From wiki, In physics, Lagrangian mechanics is a formulation of classical mechanics founded on the stationary-action principle (also known as the principle of least action). It was introduced by the Italian-French mathematician and astronomer Joseph-Louis Lagrange in his 1788 work, Mécanique analytique.
Euler Lagrange Equation is to describe the e.o.m, equation of motion, it’s always composed of two parts: qi and qi first order derivative, L = Kinetic Energy – Potential Energy, hence after meticulous and rigorous mathematical deduction with Taylor expansion involved, the final second order differentiation is to be solved as shown below.
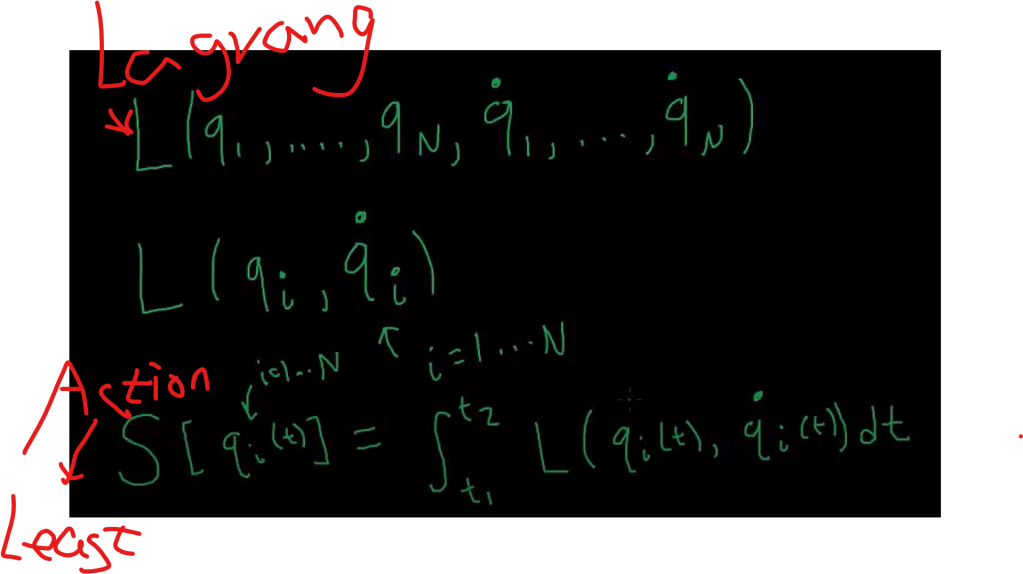
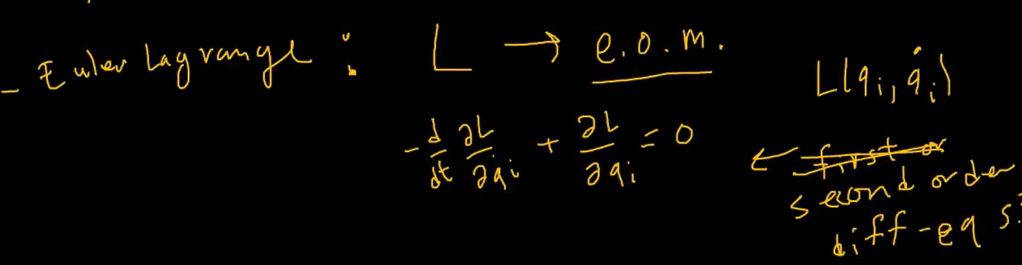
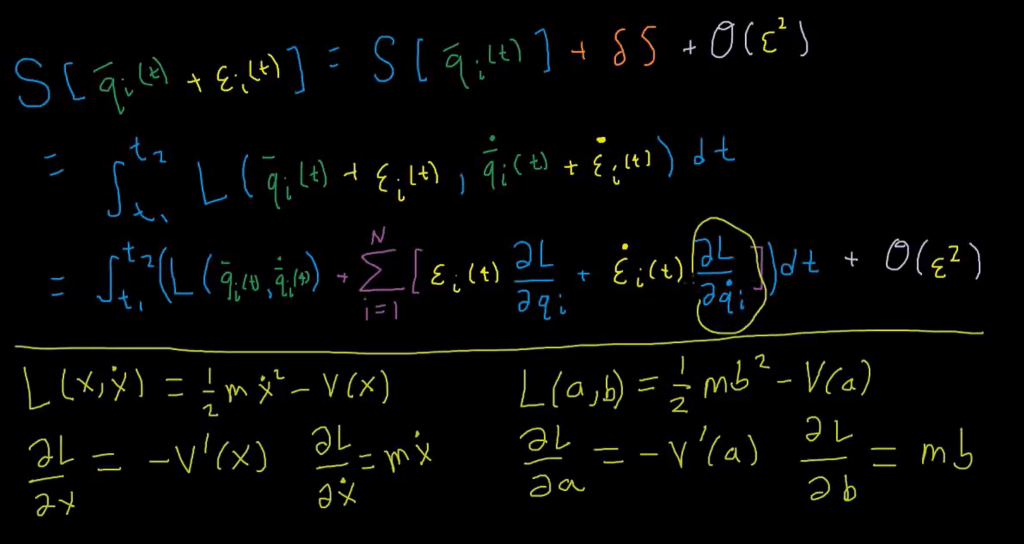

Hence in complete generality, we reach the Euler Lagrange Equation:
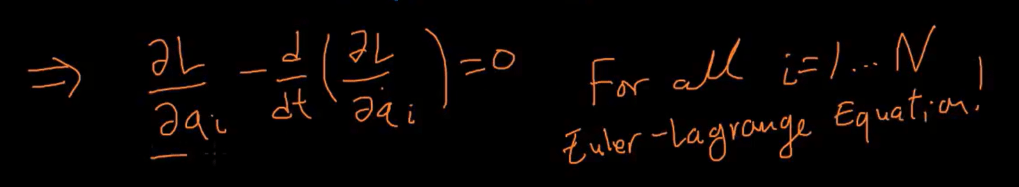
It’s very important of Euler Lagrange Equation, why?

for example
Once have the tool of Lagrange Mechanics, one would discard Newtonian Mechanics, because Lagrange Mechanics makes solving complex system problem much easier compared to Newtonian Mechanics.
It’s also the key to further understand Noether’s Theorem of conservation. A significant theorem in physics.