ROS system installation (from Aleksandar Haber and ROS page), after repository configuration, we need to have ROS package compatible by sudo sh -c ‘echo “deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc) main” > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list’, then set up keys, sudo apt install curl, curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ros/rosdistro/master/ros.asc | sudo apt-key add -, sudo apt update, sudo apt install ros-noetic-desktop-full, it will take a while to get ROS installed
Then we need to setup the environment by source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash, to avoid manually source the bash file every time a new terminal started, we can echo “source/opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash” >> ~/.bashrc, then source ~/.bashrc, then need to install “rosinstall” tool for downlading source tree for ROS packages with a single command, we sudo apt install python3-rosdep python3-rosinstall python3-rosinstall-generator python3-wstool build-essential, after that, we need to Initialize rosdep sudo apt install python3-rosdep, sudo rosdep init, rosdep update
Now it’s time to test by writing “hello world” in ROS:
open new terminal type roscore, check all up working; then open new terminal, type rosrun roscpp_tutorials talker, open a new terminal, run rosrun roscpp_tutorials listener, another terminal type rostopic list, you can see /chatter, /rosout, /rosout_agg
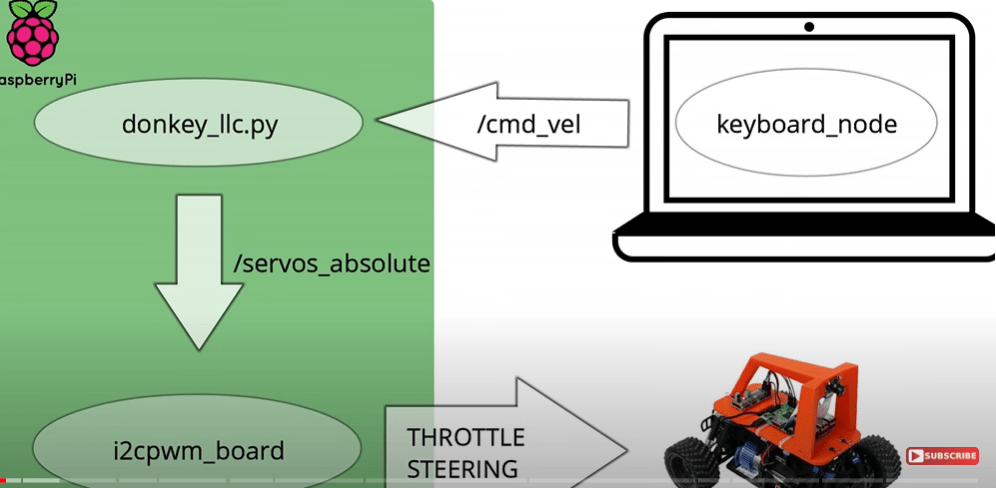
then knowing the concept of nodes, topic, subscriber publisher: in below screenshot, the donkey_llc.py and i2cpwm_board are two nodes, while /servos_absolute and /cmd_vel are topics.
in his tutorials, we start from sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-desktop-full, then sudo rosdep init, sudo rosdep update, source /../kinetic/setup.bash, mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src, cd catkin_ws/, catkin_make to build the environment, then in catkin_ws, source devel/setup.bash, to avoid the trouble of sourcing everytime, we do sudo nano ~/.bash.bashrrc, (nano is editting?), in the end of this bash.bashrc file, add the line: source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash.
Then we need to connect to ssh ubuntu@ubiquityrobot.local, need the password to get in, sudo apt install samba (for sharing the folder), then sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf, in which we need to set up windows=support, and another setting on sharing, then sudp smbpasswd -a ubuntu
then go back to new terminal run roscore
install servo control mode, install from github, sudo apt-get install libi2c-dev, roscd, ~/catkin_ws/devel$ cd .., to catkin_ws$, cd src/ git clone https://gitlab.com/bradanlane/ros-i2cpwmboard, cd .., catkin_make, build up the environment, then source devel/setup.bash
Editing the launch file, then edit the ServoArray.msg file, each package has a package.xml and CMakeLists files.
now on one terminal, run rosrun i2cpwm_board i2cpwm_board, if we want to publish message, rostopic pub /servos_absolute i2cpwm_board/ServoArray “sevos: -servo:1 value: 333.0” (333.0 is idle)
Now we go to new terminal, to catkin_ws/src folder, then catkin_create_pkg donkey_lls rospy
the codes are:
#!/usr/bin/python
"""
Class for low level control of our car. It assumes ros-12cpwmboard has been
installed
"""
import rospy
from i2cpwm_board.msg import Servo, ServoArray
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
import time
class ServoConvert():
def __init__(self, id=1, center_value=333, range=90, direction=1):
self.value = 0.0
self.value_out = center_value
self._center = center_value
self._range = range
self._half_range= 0.5*range
self._dir = direction
self.id = id
#--- Convert its range in [-1, 1]
self._sf = 1.0/self._half_range
def get_value_out(self, value_in):
#--- value is in [-1, 1]
self.value = value_in
self.value_out = int(self._dir*value_in*self._half_range + self._center)
print self.id, self.value_out
return(self.value_out)
class DkLowLevelCtrl():
def __init__(self):
rospy.loginfo("Setting Up the Node...")
rospy.init_node('dk_llc')
self.actuators = {}
self.actuators['throttle'] = ServoConvert(id=1)
self.actuators['steering'] = ServoConvert(id=2, direction=1) #-- positive left
rospy.loginfo("> Actuators corrrectly initialized")
self._servo_msg = ServoArray()
for i in range(2): self._servo_msg.servos.append(Servo())
#--- Create the servo array publisher
self.ros_pub_servo_array = rospy.Publisher("/servos_absolute", ServoArray, queue_size=1)
rospy.loginfo("> Publisher corrrectly initialized")
#--- Create the Subscriber to Twist commands
self.ros_sub_twist = rospy.Subscriber("/cmd_vel", Twist, self.set_actuators_from_cmdvel)
rospy.loginfo("> Subscriber corrrectly initialized")
#--- Get the last time e got a commands
self._last_time_cmd_rcv = time.time()
self._timeout_s = 5
rospy.loginfo("Initialization complete")
def set_actuators_from_cmdvel(self, message):
"""
Get a message from cmd_vel, assuming a maximum input of 1
"""
#-- Save the time
self._last_time_cmd_rcv = time.time()
#-- Convert vel into servo values
self.actuators['throttle'].get_value_out(message.linear.x)
self.actuators['steering'].get_value_out(message.angular.z)
rospy.loginfo("Got a command v = %2.1f s = %2.1f"%(message.linear.x, message.angular.z))
self.send_servo_msg()
def set_actuators_idle(self):
#-- Convert vel into servo values
self.actuators['throttle'].get_value_out(0)
self.actuators['steering'].get_value_out(0)
rospy.loginfo("Setting actutors to idle")
self.send_servo_msg()
def send_servo_msg(self):
for actuator_name, servo_obj in self.actuators.iteritems():
self._servo_msg.servos[servo_obj.id-1].servo = servo_obj.id
self._servo_msg.servos[servo_obj.id-1].value = servo_obj.value_out
rospy.loginfo("Sending to %s command %d"%(actuator_name, servo_obj.value_out))
self.ros_pub_servo_array.publish(self._servo_msg)
@property
def is_controller_connected(self):
print time.time() - self._last_time_cmd_rcv
return(time.time() - self._last_time_cmd_rcv < self._timeout_s)
def run(self):
#--- Set the control rate
rate = rospy.Rate(10)
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
print self._last_time_cmd_rcv, self.is_controller_connected
if not self.is_controller_connected:
self.set_actuators_idle()
rate.sleep()
if __name__ == "__main__":
dk_llc = DkLowLevelCtrl()
dk_llc.run()Now officially run, turn up two ssh ubuntu terminals, then on local ubuntu laptop, export ROS_MASTER_RUI=http://ubiquityrobot.local:11311, export ROS_IP=’hostname -I’, hostname-I you get the ip address