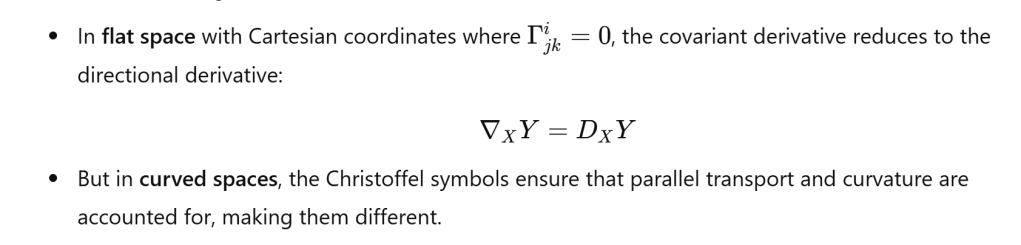When undertaking the transition to advanced studies of curved space, in contrast to Euclidean space, it is essential to comprehend the notion of covariant derivatives, while also further exploring our established understanding of directional derivatives to effectively distinguish between the two.

Key Differences
- Curvature Effects
- The directional derivative does not consider curvature—it is simply the derivative in a direction.
- The covariant derivative accounts for curvature through the Christoffel symbols.
- Tensorial Property
- The directional derivative does not preserve tensorial properties—it does not give a tensor when applied to tensors.
- The covariant derivative preserves tensorial properties, ensuring results remain valid in any coordinate system.
- Application
- The directional derivative is sufficient for flat space (Euclidean).
- The covariant derivative is necessary in curved space (Riemannian geometry, general relativity) to properly describe changes in vector fields.