First the concept of dual and representation: representation is a way to concretely realize abstract structures using matrices or linear transformations. for example, rotation by angles can be represented by matrix While dual is a complementary or mirror image of a given structure, for example, in a 3d vector space, the dual space consists of linear functionals that map vectors to scalars, in row form.
what is r twirl, which is equal to gr, it’s dual representation of r (?, my wording).
what is metric? metrics in physics provide the fundamental rules, units, and mathematical frameworks to quantitatively describe and analyze physical phenomena. metric is symmetric!
Given the characteristic of dual r twirl is to be coupled with r to form a invariant scalar, the following is sensible:

if the metric g is not known but the group G is given then we can figure out g from A by above equation; conversely, is the metric g is known, by forcing invariant to hold, we can find the transformations A . that’s how the symmetries are encountered in this area.

Further, we found just O(3) is not complete or accurate, it could have two subgroups with determinant 1 and -1, so SO(3) is the A.
what is tensor? straightforward, could be thought of a matrices of higher dimensions but it’s not accurate, tensors are more than matrices. it’s a symbol to denote transformation like ‘tensor’.

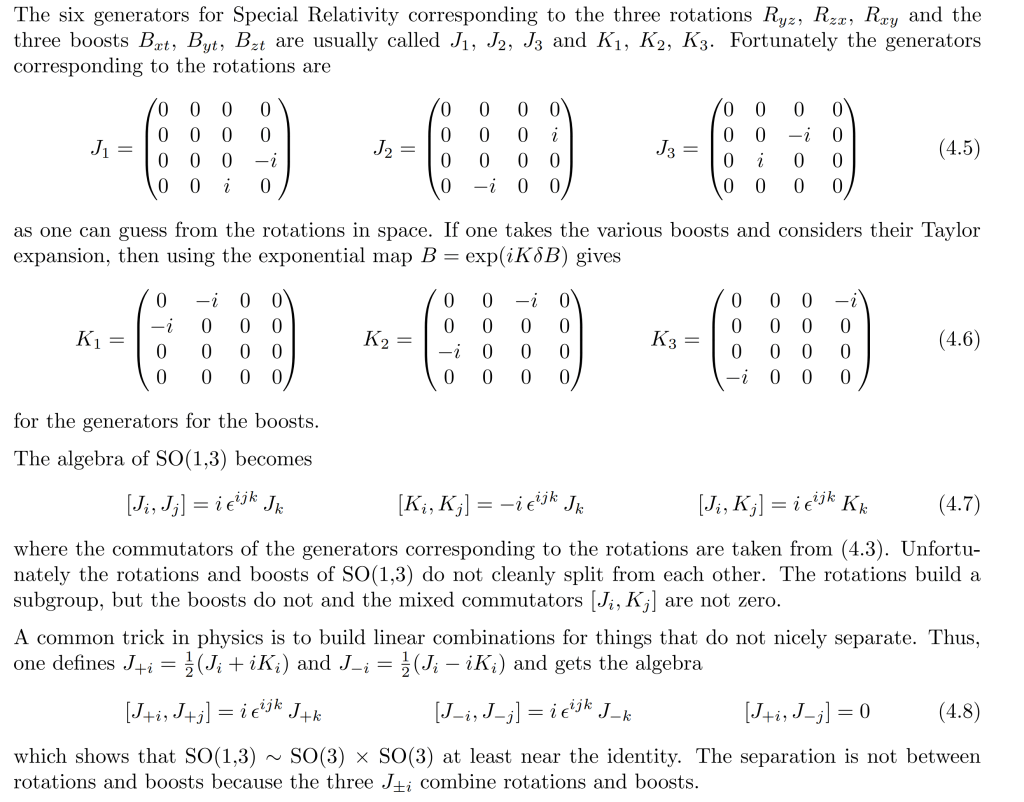
Lie Algebra comes in to a play because the generator serves perfectly in the transformation A:
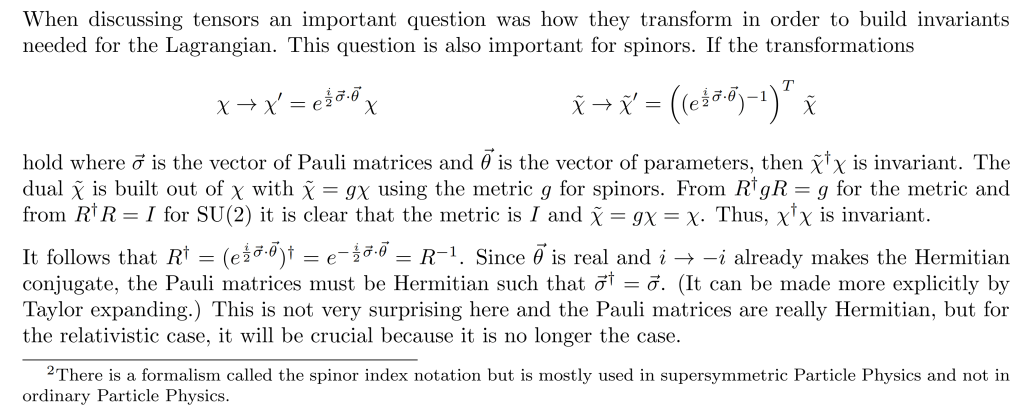
in the attempt to explain Special Relativity, using SO(1,3) and with some combination trick to form SO(3)xSO(3) is not ideal thus we need to interpret using SU(2)xSU(2), introducing SPINOR.