definition of trace is the sum of all elements in the diagonal of the matrix, it naturally leads to thought that such matrix must be square and related to rotation.
It is worth noting that the trace of a matrix has some interesting properties:
- The trace of a matrix is equal to the sum of its eigenvalues.
- The trace is invariant under cyclic permutations i.e., Trace(ABC) = Trace(CAB) = Trace(BCA), as long as the resulting matrices are square.
- trace(A + B) = trace(A) + trace(B)
- trace(kA) = k * trace(A), where k is a scalar.
- If A is an n × k matrix and B is a k × n matrix, then trace(AB) = trace(BA). This is not necessarily true if both matrices are square.
But to deeply understand what trace of matrix really means, we can think of how a rotating matrix is composed, clarified and animated by mathemaniac:
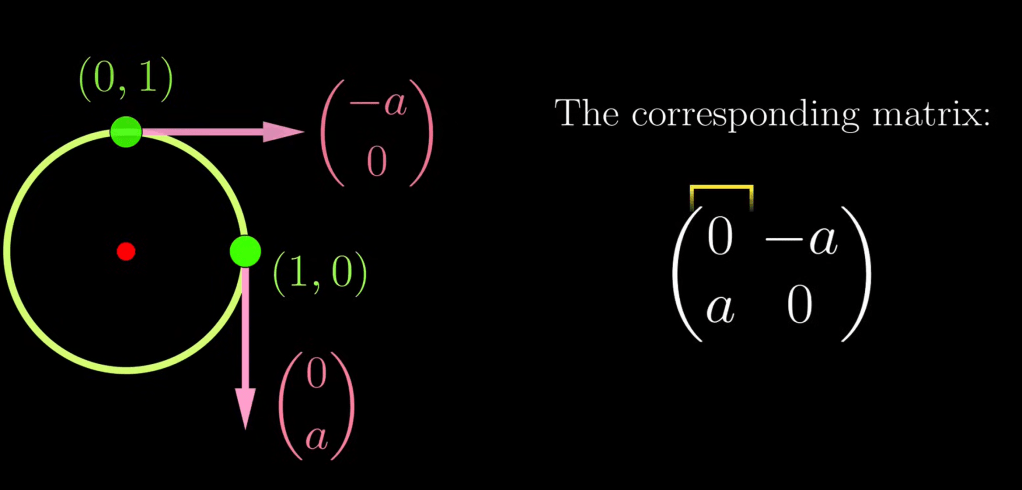
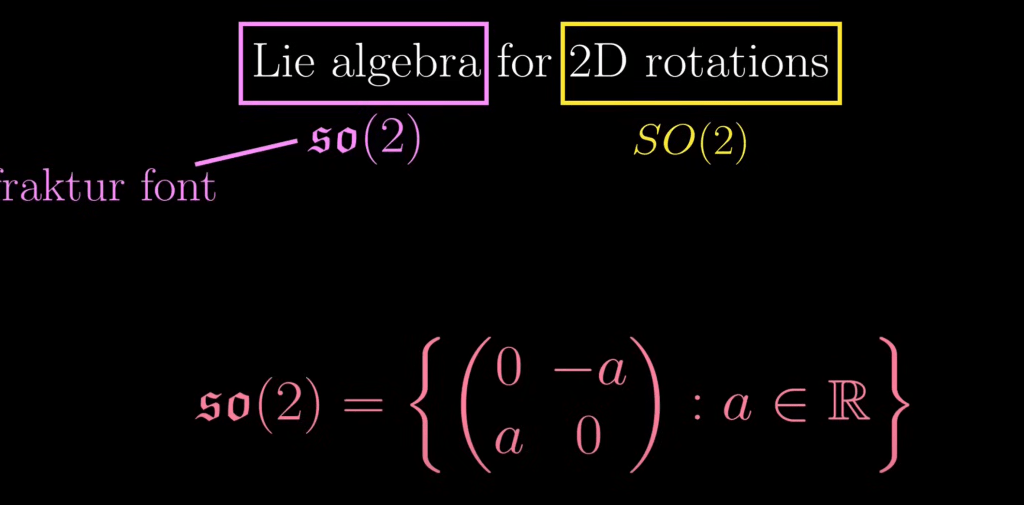
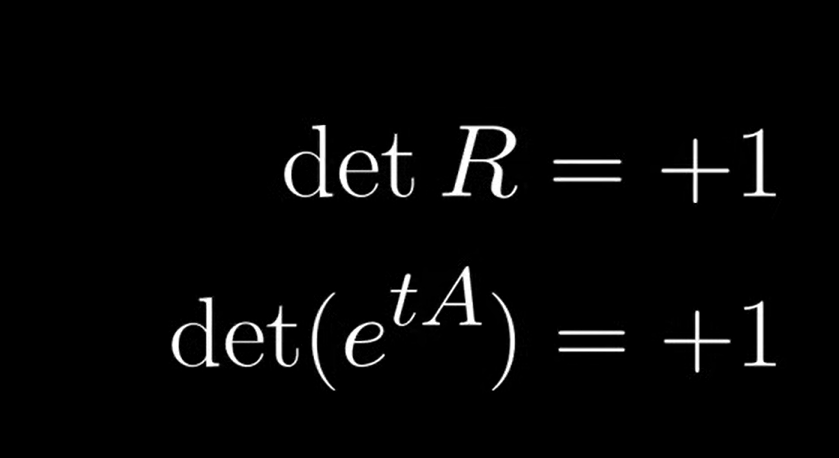

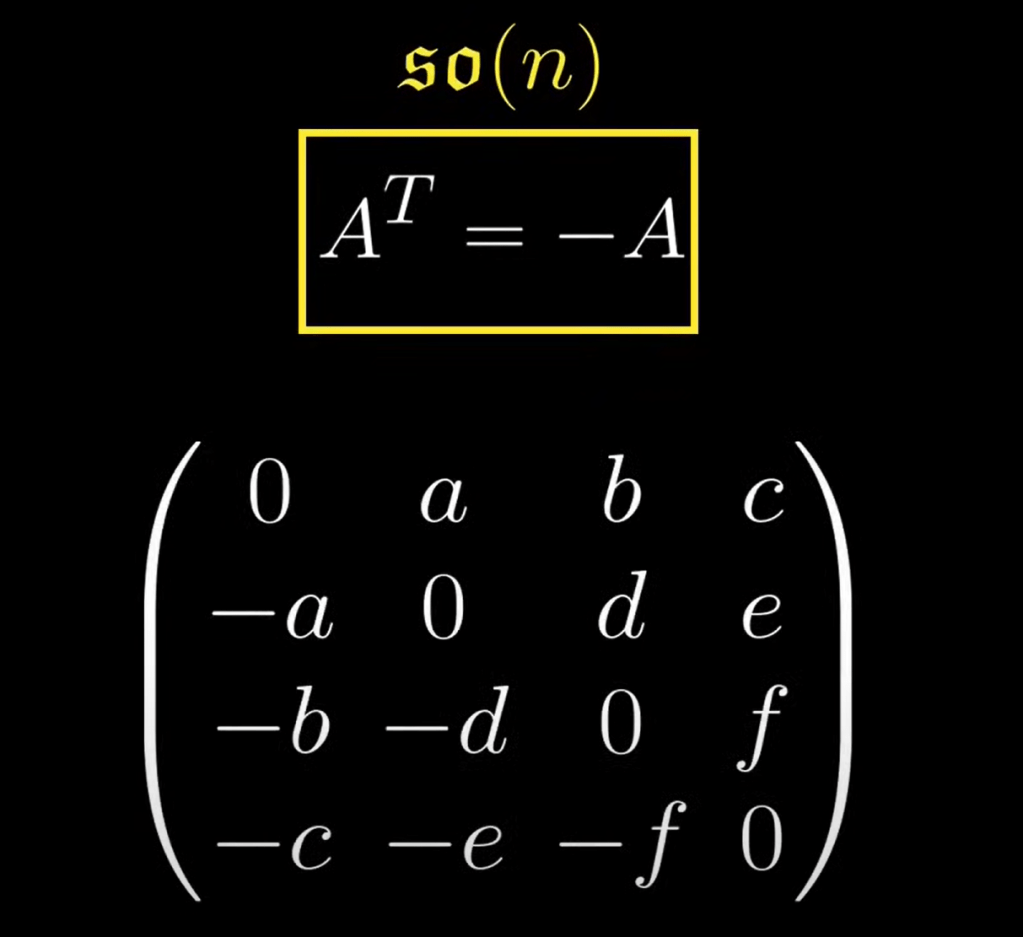
There are two main important properties of Lie Algebra:
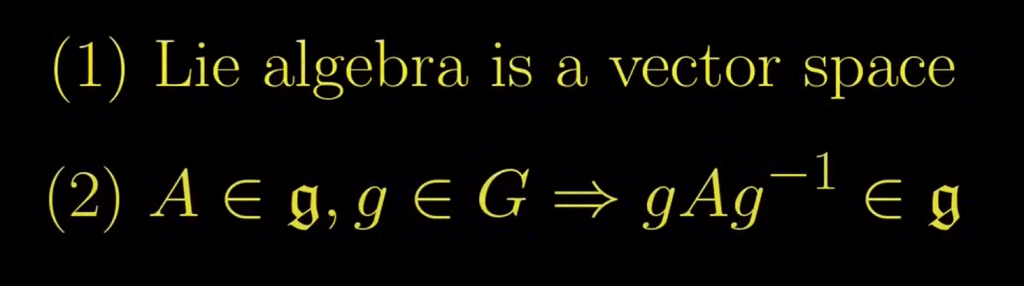
Further explore this explanation to deepen my understanding.