Project Packaging & Metadata
setup.py: Used to package and distribute Python projects.- Build tool: Use
setuptoolsto define package name, version, dependencies, etc. - Semantic Versioning: Follows
MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH, e.g.,1.0.0. - Special package attributes:
Logging
- Import logger directly: from logging import Logger
- Common methods of logging.Logger instance: debug(), info(), warning(), error(), critical()
- Logger setup best practices (setup_logging)
- Create a logs directory
- Define a formatter
- Get or create a named logger
- Set
logger.propagate = Falseto stop duplicate logs - Add file & console handlers only if not already added
Retry Logic with tenacity, @retry it’s a decorator
Context Manager Protocol
To create a custom context manager (used with with), implement:
__init__(self, ...): Constructor (e.g., accept config path)__enter__(self): Called at start ofwithblock__exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb): Called at the end (even on error)
with DatabaseConnection("config.yml") as conn:
df = pd.read_sql("SELECT * FROM table", conn.engine)
A hash function is a function that takes an input (called a key) and produces a fixed-size string of bytes (usually a number), which is called a hash. maps data of arbitrary size to data of fixed size — often a numeric value (e.g. int or hex). In Python, the built-in hash() function is not consistent across sessions for security reasons (hash randomization). For persistent hashes, use hashlib.
Add concurrent, safety thread considerations: first we can Use Locks or Synchronization
import threading
class Spot:
def __init__(self):
self.lock = threading.Lock()
self.is_occupied = False
def assign_vehicle(self):
with self.lock:
if not self.is_occupied:
self.is_occupied = True
return True
return False
Or use Thread-Safe Data Structures: queue.Queue; threading.Lock; multiprocessing.Value
Consider Message Queues (Advanced)
Decouple entry/exit panels from the core system:
Panel sends “assign vehicle” or “free spot” event to a queue; A central service processes events serially.
Without lock vs. with lock
import threading
counter = 0
lock = threading.Lock()
def increment():
global counter
for _ in range(10000):
with lock: # only one thread can enter this block at a time
counter += 1
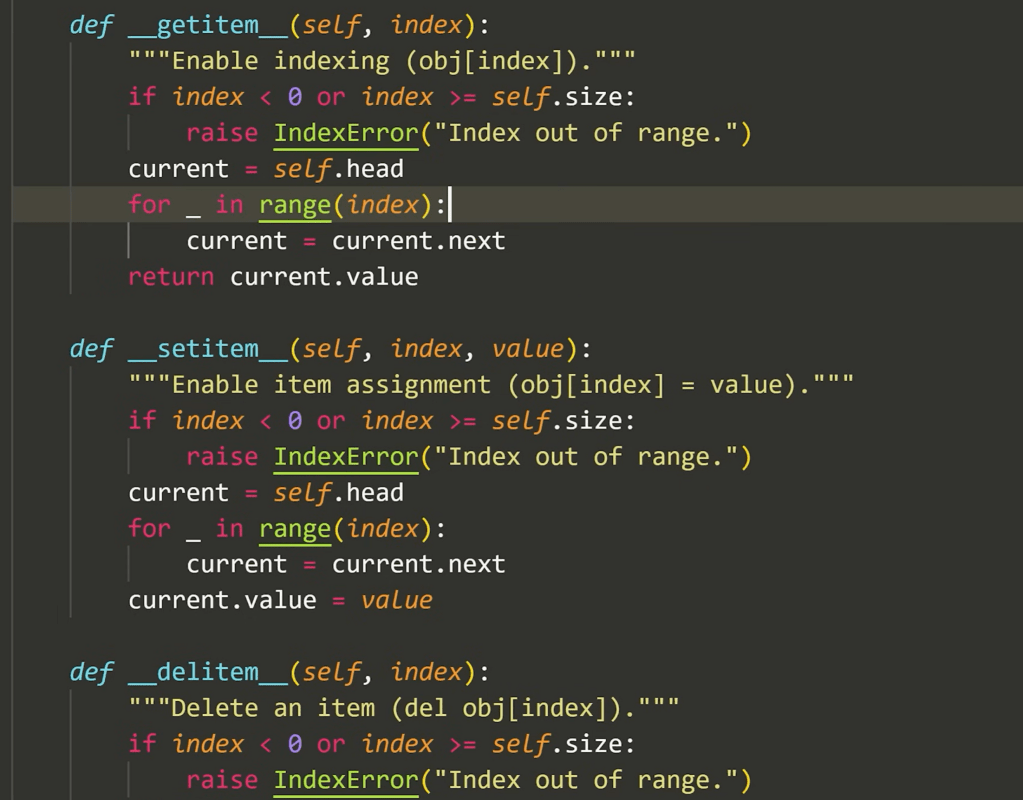
thundermethod:
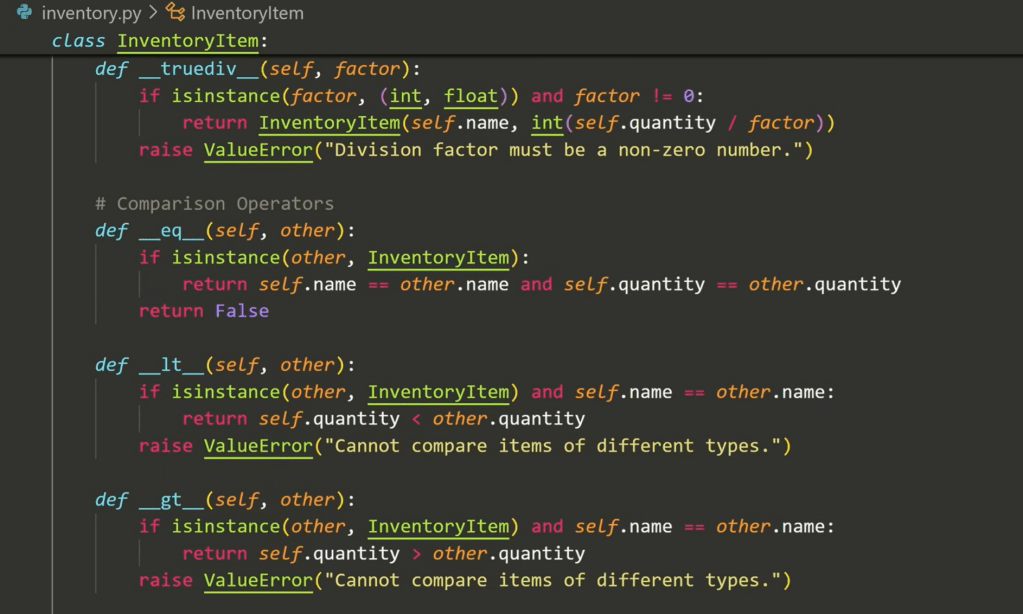
Note the index operation is also a thundermethod
Context manager has enter and exit thundermethod.
Iterator has iter and next thundermethod.
