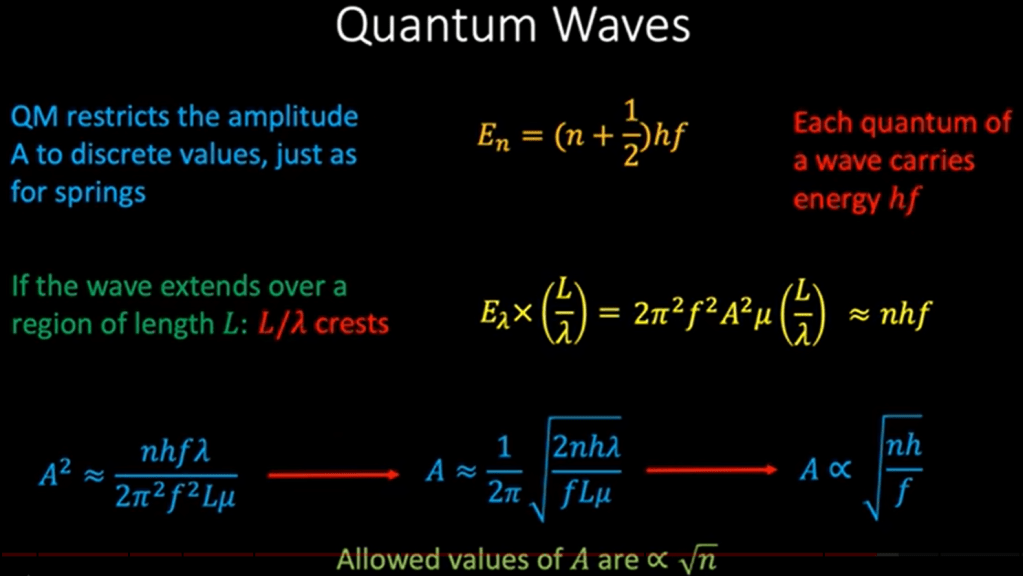
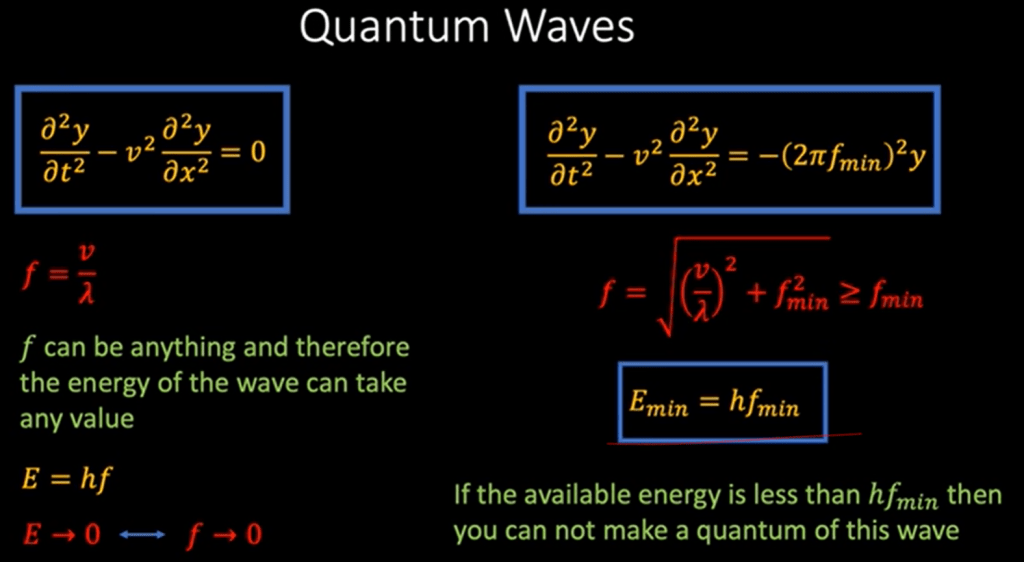
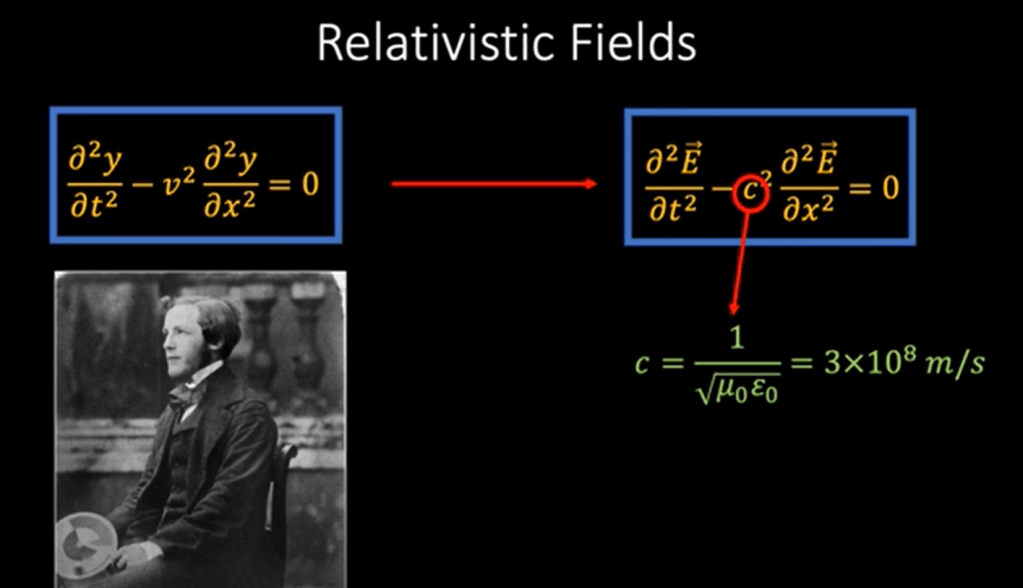
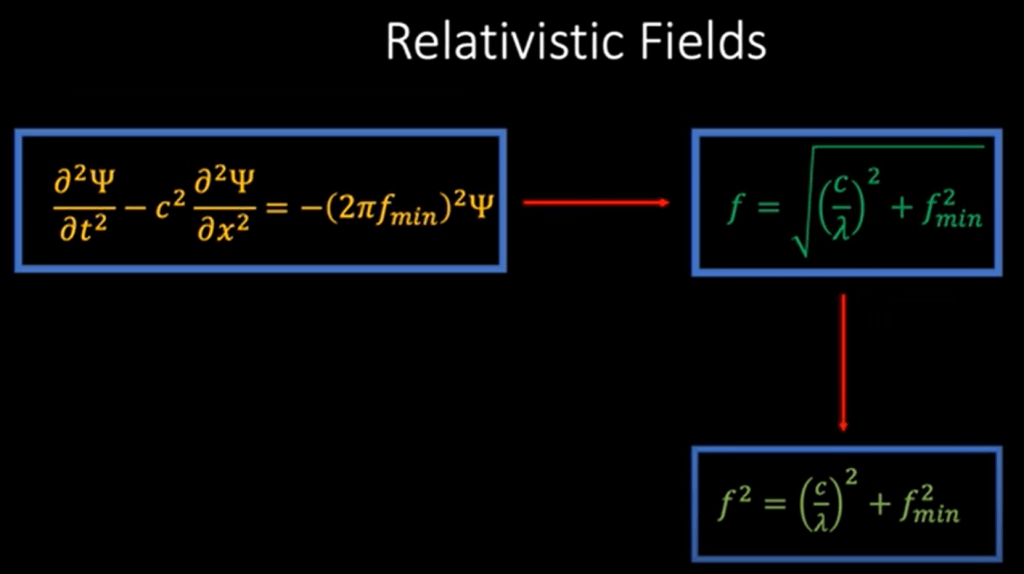
What’s the definition of relativistic field? Einstein postulate that light travel at the constant speed irrespective to any frames of reference, so it is in the relativistic field.
A relativistic field is a field that is described by a set of physical quantities that vary over space and time, and are subject to the laws of special or general relativity. Examples of relativistic fields include the electromagnetic field, the gravitational field, and the Higgs field. These fields are described by tensor equations and their behavior is determined by the curvature of spacetime.
The Higgs field is a field of energy that is thought to permeate all of space and is associated with the Higgs boson, a particle that was discovered in 2012 at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). The Higgs field is responsible for giving other elementary particles mass. The Higgs boson is a particle that is associated with the Higgs field and is sometimes referred to as the “God particle” because its discovery was crucial for confirming the existence of the Higgs field and completing the Standard Model of particle physics.
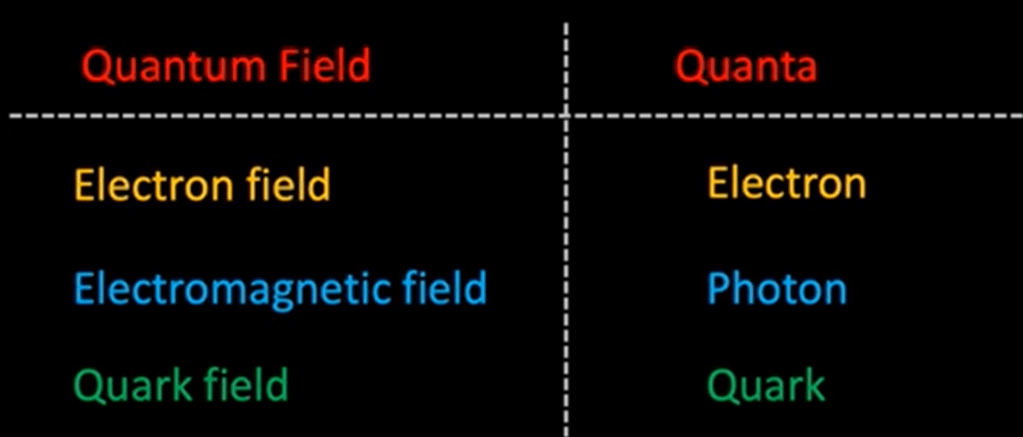
Fermions and bosons are types of subatomic particles that have different properties and behavior.
Fermions are particles that make up matter, such as electrons and protons. They obey the Pauli exclusion principle, which states that no two fermions can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously. This is why atoms cannot collapse, and explains the stability of matter.
Bosons are particles that carry force, such as photons (carriers of electromagnetic force) and gluons (carriers of the strong force that holds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus of an atom). Unlike fermions, multiple bosons can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously. This is what allows light to behave as both particles and waves.
Fermions have half-integer spin, while bosons have integer spin.