A generator matrix is a matrix used to generate a linear code, which is a set of vectors that can be used to transmit information over a noisy channel. It is defined by a set of basis vectors, which can be used to generate all of the codewords in the code. In coding theory, the generator matrix is a useful tool for encoding and decoding messages in a systematic and efficient manner.
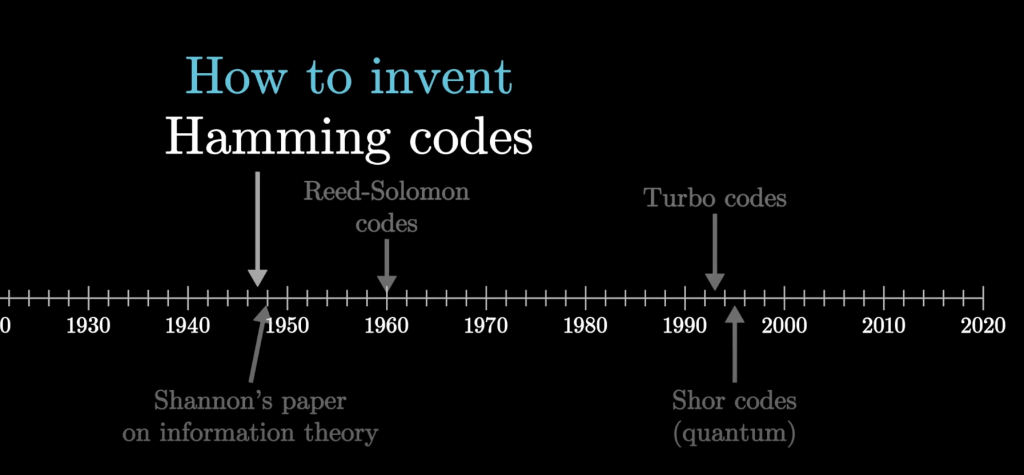
Hamming codes are a method of error correction used in coding theory. They are named after their inventor, Richard Hamming, who introduced them in 1950. Hamming codes work by adding redundant data to a message, allowing errors to be detected and corrected based on the value of the redundant data. The redundant data is added using a special encoding technique that ensures that the number of errors that can be corrected is proportional to the size of the redundant data. Hamming codes are commonly used in applications such as computer memory and data transmission, where the accuracy of the data is important and errors must be corrected to ensure reliable operation.

Hamming codes are improved to be used as Reed-Solomon codes after Shnnon’s paper on information theory.
several YouTube courses on information theory that provide a good introduction to the topic:
- “Information Theory” by 3Blue1Brown: This series of videos provides an intuitive and visual introduction to information theory concepts such as entropy, mutual information, and channel capacity.
- “Information Theory – MIT 6.451” by MIT OpenCourseWare: This video series is a recorded lecture from the course “Information Theory” at MIT. It covers the basics of information theory as well as advanced topics.
- “Information Theory | Full Course | Part 1/3” by Eduonix Learning Solutions: This video course provides a comprehensive introduction to information theory, covering topics such as entropy, coding, and data compression.
