The Orbit-Stabilizer Theorem is a fundamental result in group theory, specifically in the study of group actions. It relates the size of the orbit of an element under a group action to the size of the stabilizer of that element.
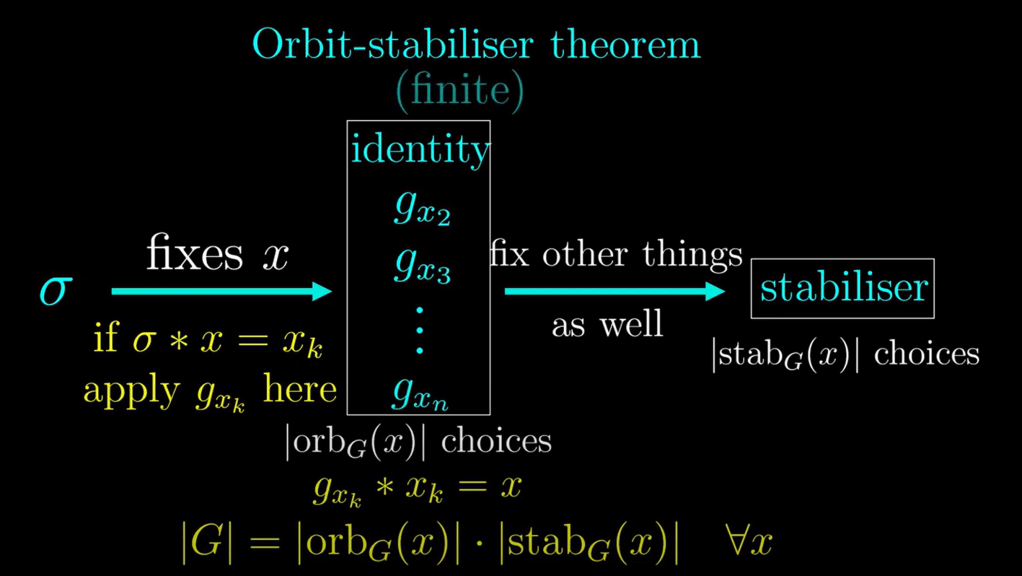
note the concept of stabilizer: the stabilizer of an element under a group action is a key concept that helps in understanding how a group acts on a set.

Lagrange’s theorem,:

Why Lagrange’s theorem, it’s very useful because it narrows down our knowledge of order/number of subgroups if we know the number/order of the group G. the proof is laid out by socratica

learning orbit-stabliser theorem and Lagrange’s theorem helps to understand a very important concept of CONJUGATION! the action g is not same as ghg-1anymore, the only difference is the PERSPECTIVE!
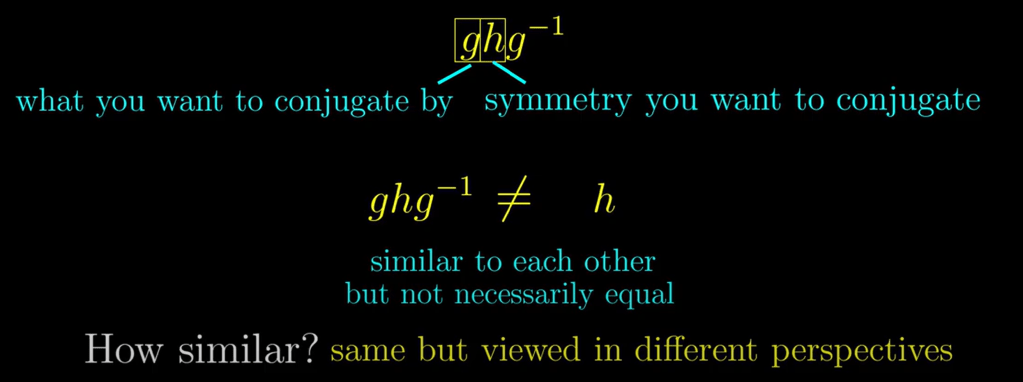
Another combination reveals how different perspective caused (tb studied further later)
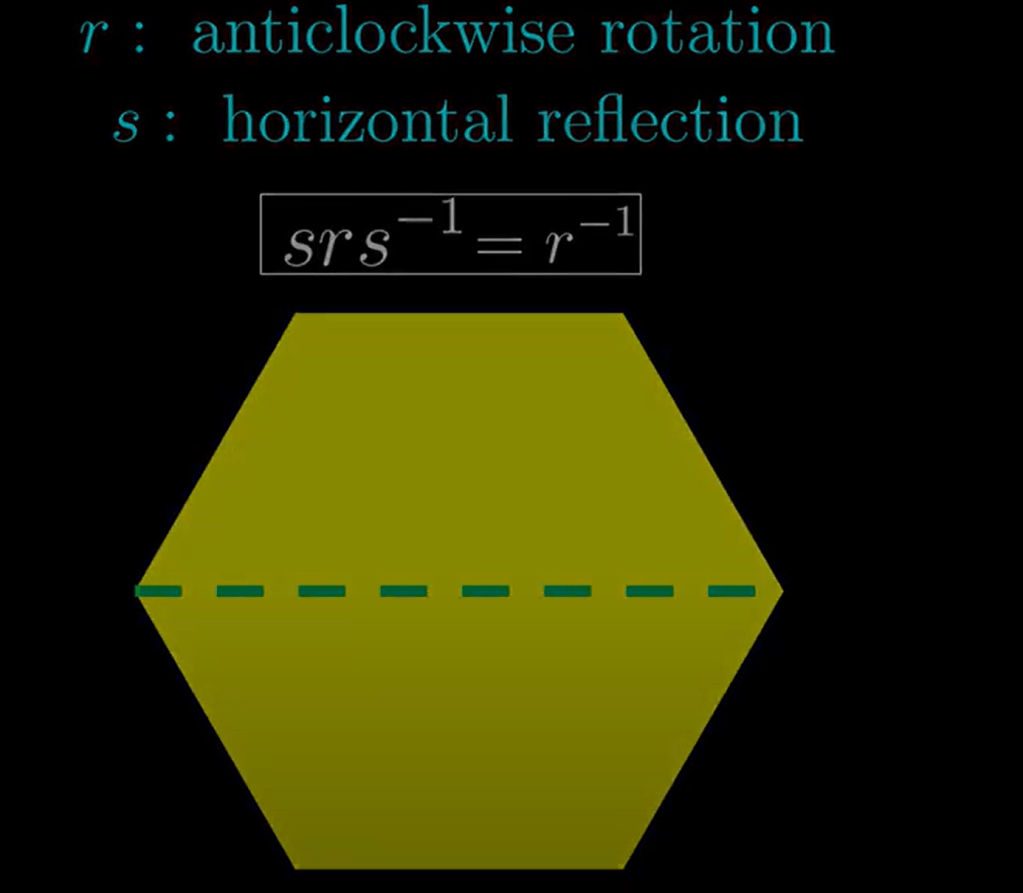
in matrix, we use the conjugation to find similar matrix.
Understanding conjugation leads to the understanding of normal subgroup, like shown below, in some case when gHg-1 = H, meaning the action leads to an element in H, we say g normalizes H. if every element normalizes H, we call this group H normal group. that means H looks same in all perspectives!
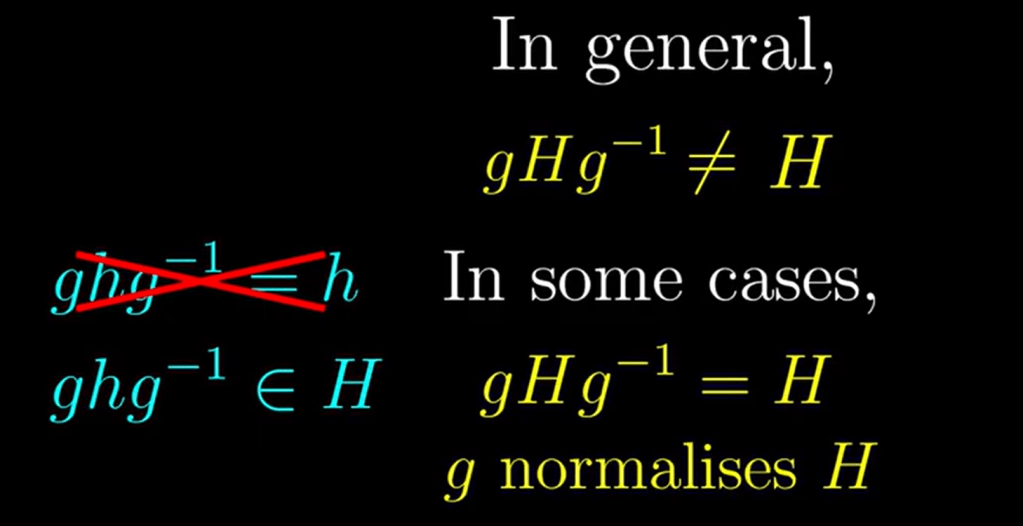
Apparently identity group and whole group G is also normal group. when we say a group is normal it means every element looks same in this group.
This leads to concept of QUOTIENT Group and FACTOR Group.
Conditioned on H is normal, then cosets become quotient group
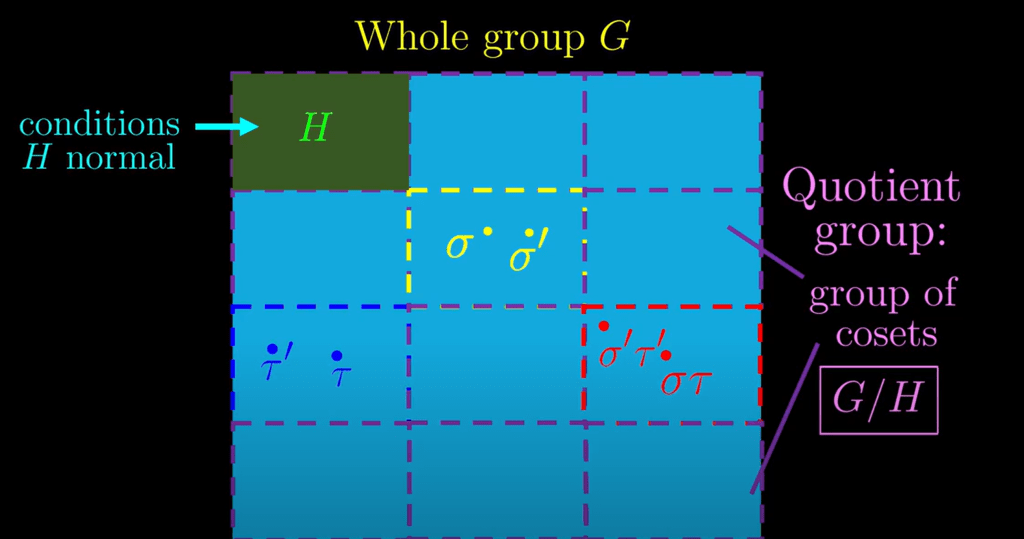

coset group is called factor group, written as G/N, or like above case, Z/5Z is the coset or factor or quotient group, it’s made uof 0+5Z, 1+5Z…
This concept derives homomorphism and isomorphism.
from G to H the phi is homomorphism:

if it’s an one-to-one element between G and H, its isomorphism.
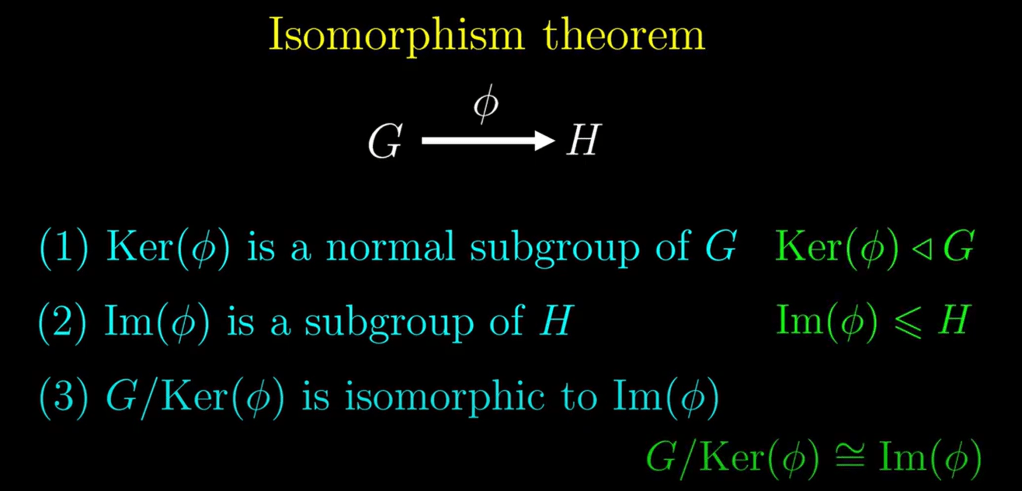
These are the first isomorphism theorem. Very important in later diving into homology and cohomology.

this is from mathmaniac’s essence of group theory.