Concept of simplex, complex and chain, what’s the difference? The p in both p-simplex and p-chain r refers to dimension, so 0 simplex is vertex. p-chain is sum of p-simplices in K(complex)

Example of 0-chain, 1-chain and 2-chain, note in 0-chain, 1+2 is included as it’s the sum of 0-simplex.

The notation matters here: 1+2 is in 0-chain, while 12 or 21 in 1-chain, more officially, the form should be [1, 2]. Then to go over the concept of boundary again in linear algebra aspect: boundary of a p-simplex (an object) is the sum of its (p-1) dimensional faces, or p-1 chain, i.e. boundary of a 2-simlex (triangle sigma = [1, 2, 3]) is the sum of it’s 1 dimensional faces (edges):

Grasp the concept of homeomorphism, it’s a map between groups that can be broken down to maps in individual elements in group. Boundary operation is a homeomorphism.

Complex of chain, or chain complex is sequence of chain groups connected by boundary homomorphism

Concept of cycle: p-cycle is a p-chain with empty boundary, i.e. boundary of p-chain = 0. it forms a subgroup of Cp, denoted as Zp (always for subgroup), it’s the kernel of boundary operation sigma p. Note the definition of kernel is the subgroup in original group that is mapped to null space in image group.

p-boundary is a p-chain that is the boundary of p+1 chain.

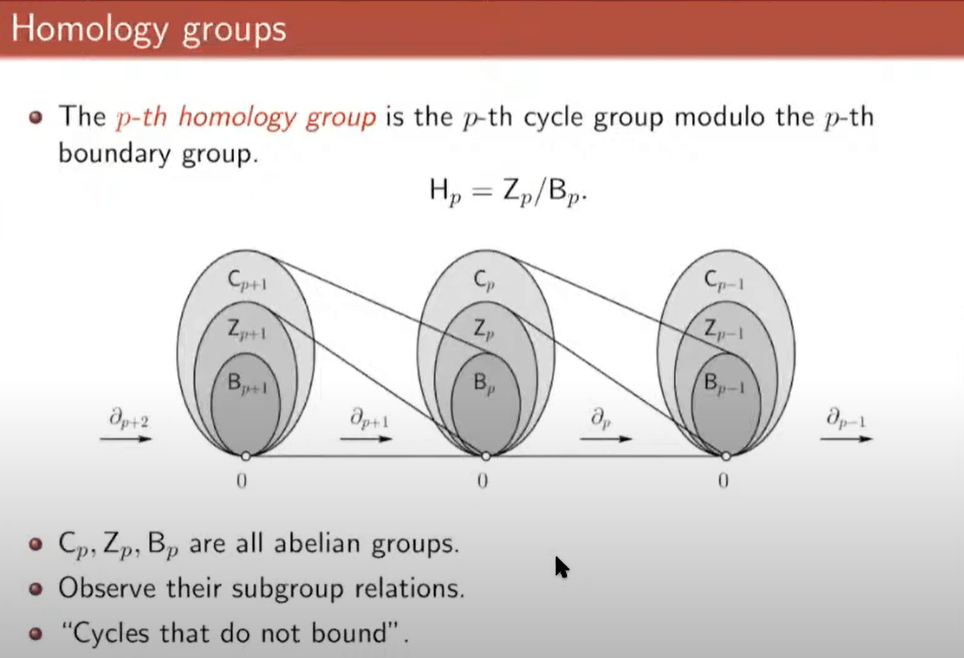
Bp is the image of Cp+1, while Zp+1 is the kernel of boundaryp+1:

Concrete example to illustrate:
homology H1 = Z1/B1, reflected on above Zp/Bp. To be elaborated later, particularly, boundary of a filled triangle is verses loop triangle, why the first output is not zero, the latter is zero, hence forming a cycle?
Why the Outputs Differ:
- Filled Triangle: The boundary of a filled triangle (or any 2-dimensional simplex) consists of its oriented edges, which do not sum to zero. Therefore, ∂(triangle)≠0\partial(\text{triangle}) \neq 0∂(triangle)=0, indicating it is not a cycle.
- Loop Triangle: In contrast, the loop triangle is constructed such that its boundary forms a closed loop. The sum of its oriented edges (boundary) is zero: ∂(loop triangle)=0\partial(\text{loop triangle}) = 0∂(loop triangle)=0. Hence, it forms a cycle in the homology sense.

These cited explanation from chatGPT is not accurate if not wrong. to be homology, it module OUT boundaries. solid triangle and empty triangle differ here, the solid one is boundary one is not!
Then concept of betti number again, it’s measuring number of holes H, also it’s same as the rank of Hp.
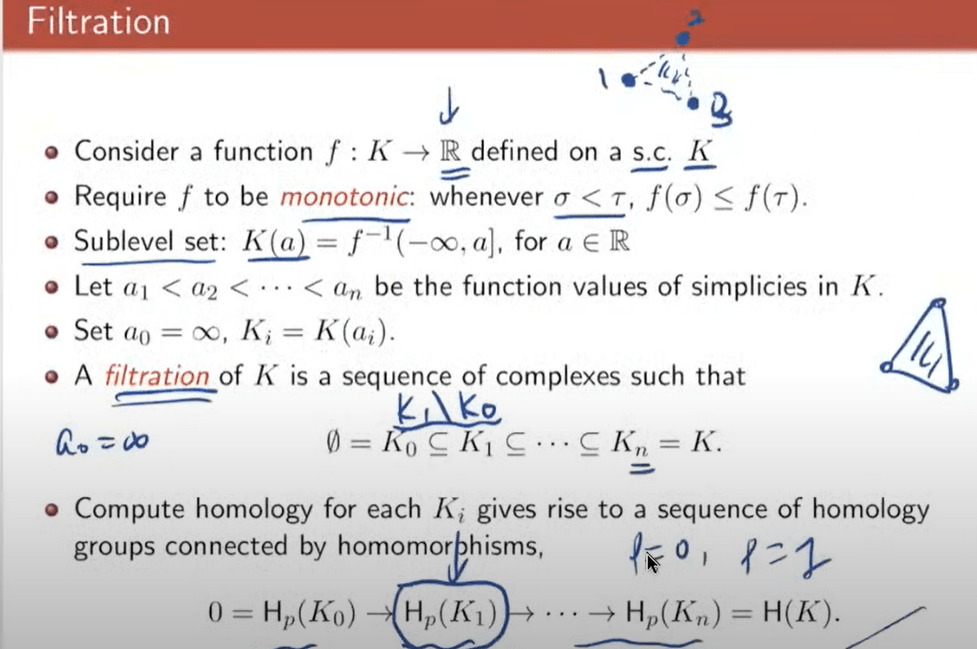
lastly the concept of filtration! Filtration of K is a sequence of complexes such that requires f to be monotonic, sequentially.
boundary around a tunnel/loop/void is not really boundary, only when it’s filled solid, the boundary becomes boundary, it’s to be perceived in terms of open set close set kind of sense.