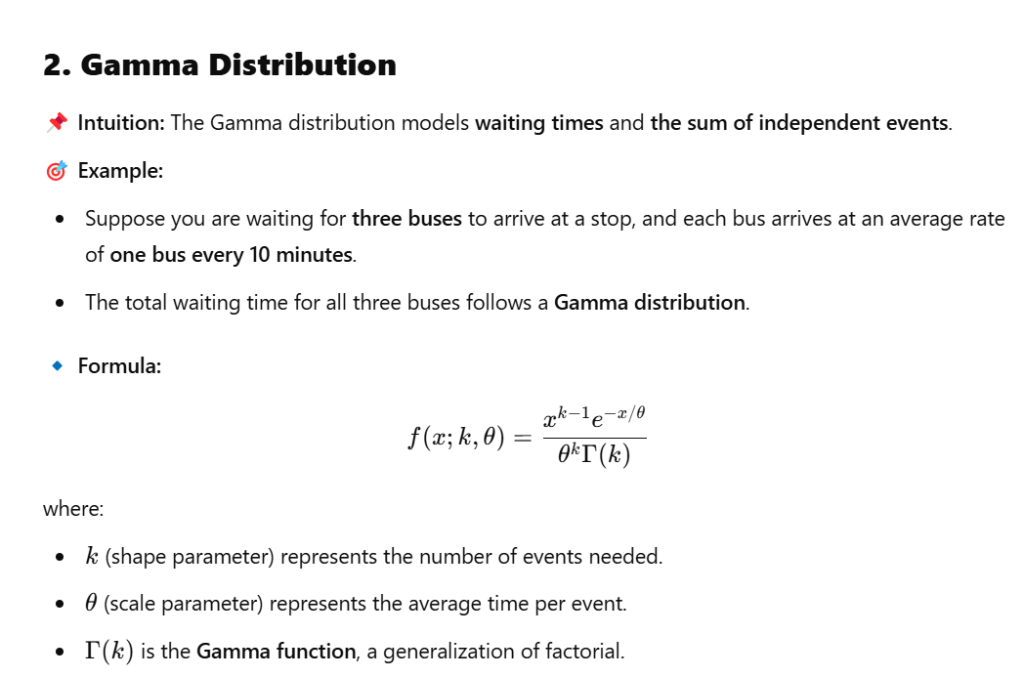
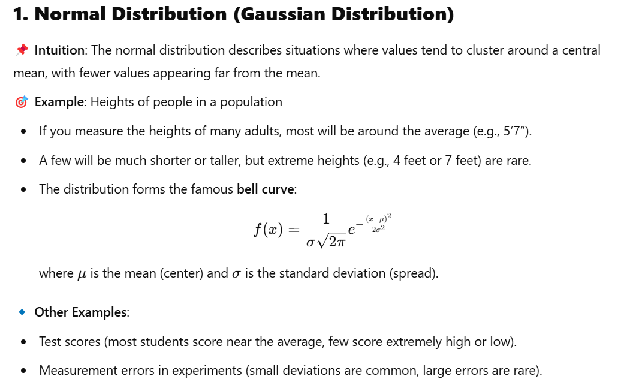
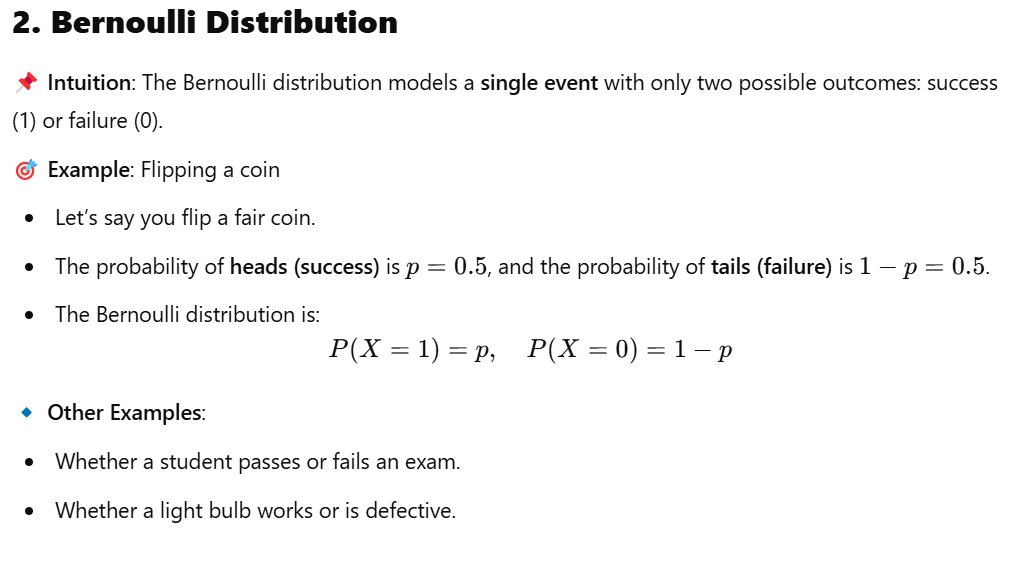
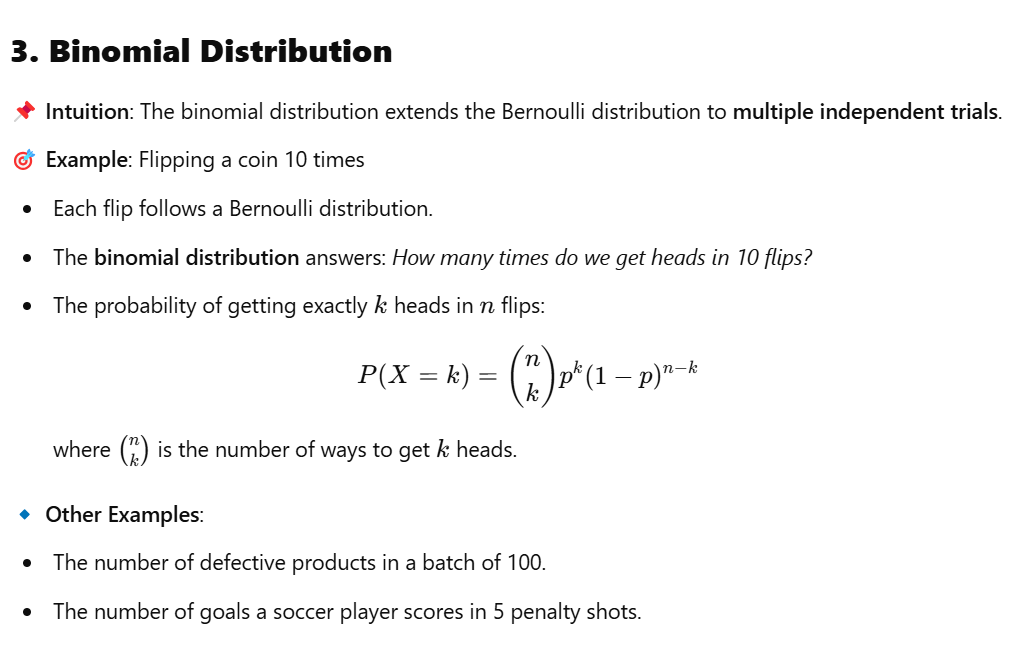
We’d go through normal distribution, Bernouli distribution, binomial distribution, Poisson distribution, chi-square distribution, etc.

ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) is primarily associated with the F-test, but its scope extends beyond just the F-test.
ANOVA tests whether the means of three or more groups are equal by comparing:
- Between-group variability (differences across group means).
- Within-group variability (differences within each group).
The F-test is the default hypothesis test in ANOVA:
[ F = \frac{\text{Between-group variability}}{\text{Within-group variability}} ]
- A large ( F )-value implies group means differ significantly.
While the F-test is central to ANOVA, other tools and adjustments are used depending on the context:
- Post Hoc Tests:
- After ANOVA detects significant differences, post hoc tests (e.g., Tukey’s HSD, Bonferroni) identify which specific groups differ.
- These use t-tests with adjusted significance levels.
- Non-Parametric Alternatives:
- When ANOVA assumptions (normality, equal variances) fail, use:
- Kruskal-Wallis Test: Rank-based alternative (does not use the F-distribution).
- Welch’s ANOVA: Adjusts for unequal variances (uses a modified F-test).
- When ANOVA assumptions (normality, equal variances) fail, use:
- Repeated Measures/Mixed ANOVA: