Mapper starts from understanding concept of “covering”. Covering on a manifold setting and then to be on point cloud setting, what’s the right cover? we need to consider scale. Advantage of mapper algorithm in high dimensional data analysis can be elaborated later.
The math behind the Mapper: note to know Reeb graph, first, what is the quotient space? A quotient space is a mathematical concept in linear algebra and topology that allows us to create a new vector space or topological space by “collapsing” or identifying certain elements of an original space. Cosets are elements of a quotient space. Specifically, a coset is a subset of the original vector space V that takes the form v + W, where v is a vector in V and W is a subspace of V. The quotient space V/W is the set of all cosets of W in V. In other words, V/W = {v + W | v ∈ V}. This means that each element of the quotient space is actually a coset. In this case, I understand it as “EQUIVALENT” – “collapse due to equivalent” (equivalent has strict math definition that not only its mapped value is same but also they are “path-connected” components. X/~ is “X mod quotient ~”.

Note the filter function can be R2 or higher, can also be other function like below graphs to show word distance similarity. DBSCAN is widely used in constructing mapper.
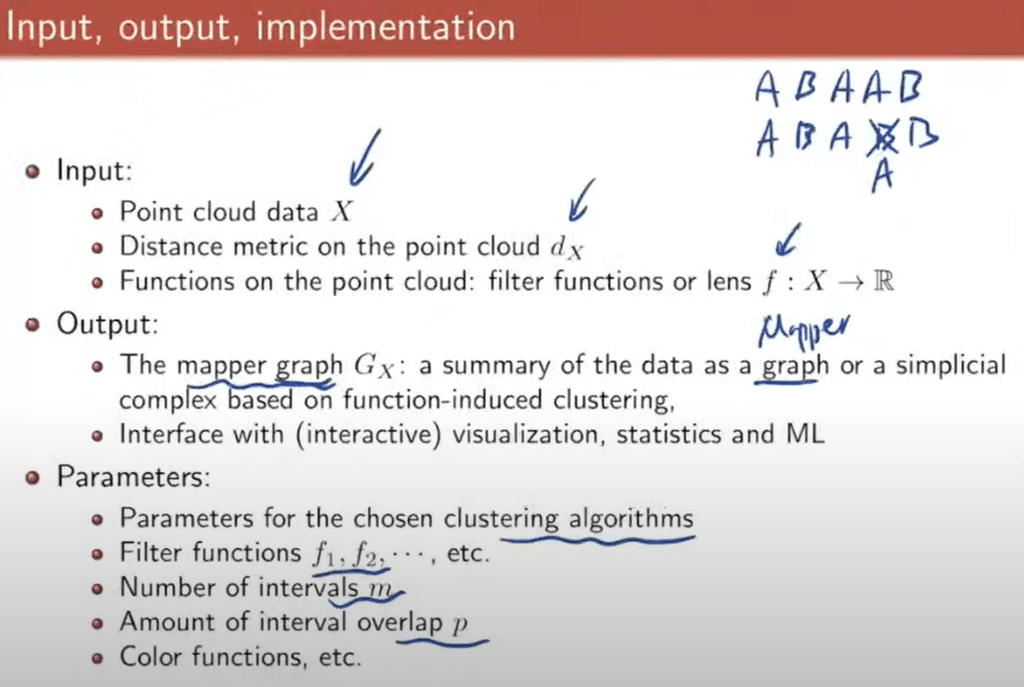
So inside this mapping algo, there is the clustering technique (which is filter function?), could be k-means etc.

Is Mapper Algorithm widely used in having robot to learn any motions?