What is residual pathway? A residual pathway (or residual connection) is a mechanism in neural networks that allows the original input of a layer to be added directly to its output. It was introduced in ResNet (Residual Networks) and has since become a fundamental component in modern architectures like Transformers. In a Transformer block, the residual pathway is used after components like self-attention and feed-forward layers.
Why use residual pathway? let’s take a look at an example, Let’s say GPT is generating text, and the input sequence is:”The cat sat”\text{“The cat sat”}”The cat sat”

What is Multi-Head Attention? Multi-head attention allows the model to focus on different aspects of the input sequence simultaneously, extracting nuanced relationships between words. Each “head” in multi-head attention looks at the sequence from a different perspective, capturing patterns like:
- How “cat” relates to “sat” (subject-action).
- How “cat” relates to “The” (determiner-subject).
- How “sat” relates to “The” (overall sentence structure).
Without multi-head attention, GPT would struggle to grasp complex relationships and patterns, limiting its ability to generate coherent and contextually relevant text.
Using the same ‘The cat sat’ example,
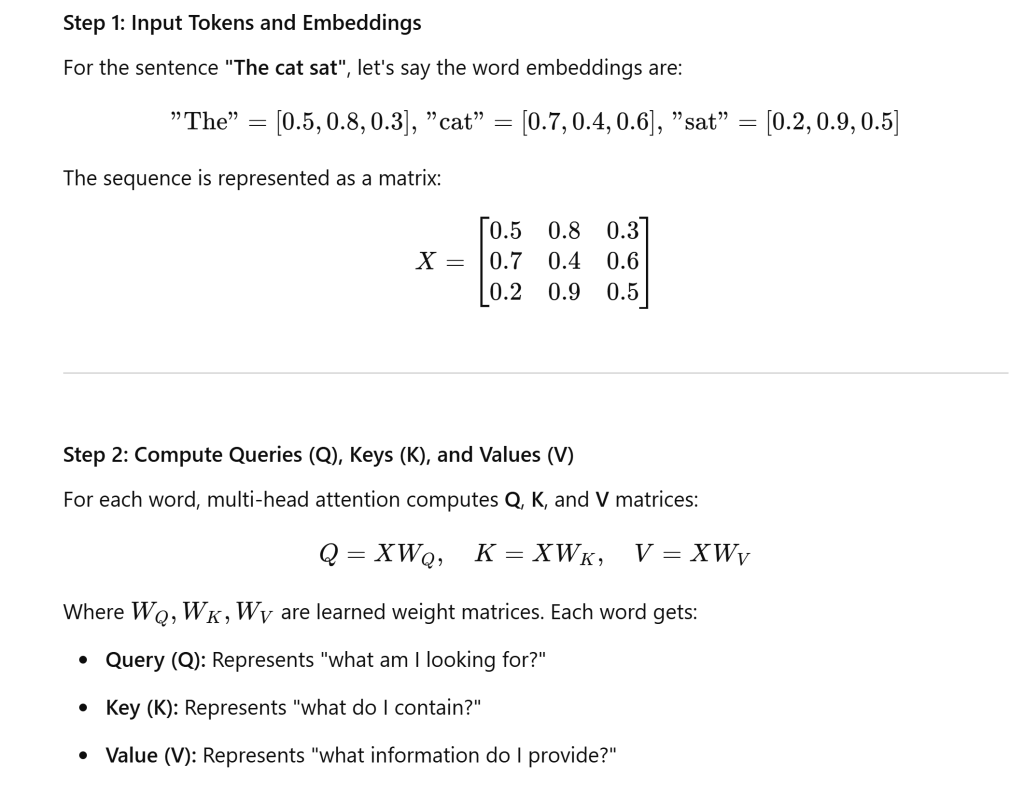
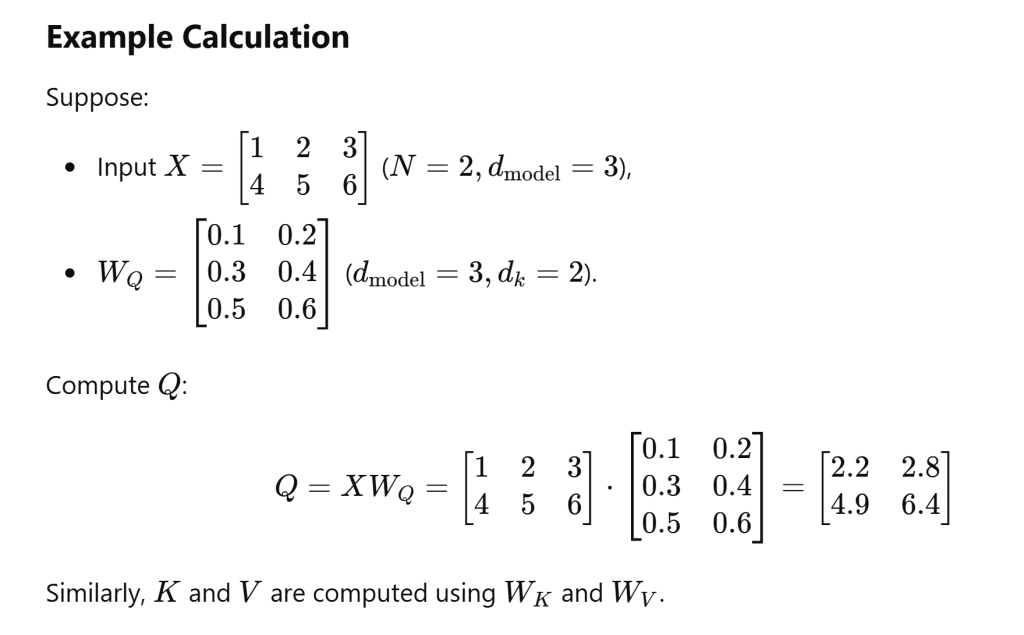
How are these weight matrix Q, K and V calculated?
- Initialization:
- WQW_QWQ, WKW_KWK, and WVW_VWV are initialized randomly (e.g., using Xavier or He initialization).
- Forward Pass:
- The input embeddings (XXX) are transformed into Q,K,Q, K,Q,K, and VVV using the weight matrices.
- Loss Computation:
- The model computes a loss based on its predictions and the ground truth (e.g., cross-entropy loss for text generation tasks).
- Backpropagation:
- Gradients of the loss with respect to WQ,WK,W_Q, W_K,WQ,WK, and WVW_VWV are computed.
- Weight Update:
- Using optimization algorithms (e.g., Adam), WQ,WK,W_Q, W_K,WQ,WK, and WVW_VWV are updated to minimize the loss.
What is Causal Self-Attention? Causal self-attention is a variation of the self-attention mechanism designed to respect the temporal or sequential nature of input data. It ensures that each token in the input sequence only attends to itself and the tokens before it, not the tokens that come after. This property is crucial for tasks like language modeling, where future tokens should not influence predictions for the current token.
intuitively you can understand why mask matrix like below is used to realize Causal self-attention:

import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class CausalSelfAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, n_head, block_size):
super().__init__()
self.n_head = n_head
self.d_model = d_model
self.block_size = block_size
self.qkv_proj = nn.Linear(d_model, 3 * d_model)
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.register_buffer("mask", torch.tril(torch.ones(block_size, block_size)))
def forward(self, x):
B, T, C = x.size() # Batch size, sequence length, embedding size
qkv = self.qkv_proj(x) # Compute Q, K, V
q, k, v = qkv.chunk(3, dim=-1)
# Compute attention scores
attn_scores = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) / (C ** 0.5)
# Apply causal mask
attn_scores = attn_scores.masked_fill(self.mask[:T, :T] == 0, float('-inf'))
attn_probs = torch.softmax(attn_scores, dim=-1)
# Compute output
out = attn_probs @ v
return self.out_proj(out)
In sequence processing and attention mechanisms, B, T, and C are often used to describe the dimensions of a tensor (multi-dimensional array).
Batch Size (B): Affects the throughput of training. Larger batches improve parallelism but require more memory. Sequence Length (T): Determines the amount of context a model processes. Longer sequences provide more information but are computationally expensive. Embedding Size (C): Encodes the richness of features. Higher CCC captures more details but increases model size.
so in Andrej’s names.txt., he used character/letter to predict next letter in name, if bigram and if use emma as example, .e, em, mm, ma provides batch size B=4, sequence length T = 2 ; Feature Dimension (C) refers to the representation size of each token. If each character is mapped to a one-hot vector of size 27 (for 26 letters + 1 special token for .), C=27.If an embedding table maps characters to a smaller embedding size (e.g., 2), then C=2.