CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) model developed by NVIDIA. It allows developers to use NVIDIA GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) for general-purpose processing, which means tasks that were traditionally handled by the CPU can be offloaded to the GPU for accelerated performance.
Key Features of CUDA:
- Parallel Computing Framework: CUDA enables applications to execute complex computations in parallel, taking advantage of the thousands of cores in modern GPUs.
- C/C++ Programming: CUDA extends C and C++ with keywords and functions, making it easier for developers familiar with these languages to write GPU code.
- Kernel Functions: These are special functions written in C/C++ and executed on the GPU. They run in parallel across many threads.
- Memory Management: CUDA provides mechanisms for allocating and transferring data between the host (CPU) and device (GPU) memory.
Basic Structure of a CUDA Program:
- Host Code (runs on the CPU): Handles setup, memory allocation, data transfer, and kernel launch.
- Device Code (runs on the GPU): Defines the computation to be performed in parallel using kernel functions.
Here is an simple example of square numbers
#include <stdio.h>
// CUDA kernel to square numbers
__global__ void square(float *d_out, float *d_in, int size) {
int idx = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
if (idx < size) {
float f = d_in[idx];
d_out[idx] = f * f;
}
}
int main(void) {
const int ARRAY_SIZE = 1000;
const int ARRAY_BYTES = ARRAY_SIZE * sizeof(float);
// Host arrays
float h_in[ARRAY_SIZE];
float h_out[ARRAY_SIZE];
// Initialize input array
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++) {
h_in[i] = float(i);
}
// Device arrays
float *d_in;
float *d_out;
// Allocate device memory
cudaMalloc((void**) &d_in, ARRAY_BYTES);
cudaMalloc((void**) &d_out, ARRAY_BYTES);
// Copy input array from host to device
cudaMemcpy(d_in, h_in, ARRAY_BYTES, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// Launch kernel on 1M elements with 256 threads per block
int blockSize = 256;
int numBlocks = (ARRAY_SIZE + blockSize - 1) / blockSize;
square<<<numBlocks, blockSize>>>(d_out, d_in, ARRAY_SIZE);
// Copy result back to host
cudaMemcpy(h_out, d_out, ARRAY_BYTES, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// Verify results
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++) {
printf("%f\n", h_out[i]);
}
// Free device memory
cudaFree(d_in);
cudaFree(d_out);
return 0;
}familiar with terminologies: thread, block and grid;
parallel communicaiton patterns: map, gather, scatter, stencil, transpose, …
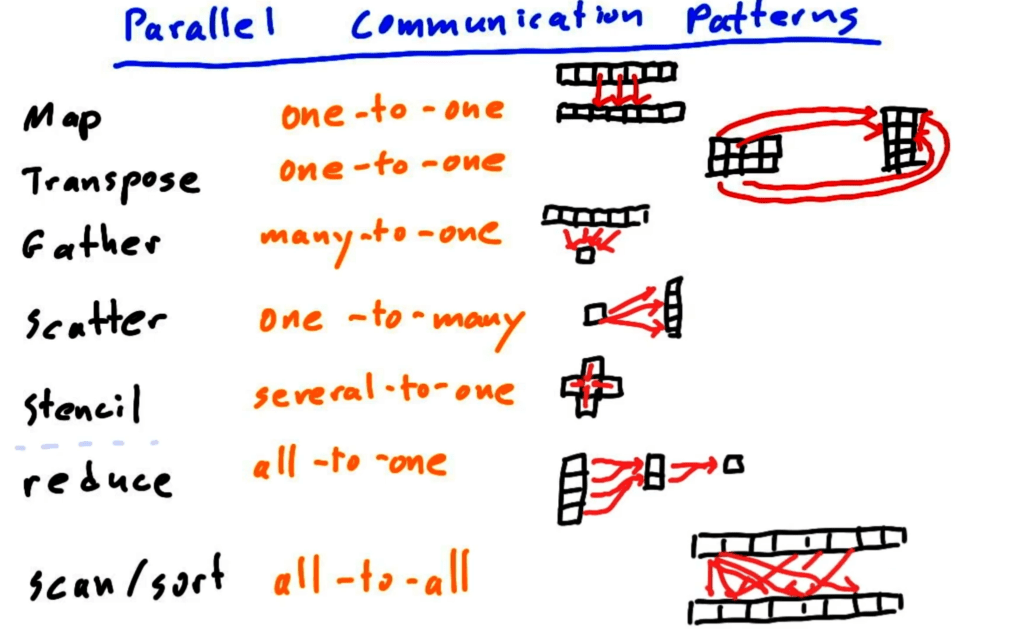
it’s from parallel programing from udacity.