Function overloading: for various types of parameters to do sum, you don’t have to create three different names but use sum as function for all
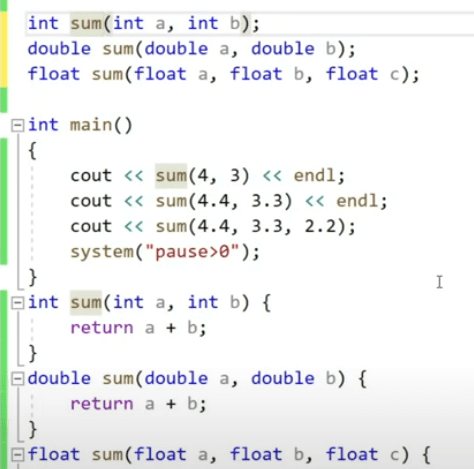
2. what does that system pause mean? The program runs, waits for the user to press a key, and then exits. This is often used in simple console applications or while debugging to keep the window open.

3. use the generic or template to replace function overloading with efficient way. Note it is to pass the reference of variable a and b hence put ampersand to the right of two Ts.

what about to pass it is a pointer to a variable n, note pointer is a variable that points to address of other variable.
these to pass to define all sit at the left side the assigning or equation per se. what about these signs (asterisk and ampersand) at the right side? see below &n is to get the address of variable n. and we know if *n means to get the dereferenced value of n. we can do *n = 10 to reassign a value 10 to that memory address.

4. operator (): operator() allows objects to be called like functions. It’s useful for creating function objects (functors) that can store state and be passed to algorithms. Often used in scenarios where you need a function-like behavior but with additional flexibility and efficiency. for example

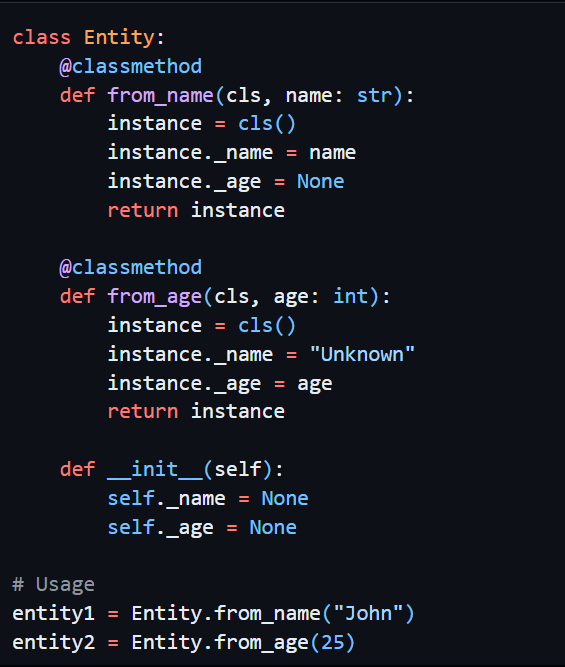
5. Explicit keyword, in below class,

compare to the pythonic way in creating such a simple class
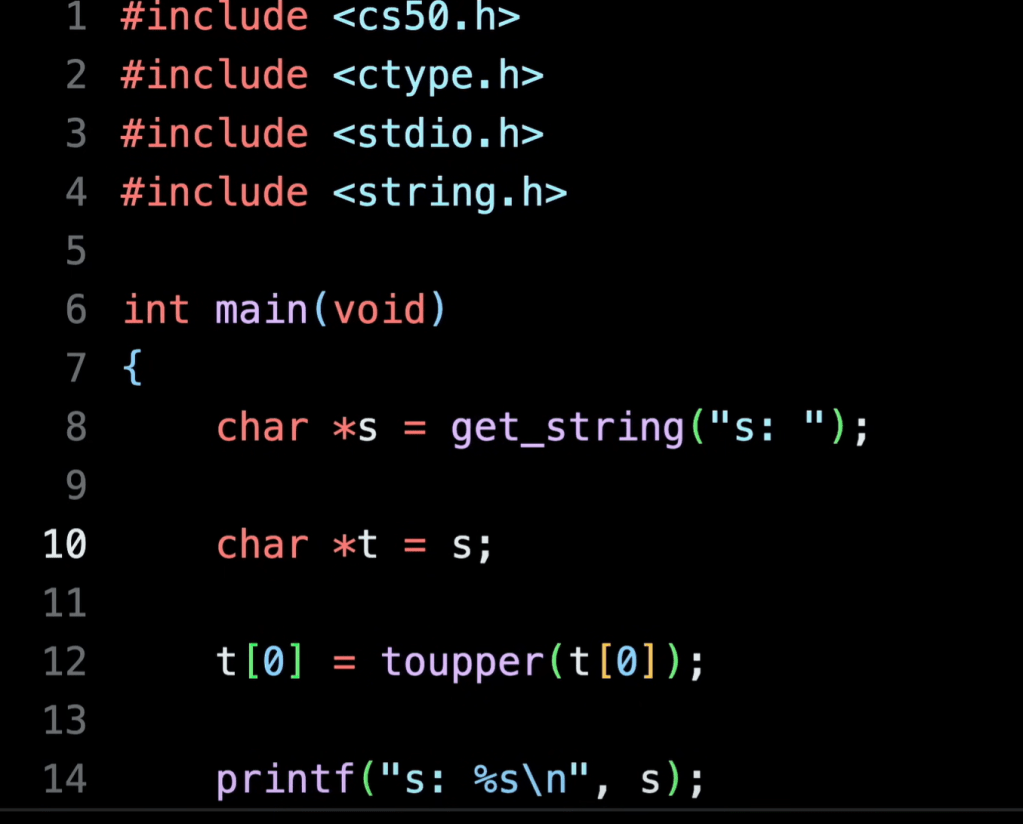
there is no string per se, it’s actually char *s, pointer! for example, below to manipulate the address and values at ease. if replace s+2 to a large number s + 5000, you can get a segment fault error.

so making a copy in C is clear and explicit, you are just copy the address rather than what the address holds:
another greate example is swap function
the first one is false, the next is correct version


malloc and free: continue from above, to copy literally a string, you need to do the following using malloc

knowing this iteration is not optimized as we never want to call a function and put in as a condition, it’s wasteful so instead, say n=strlen(s) + 1 and then i < n. and this is already written and wrapped in strcpy. after using malloc, don’t forget to say free(t). NULL: NULL is synonym for zero, nothing an address holding nothing in the top left corner of computer memory. Inspecting above snippet, always look out for potential bugs, here is the string or memory asked is too long, NULL will be thrown at, hence add below lines

valgrind to check/debug your codes. it’s arcane and does give a hint.
garbage values.
memory physically you can see machine code on top, then global values, then heap, bottom is the stack where function arguments and variables are stored, while malloc starts from heap on top of stack. the two could crash if greedily asked too much on either or both sides.
haep overflow, stack overflow, buffer overflow.