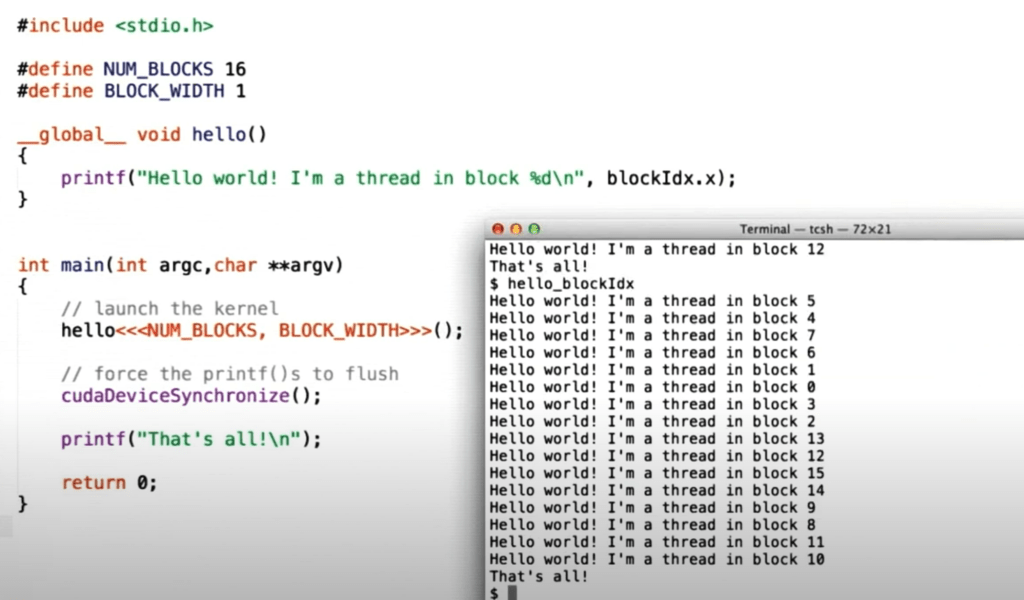
Here is a thread block programming example
there local memory, shared memory and global memory, local memory only accessible by a thread.

synchronization is important, one way is to set barrier. what is coalesce memory? Coalesced memory access is a concept in CUDA programming that refers to the efficient way threads access global memory on a GPU. When memory accesses by threads are coalesced, they are combined into fewer memory transactions, which results in significantly better performance.
what is atomic memory operations? Atomic memory operations are operations that ensure a variable is updated without interruption by any other thread. In other words, an atomic operation allows multiple threads to read, modify, and write a shared variable in a way that prevents race conditions, ensuring the operation is completed as a single, indivisible step.
Thread divergence:
SMs (Streaming Multiprocessors) are the fundamental processing units in NVIDIA GPUs. Here are the key points about SMs:
Architecture: Each SM contains multiple CUDA cores; Can execute multiple thread blocks concurrently
Has its own: L1 cache; Shared memory; Register file; Warp schedulers;
Function: Manages and executes thread blocks
Schedules warps (groups of 32 threads)
Handles resource allocation
Controls shared memory access
Performance Impact:
More SMs = more parallel processing capability
Each SM can handle multiple blocks simultaneously
Number of SMs affects how many blocks can run in parallel
Example:
Understanding SMs is crucial for CUDA optimization as they determine the GPU’s parallel processing capacity.
// A GPU with 16 SMs running blocks of 256 threads
const int numSMs = 16;
const int threadsPerBlock = 256;
const int blocksPerSM = 2; // Each SM handles 2 blocks
// Total parallel threads = numSMs * blocksPerSM * threadsPerBlock
const int totalThreads = numSMs * blocksPerSM * threadsPerBlock;