🔰 Stage 1: Foundations of Networking
✅ Concepts:
- What is a network (LAN, WAN, WLAN, internet)
- Packet-switched vs. circuit-switched networks
- Basic networking terminology
✅ Topics to Study:
- OSI & TCP/IP Models
- 7-layer OSI model: physical to application
- TCP/IP 4-layer model
- IP Addressing & Subnetting
- IPv4 vs IPv6
- Public vs private IP
- CIDR, subnet masks
- MAC Addresses & ARP (A MAC address (Media Access Control address) is a unique identifier assigned to a device’s network interface card (NIC) for communication on a local network (LAN). It’s a 12-digit hexadecimal address like
00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E, used at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model.)- Device-level addressing
- Address Resolution Protocol
- Devices & Roles
- Modem, router, switch, access point, repeater, hub
- Protocols (Basic Overview)
- TCP, UDP
- ICMP (ping)
- DNS, DHCP
TCP use curl http://example.com/, ICM use Ping, DNS nslookup
TCP:
[SYN] → [SYN-ACK] → [ACK]
→ Data1 [ACK]
→ Data2 [ACK]
→ FIN/ACK to close
UDP:
→ Data (sent)
→ Data (maybe arrives, maybe not)
→ No ACK, no connection, no close
📡 Stage 2: Internet Communication & Protocols
✅ Topics to Study:
- TCP/IP Deep Dive
- Three-way handshake (SYN, ACK)
- we can use wireshark, or write a python socket file as below to see how three-way handshake is realized:
output in console is HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 1256
Connection: close
…
then actual html body<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Example Domain</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
...
</head>
<body>
<div>
<h1>Example Domain</h1>
<p>This domain is for use in illustrative examples in documents...</p>
</div>
</body>
</html> - HTTP/HTTPS
- Request/response cycle
- Headers, status codes
- HTTPS (TLS encryption)
- DNS (Domain Name System)
- How names resolve to IPs
- Recursive vs authoritative DNS
- Ports & Sockets
- Well-known ports (e.g., 80, 443, 22)
- Client/server architecture
- Binding to IP and port
HTTP or HTTPS is just one protocol devices communicate with each other, we can have others like the following table, we can also create our own custom protocol as shown in below python codes
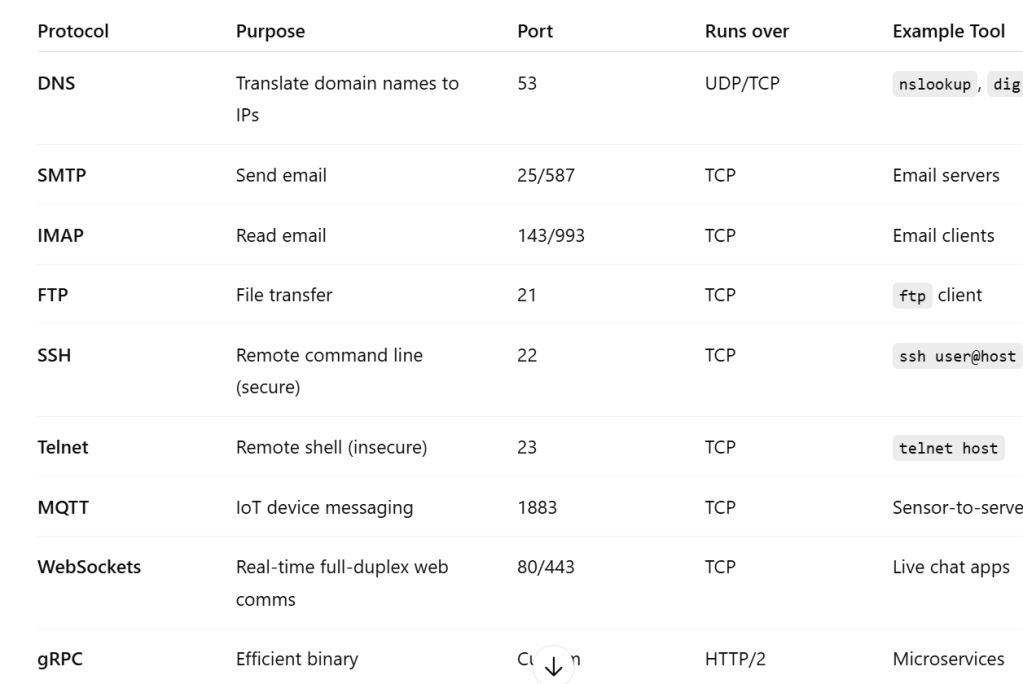
📶 Stage 3: Wireless & Mobile Networking
✅ Topics to Study:
- Wi-Fi (802.11 standards)
- 2.4GHz vs 5GHz vs 6GHz
- Channels, interference, SSID, WPA3 security
- Bluetooth & BLE
- Pairing and communication
- Device roles (peripheral, central)
- Cellular Networks
- 3G, 4G, 5G architecture
- SIM cards, mobile data, roaming
- IoT Communication Protocols
- MQTT, CoAP, Zigbee, Z-Wave
- Low-power wide-area networks (LoRaWAN, NB-IoT)
🌐 Stage 4: Application Layer & Modern Use Cases
✅ Topics to Study:
- WebSockets & Real-Time Communication
- WebSockets vs HTTP
- Pub/Sub patterns
- REST vs gRPC vs GraphQL
- API design and communication models
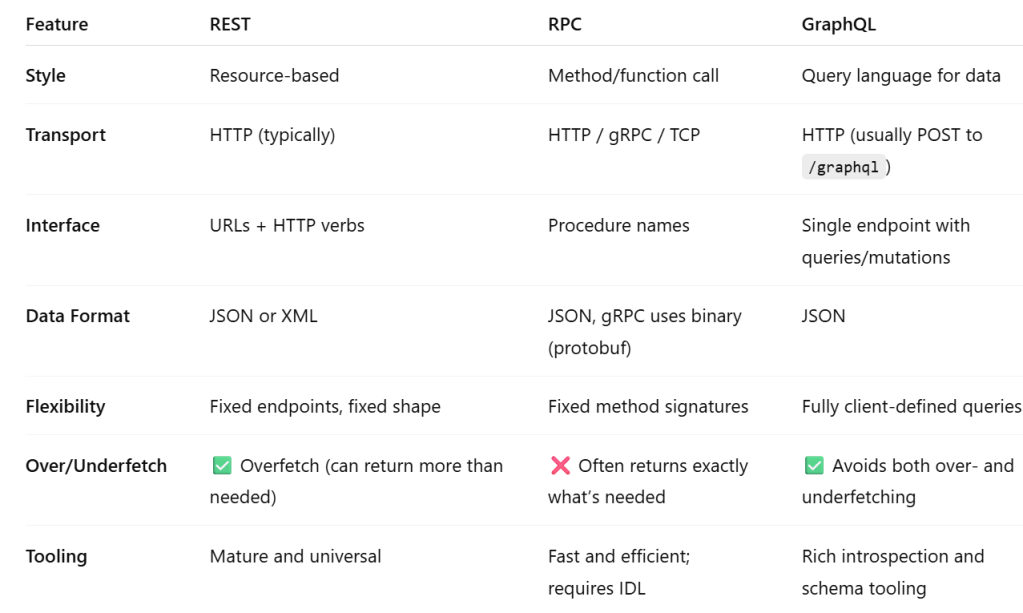
- Network Security Essentials
- TLS/SSL
- VPNs
- Firewalls and NAT
- Zero Trust networking
- Cloud Networking Concepts
- VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
- Load balancers
- CDN (Cloudflare, Akamai)
- Network-as-a-Service (AWS VPC, Azure VNets)
When we build a RESTful API, we’re designing an interface that exposes resources over HTTP, using URLs and standard HTTP methods. The server responds with data — often in JSON or XML — which is transported over TCP.
🔬 Stage 5: Tools, Troubleshooting & Advanced Concepts
✅ Tools to Learn:
ping,traceroute,netstat,ifconfig/ip- Wireshark (packet analysis)
- Nmap (network scanning)
curl,telnet,dig,nslookup
✅ Advanced Topics:
- SDN (Software Defined Networking)
- Network virtualization
- Network performance metrics (latency, jitter, throughput)
- Routing algorithms (BGP, OSPF)
socket.py
import socket
# Create a TCP socket
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# Connect to the server (this performs SYN → SYN-ACK → ACK under the hood)
server_address = ('example.com', 80)
sock.connect(server_address)
# Send HTTP GET request
request = b"GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: example.com\r\nConnection: close\r\n\r\n"
sock.sendall(request)
# Receive the response
response = b""
while True:
data = sock.recv(4096)
if not data:
break
response += data
print(response.decode(errors='ignore'))
# Close the connection (initiates FIN → ACK teardown)
sock.close()
custom protocol to communicate
import socket
s = socket.socket()
s.bind(('0.0.0.0', 12345)) # your custom port
s.listen(1)
conn, addr = s.accept()
data = conn.recv(1024)
print("Received:", data)
conn.send(b'Hello from custom protocol!')