Kernel perceptron replace dot product in the dual perceptron by an arbitrary kernel function to get the effect of a feature map phi without computing phi(x) explicitly for any samples. By turning regular dot product to kernel function, it’s to turn non-linear classifiable data points linear. for example data points are not separatable in R2, but if use phi to turn (x1, x2) to (x1, x2, x1x2) in R3, it’s classifiable. There are Gaussian kernel, Laplace kernel, ball kernel, triangle kernel etc.
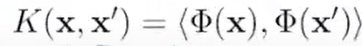
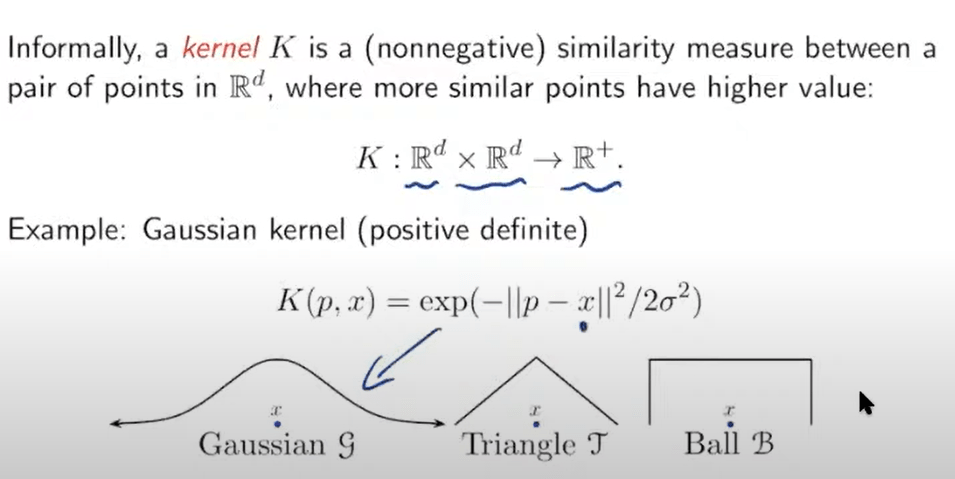
so we apply kernel to compute similarity but what similarity. first to define persistent diagram
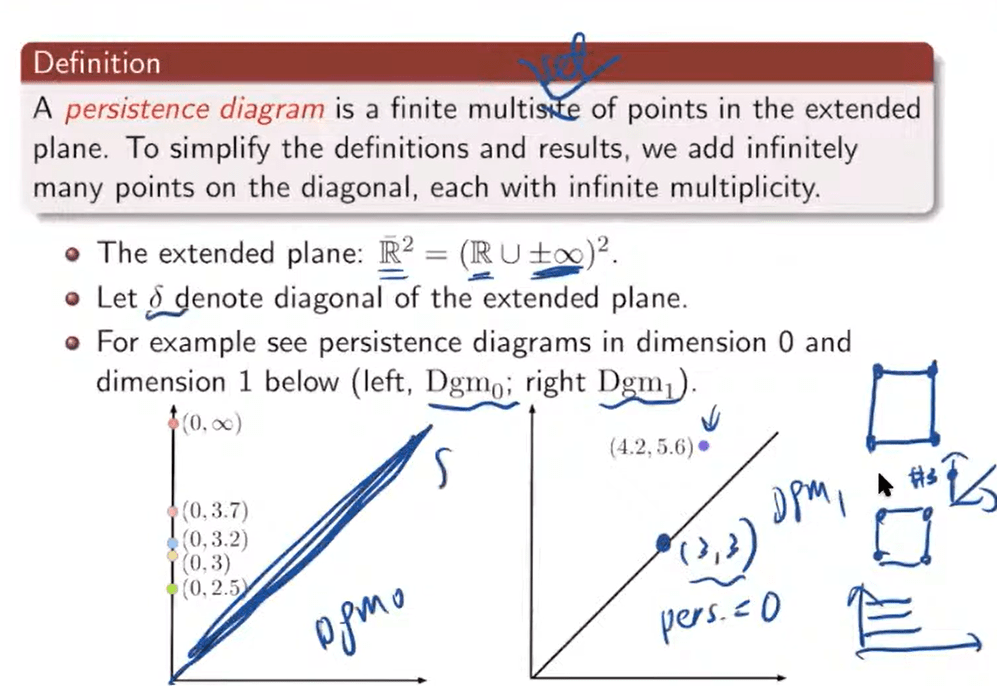
The metric is important, first introduce bottleneck distance
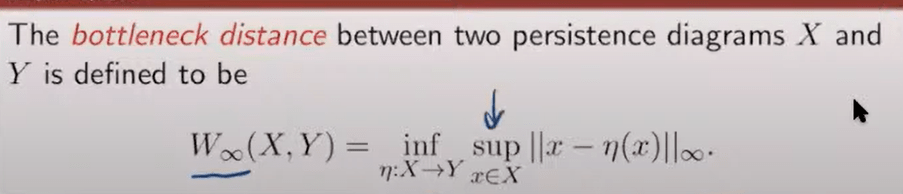

There is the theorem of the stability of filtration:
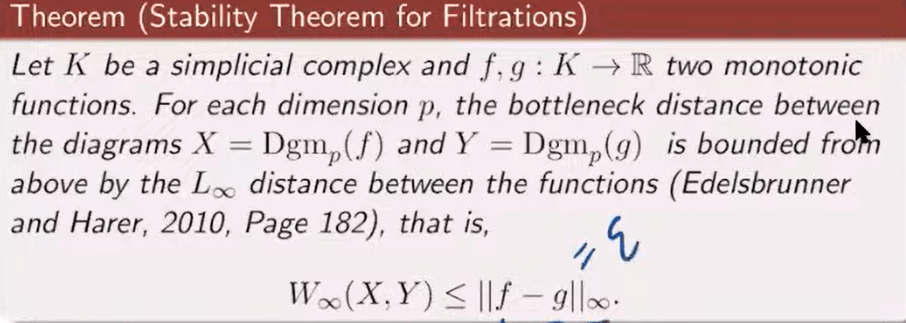
Define Tame Function
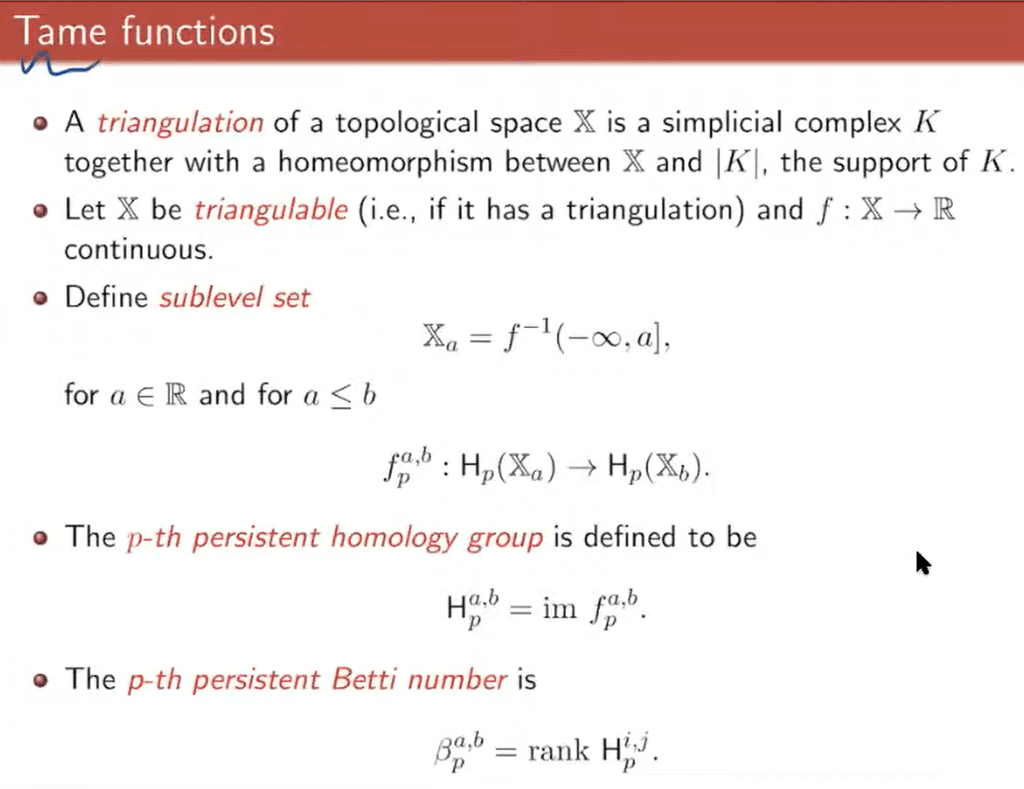
tame function basically means the function is well-behaving colloquially, formally, f is tame if it has only finitely many homological critical values and all homology groups of all sub level sets have finite rank. a group isomorphism is a fucntion between two groups that sets up a one-to-one correspondence between the elements of the groups that respects each group operations/relations among the elements. compare to homomorphism.
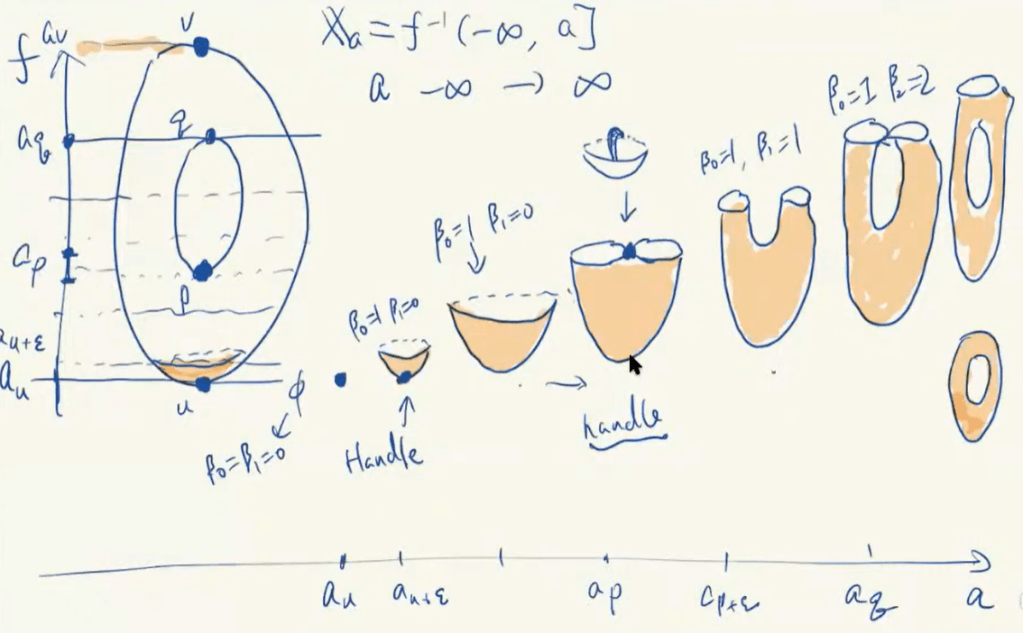
Morse Theory, following on tame function such as height function on a torus to illustrate morse theory: every time when the critical value is passed, the isomorphism property of the sublevel set is changed, we call add a handle.

Other than bottleneck distance, there is degree q wasserstein distance, it takes account all distance instead of bottleneck just consider the largest distrance:
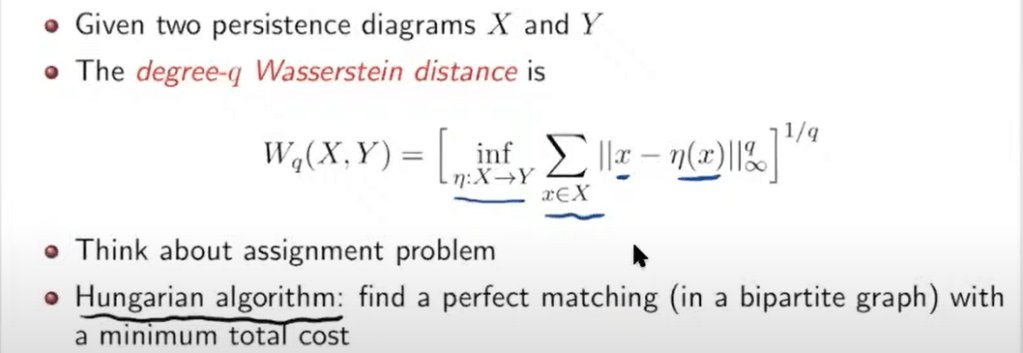
great explanation from Dr.Bei Wang.