Monte Carlo simulation is a statistical technique used to understand the impact of risk and uncertainty in prediction and forecasting models. It involves running a model many times with a random selection of variables to simulate a wide range of possible scenarios. This method helps in understanding the probability of different outcomes in a process that cannot easily be predicted due to the intervention of random variables.
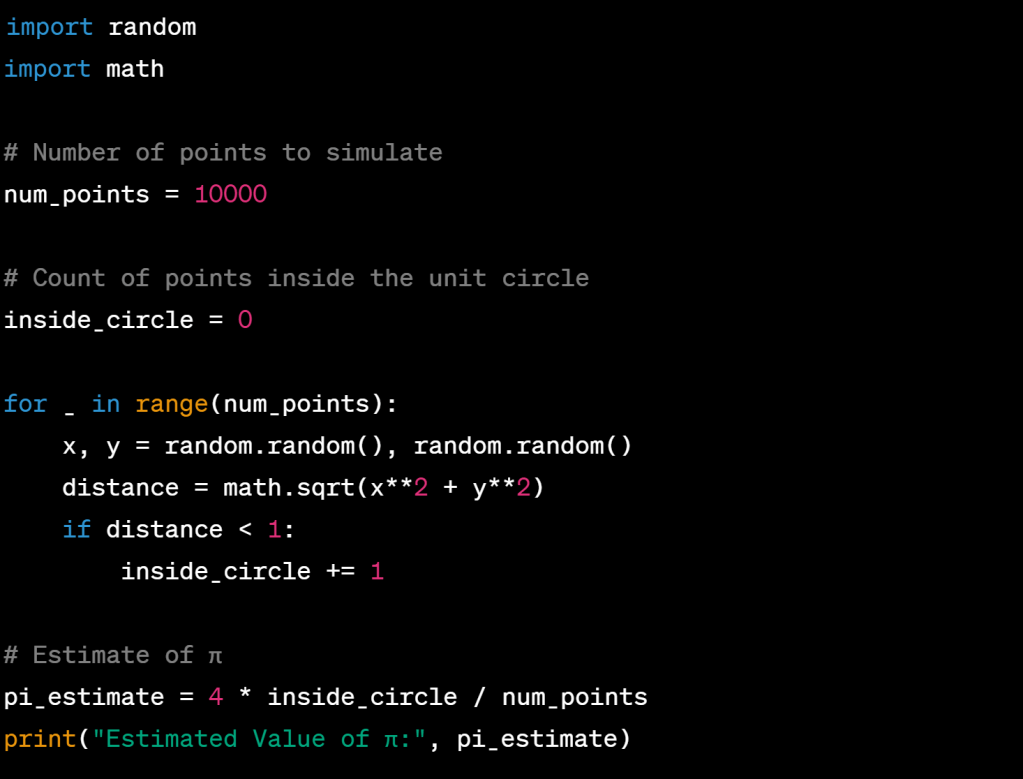
Here’s a Python example using Monte Carlo simulation for estimating the value of π:

ETL expected tail loss (ETL), also known as Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR), is a risk assessment measure used in portfolio optimization. It estimates the expected loss in the worst-case scenario of an investment portfolio. Unlike Value at Risk (VaR), which provides the maximum loss that can occur with a certain probability, ETL gives an average of the most extreme losses beyond the VaR threshold. This makes ETL a more comprehensive measure, as it takes into account not just the threshold of extreme losses but also the severity of losses beyond that point. ETL is particularly useful in assessing the risk of portfolios with asymmetric or fat-tailed return distributions, providing a more realistic view of potential extreme losses.

