I’ve built a basic data science AI agent already so would be great to learn from other similar agents, this one ai-data-science-team/examples/README.md at master · business-science/ai-data-science-team is a good reference.
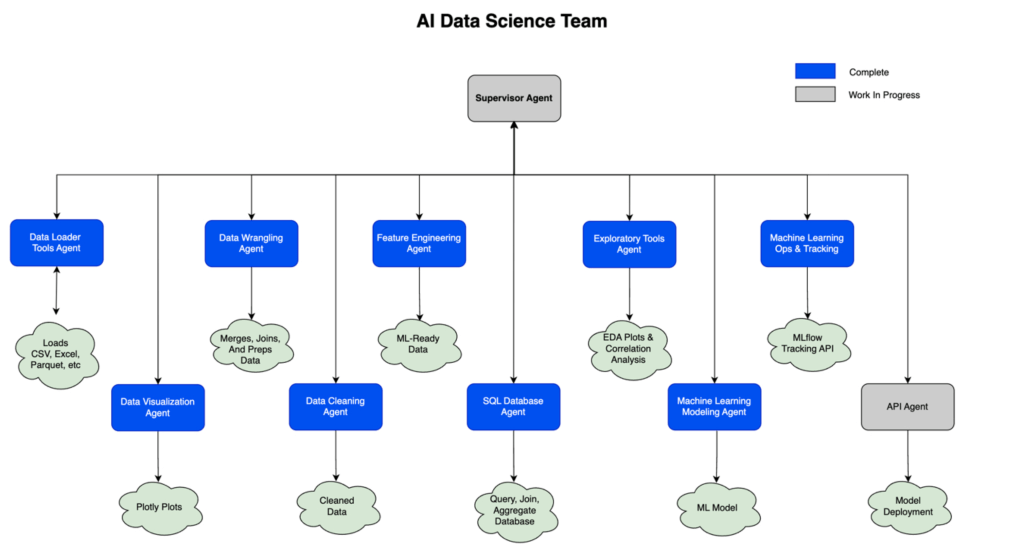
The structure mainly is at
Dive to the sql_database_agent.py to view how it leverage LLM to write sql queries. It calls upon a sql tool from tools folder:
import pandas as pdimport sqlalchemy as sqlfrom sqlalchemy import inspectdef get_database_metadata(connection, n_samples=10) -> dict: """ Collects metadata and sample data from a database, with safe identifier quoting and basic dialect-aware row limiting. Prevents issues with spaces/reserved words in identifiers. Parameters ---------- connection : Union[sql.engine.base.Connection, sql.engine.base.Engine] An active SQLAlchemy connection or engine. n_samples : int Number of sample values to retrieve for each column. Returns ------- dict A dictionary with database metadata, including some sample data from each column. """ is_engine = isinstance(connection, sql.engine.base.Engine) conn = connection.connect() if is_engine else connection metadata = { "dialect": None, "driver": None, "connection_url": None, "schemas": [], } try: sql_engine = conn.engine dialect_name = sql_engine.dialect.name.lower() metadata["dialect"] = sql_engine.dialect.name metadata["driver"] = sql_engine.driver try: metadata["connection_url"] = sql_engine.url.render_as_string( hide_password=True ) except Exception: metadata["connection_url"] = str(sql_engine.url) inspector = inspect(sql_engine) preparer = inspector.bind.dialect.identifier_preparer # For each schema for schema_name in inspector.get_schema_names(): schema_obj = {"schema_name": schema_name, "tables": []} tables = inspector.get_table_names(schema=schema_name) for table_name in tables: table_info = { "table_name": table_name, "columns": [], "primary_key": [], "foreign_keys": [], "indexes": [], } # Get columns columns = inspector.get_columns(table_name, schema=schema_name) for col in columns: col_name = col["name"] col_type = str(col["type"]) table_name_quoted = f"{preparer.quote_identifier(schema_name)}.{preparer.quote_identifier(table_name)}" col_name_quoted = preparer.quote_identifier(col_name) # Build query for sample data query = build_query( col_name_quoted, table_name_quoted, n_samples, dialect_name ) # Retrieve sample data try: df = pd.read_sql(query, conn) samples = df[col_name].head(n_samples).tolist() except Exception as e: samples = [f"Error retrieving data: {str(e)}"] table_info["columns"].append( {"name": col_name, "type": col_type, "sample_values": samples} ) # Primary keys pk_constraint = inspector.get_pk_constraint( table_name, schema=schema_name ) table_info["primary_key"] = pk_constraint.get("constrained_columns", []) # Foreign keys fks = inspector.get_foreign_keys(table_name, schema=schema_name) table_info["foreign_keys"] = [ { "local_cols": fk["constrained_columns"], "referred_table": fk["referred_table"], "referred_cols": fk["referred_columns"], } for fk in fks ] # Indexes idxs = inspector.get_indexes(table_name, schema=schema_name) table_info["indexes"] = idxs schema_obj["tables"].append(table_info) metadata["schemas"].append(schema_obj) finally: if is_engine: conn.close() return metadatadef build_query( col_name_quoted: str, table_name_quoted: str, n: int, dialect_name: str) -> str: # Example: expand your build_query to handle random sampling if possible if "postgres" in dialect_name: return f"SELECT {col_name_quoted} FROM {table_name_quoted} ORDER BY RANDOM() LIMIT {n}" if "mysql" in dialect_name: return f"SELECT {col_name_quoted} FROM {table_name_quoted} ORDER BY RAND() LIMIT {n}" if "sqlite" in dialect_name: return f"SELECT {col_name_quoted} FROM {table_name_quoted} ORDER BY RANDOM() LIMIT {n}" if "mssql" in dialect_name: return f"SELECT TOP {n} {col_name_quoted} FROM {table_name_quoted} ORDER BY NEWID()" # Oracle or fallback return f"SELECT {col_name_quoted} FROM {table_name_quoted} WHERE ROWNUM <= {n}"and here is the sql_database_agent.py
from typing_extensions import TypedDict, Annotated, Sequence, Literalimport operatorfrom langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplatefrom langchain_core.messages import BaseMessagefrom langchain_core.output_parsers import JsonOutputParserfrom langgraph.types import Commandfrom langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaverimport osimport jsonimport pandas as pdimport sqlalchemy as sqlfrom IPython.display import Markdownfrom ai_data_science_team.templates import ( node_func_execute_agent_from_sql_connection, node_func_human_review, node_func_fix_agent_code, node_func_report_agent_outputs, create_coding_agent_graph, BaseAgent,)from ai_data_science_team.parsers.parsers import SQLOutputParserfrom ai_data_science_team.utils.regex import ( add_comments_to_top, format_agent_name, format_recommended_steps, get_generic_summary,)from ai_data_science_team.tools.sql import get_database_metadatafrom ai_data_science_team.utils.logging import log_ai_function, log_ai_errorfrom ai_data_science_team.utils.messages import get_last_user_message_content# SetupAGENT_NAME = "sql_database_agent"LOG_PATH = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "logs/")MAX_SCHEMA_CHARS = 5000DEFAULT_SQL_STEPS = format_recommended_steps( """1. Inspect available schemas/tables and note key columns and primary keys.2. Identify tables needed to answer the question and the join keys between them.3. Select only the columns required; avoid SELECT * unless explicitly requested.4. Apply filters from user instructions; avoid modifying data (read-only SELECT).5. Aggregate or sort as instructed; do not add LIMIT unless the user asks.6. Return a single SELECT query that can run on the provided database dialect. """, heading="# Recommended SQL Database Steps:",)# Classclass SQLDatabaseAgent(BaseAgent): """ Creates a SQL Database Agent that can recommend SQL steps and generate SQL code to query a database. The agent can: - Propose recommended steps to answer a user's query or instructions. - Generate a SQL query based on the recommended steps and user instructions. - Execute that SQL query against the provided database connection. - Return the resulting data as a dictionary, suitable for conversion to a DataFrame or other structures. - Log generated code and errors if enabled. Parameters ---------- model : ChatOpenAI or langchain.llms.base.LLM The language model used to generate the SQL code. connection : sqlalchemy.engine.base.Engine or sqlalchemy.engine.base.Connection The SQLAlchemy connection (or engine) to the database. n_samples : int, optional Number of sample rows (per column) to retrieve when summarizing database metadata. Defaults to 1. log : bool, optional Whether to log the generated code and errors. Defaults to False. log_path : str, optional Directory path for storing log files. Defaults to None. file_name : str, optional Name of the file for saving the generated response. Defaults to "sql_database.py". function_name : str, optional Name of the Python function that executes the SQL query. Defaults to "sql_database_pipeline". overwrite : bool, optional Whether to overwrite the log file if it exists. If False, a unique file name is created. Defaults to True. human_in_the_loop : bool, optional Enables user review of the recommended steps before generating code. Defaults to False. bypass_recommended_steps : bool, optional If True, skips the step that generates recommended SQL steps. Defaults to False. bypass_explain_code : bool, optional If True, skips the step that provides code explanations. Defaults to False. checkpointer : Checkpointer, optional A checkpointer to save and load the agent's state. Defaults to None. smart_schema_pruning : bool, optional If True, filters the tables and columns based on the user instructions and recommended steps. Defaults to False. safe_mode : bool, optional If True (default), enforces read-only SELECT queries; set to False to allow non-SELECT queries at your own risk. Methods ------- update_params(**kwargs) Updates the agent's parameters and rebuilds the compiled state graph. ainvoke_agent(user_instructions: str, max_retries=3, retry_count=0) Asynchronously runs the agent to generate and execute a SQL query based on user instructions. invoke_agent(user_instructions: str, max_retries=3, retry_count=0) Synchronously runs the agent to generate and execute a SQL query based on user instructions. get_workflow_summary() Retrieves a summary of the agent's workflow. get_log_summary() Retrieves a summary of logged operations if logging is enabled. get_data_sql() Retrieves the resulting data from the SQL query as a dictionary. (You can convert this to a DataFrame if desired.) get_sql_query_code() Retrieves the exact SQL query generated by the agent. get_sql_database_function() Retrieves the Python function that executes the SQL query. get_recommended_sql_steps() Retrieves the recommended steps for querying the SQL database. get_response() Returns the full response dictionary from the agent. show() Displays the agent's mermaid diagram for visual inspection of the compiled graph. Examples -------- ```python import sqlalchemy as sql from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI from ai_data_science_team.agents import SQLDatabaseAgent # Create the engine/connection sql_engine = sql.create_engine("sqlite:///data/my_database.db") conn = sql_engine.connect() llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini") sql_database_agent = SQLDatabaseAgent( model=llm, connection=conn, n_samples=10, log=True, log_path="logs", human_in_the_loop=True ) # Example usage sql_database_agent.invoke_agent( user_instructions="List all the tables in the database.", max_retries=3, retry_count=0 ) data_result = sql_database_agent.get_data_sql() # dictionary of rows returned sql_code = sql_database_agent.get_sql_query_code() response = sql_database_agent.get_response() ``` Returns ------- SQLDatabaseAgent : langchain.graphs.CompiledStateGraph A SQL database agent implemented as a compiled state graph. """ def __init__( self, model, connection, n_samples=1, log=False, log_path=None, file_name="sql_database.py", function_name="sql_database_pipeline", overwrite=True, human_in_the_loop=False, bypass_recommended_steps=False, bypass_explain_code=False, checkpointer=None, smart_schema_pruning=False, safe_mode=True, ): self._params = { "model": model, "connection": connection, "n_samples": n_samples, "log": log, "log_path": log_path, "file_name": file_name, "function_name": function_name, "overwrite": overwrite, "human_in_the_loop": human_in_the_loop, "bypass_recommended_steps": bypass_recommended_steps, "bypass_explain_code": bypass_explain_code, "checkpointer": checkpointer, "smart_schema_pruning": smart_schema_pruning, "safe_mode": safe_mode, } self._compiled_graph = self._make_compiled_graph() self.response = None def _make_compiled_graph(self): """ Create or rebuild the compiled graph for the SQL Database Agent. Running this method resets the response to None. """ self.response = None return make_sql_database_agent(**self._params) def update_params(self, **kwargs): """ Updates the agent's parameters (e.g. connection, n_samples, log, etc.) and rebuilds the compiled graph. """ for k, v in kwargs.items(): self._params[k] = v self._compiled_graph = self._make_compiled_graph() async def ainvoke_agent( self, user_instructions: str = None, max_retries=3, retry_count=0, **kwargs ): """ Asynchronously runs the SQL Database Agent based on user instructions. Parameters ---------- user_instructions : str Instructions for the SQL query or metadata request. max_retries : int, optional Maximum retry attempts. Defaults to 3. retry_count : int, optional Current retry count. Defaults to 0. kwargs : dict Additional keyword arguments to pass to ainvoke(). Returns ------- None """ messages = kwargs.pop("messages", None) if messages is None: messages = [("user", user_instructions)] response = await self._compiled_graph.ainvoke( { "messages": messages, "user_instructions": user_instructions, "max_retries": max_retries, "retry_count": retry_count, }, **kwargs, ) self.response = response return None def invoke_agent( self, user_instructions: str = None, max_retries=3, retry_count=0, **kwargs ): """ Synchronously runs the SQL Database Agent based on user instructions. Parameters ---------- user_instructions : str Instructions for the SQL query or metadata request. max_retries : int, optional Maximum retry attempts. Defaults to 3. retry_count : int, optional Current retry count. Defaults to 0. kwargs : dict Additional keyword arguments to pass to invoke(). Returns ------- None """ messages = kwargs.pop("messages", None) if messages is None: messages = [("user", user_instructions)] response = self._compiled_graph.invoke( { "messages": messages, "user_instructions": user_instructions, "max_retries": max_retries, "retry_count": retry_count, }, **kwargs, ) self.response = response return None def invoke_messages(self, messages: Sequence[BaseMessage], **kwargs): """ Runs the agent given an explicit message list (preferred for supervisors/teams). """ user_instructions = kwargs.pop("user_instructions", None) if user_instructions is None: user_instructions = get_last_user_message_content(messages) response = self._compiled_graph.invoke( { "messages": messages, "user_instructions": user_instructions, "max_retries": kwargs.pop("max_retries", 3), "retry_count": kwargs.pop("retry_count", 0), }, **kwargs, ) self.response = response return None async def ainvoke_messages(self, messages: Sequence[BaseMessage], **kwargs): """ Async version of invoke_messages. """ user_instructions = kwargs.pop("user_instructions", None) if user_instructions is None: user_instructions = get_last_user_message_content(messages) response = await self._compiled_graph.ainvoke( { "messages": messages, "user_instructions": user_instructions, "max_retries": kwargs.pop("max_retries", 3), "retry_count": kwargs.pop("retry_count", 0), }, **kwargs, ) self.response = response return None def get_workflow_summary(self, markdown=False): """ Retrieves the agent's workflow summary, if logging is enabled. """ if self.response and self.response.get("messages"): summary = get_generic_summary( json.loads(self.response.get("messages")[-1].content) ) if markdown: return Markdown(summary) else: return summary def get_log_summary(self, markdown=False): """ Logs a summary of the agent's operations, if logging is enabled. """ if self.response: if self.response.get("sql_database_function_path"): log_details = f"""## SQL Database Agent Log Summary:Function Path: {self.response.get("sql_database_function_path")}Function Name: {self.response.get("sql_database_function_name")} """ if markdown: return Markdown(log_details) else: return log_details def get_data_sql(self): """ Retrieves the SQL query result from the agent's response. Returns ------- dict or None The returned data as a dictionary of column -> list_of_values, or None if no data is found. """ if self.response and "data_sql" in self.response: return self.response["data_sql"] return None def get_sql_query_code(self, markdown=False): """ Retrieves the raw SQL query code generated by the agent (if available). Parameters ---------- markdown : bool, optional If True, returns the code in a Markdown code block. Returns ------- str or None The SQL query as a string, or None if not available. """ if self.response and "sql_query_code" in self.response: if markdown: return Markdown(f"```sql\n{self.response['sql_query_code']}\n```") return self.response["sql_query_code"] return None def get_sql_database_function(self, markdown=False): """ Retrieves the Python function code used to execute the SQL query. Parameters ---------- markdown : bool, optional If True, returns the code in a Markdown code block. Returns ------- str or None The function code if available, otherwise None. """ if self.response and "sql_database_function" in self.response: code = self.response["sql_database_function"] if markdown: return Markdown(f"```python\n{code}\n```") return code return None def get_recommended_sql_steps(self, markdown=False): """ Retrieves the recommended SQL steps from the agent's response. Parameters ---------- markdown : bool, optional If True, returns the steps in Markdown format. Returns ------- str or None Recommended steps or None if not available. """ if self.response and "recommended_steps" in self.response: if markdown: return Markdown(self.response["recommended_steps"]) return self.response["recommended_steps"] return None# Functiondef make_sql_database_agent( model, connection, n_samples=1, log=False, log_path=None, file_name="sql_database.py", function_name="sql_database_pipeline", overwrite=True, human_in_the_loop=False, bypass_recommended_steps=False, bypass_explain_code=False, checkpointer=None, smart_schema_pruning=False, safe_mode=True,): """ Creates a SQL Database Agent that can recommend SQL steps and generate SQL code to query a database. Parameters ---------- model : ChatOpenAI The language model to use for the agent. connection : sqlalchemy.engine.base.Engine The connection to the SQL database. n_samples : int, optional The number of samples to retrieve for each column, by default 1. If you get an error due to maximum tokens, try reducing this number. > "This model's maximum context length is 128000 tokens. However, your messages resulted in 333858 tokens. Please reduce the length of the messages." log : bool, optional Whether to log the generated code, by default False log_path : str, optional The path to the log directory, by default None file_name : str, optional The name of the file to save the generated code, by default "sql_database.py" overwrite : bool, optional Whether to overwrite the existing log file, by default True human_in_the_loop : bool, optional Whether or not to use human in the loop. If True, adds an interput and human in the loop step that asks the user to review the feature engineering instructions. Defaults to False. bypass_recommended_steps : bool, optional Bypass the recommendation step, by default False bypass_explain_code : bool, optional Bypass the code explanation step, by default False. checkpointer : Checkpointer, optional A checkpointer to save and load the agent's state. Defaults to None. smart_schema_pruning : bool, optional If True, filters the tables and columns with an extra LLM step to reduce tokens for large databases. Increases processing time but can avoid errors due to hitting max token limits with large databases. Defaults to False. safe_mode : bool, optional If True (default), enforces read-only SELECT queries. Set to False to allow non-SELECT queries at your own risk. Returns ------- app : langchain.graphs.CompiledStateGraph The data cleaning agent as a state graph. Examples -------- ```python from ai_data_science_team.agents import make_sql_database_agent import sqlalchemy as sql from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI sql_engine = sql.create_engine("sqlite:///data/leads_scored.db") conn = sql_engine.connect() llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini") sql_agent = make_sql_database_agent( model=llm, connection=conn ) sql_agent response = sql_agent.invoke({ "user_instructions": "List the tables in the database", "max_retries":3, "retry_count":0 }) ``` """ llm = model if human_in_the_loop: if checkpointer is None: print( "Human in the loop is enabled. A checkpointer is required. Setting to MemorySaver()." ) checkpointer = MemorySaver() # Human in th loop requires recommended steps if bypass_recommended_steps and human_in_the_loop: bypass_recommended_steps = False print("Bypass recommended steps set to False to enable human in the loop.") # Setup Log Directory if log: if log_path is None: log_path = LOG_PATH if not os.path.exists(log_path): os.makedirs(log_path) # Get the database metadata is_engine = isinstance(connection, sql.engine.base.Engine) conn = connection.connect() if is_engine else connection class GraphState(TypedDict): messages: Annotated[Sequence[BaseMessage], operator.add] user_instructions: str recommended_steps: str data_sql: dict all_sql_database_summary: str sql_query_code: str sql_database_function: str sql_database_function_path: str sql_database_function_file_name: str sql_database_function_name: str sql_database_error: str sql_database_error_log_path: str max_retries: int retry_count: int def recommend_sql_steps(state: GraphState): print(format_agent_name(AGENT_NAME)) all_sql_database_summary = _truncate_metadata( get_database_metadata(conn, n_samples=n_samples) ) all_sql_database_summary = smart_schema_filter( llm, state.get("user_instructions"), all_sql_database_summary, smart_filtering=smart_schema_pruning, ) print(" * RECOMMEND STEPS") # Prompt to get recommended steps from the LLM recommend_steps_prompt = PromptTemplate( template=""" You are a SQL Database Instructions Expert. Given the following information about the SQL database, recommend a series of numbered steps to take to collect the data and process it according to user instructions. The steps should be tailored to the SQL database characteristics and should be helpful for a sql database coding agent that will write the SQL code. IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: - Take into account the user instructions and the previously recommended steps. - If no user instructions are provided, just return the steps needed to understand the database. - Take into account the database dialect and the tables and columns in the database. - Pay attention to use only the column names you can see in the tables below. Be careful to not query for columns that do not exist. Also, pay attention to which column is in which table. - IMPORTANT: Pay attention to the table names and column names in the database. Make sure to use the correct table and column names in the SQL code. If a space is present in the table name or column name, make sure to account for it. User instructions / Question: {user_instructions} Previously Recommended Steps (if any): {recommended_steps} Below are summaries of the database metadata and the SQL tables: {all_sql_database_summary} Return steps as a numbered list. You can return short code snippets to demonstrate actions. But do not return a fully coded solution. The code will be generated separately by a Coding Agent. Consider these: 1. Consider the database dialect and the tables and columns in the database. Avoid these: 1. Do not include steps to save files. 2. Do not include steps to modify existing tables, create new tables or modify the database schema. 3. Do not include steps that alter the existing data in the database. 4. Make sure not to include unsafe code that could cause data loss or corruption or SQL injections. 5. Make sure to not include irrelevant steps that do not help in the SQL agent's data collection and processing. Examples include steps to create new tables, modify the schema, save files, create charts, etc. """, input_variables=[ "user_instructions", "recommended_steps", "all_sql_database_summary", ], ) steps_agent = recommend_steps_prompt | llm recommended_steps = steps_agent.invoke( { "user_instructions": state.get("user_instructions"), "recommended_steps": state.get("recommended_steps"), "all_sql_database_summary": all_sql_database_summary, } ) return { "recommended_steps": format_recommended_steps( recommended_steps.content.strip(), heading="# Recommended SQL Database Steps:", ), "all_sql_database_summary": all_sql_database_summary, } def create_sql_query_code(state: GraphState): if bypass_recommended_steps: print(format_agent_name(AGENT_NAME)) all_sql_database_summary = _truncate_metadata( get_database_metadata(conn, n_samples=n_samples) ) all_sql_database_summary = smart_schema_filter( llm, state.get("user_instructions"), all_sql_database_summary, smart_filtering=smart_schema_pruning, ) steps_for_prompt = state.get("recommended_steps") or DEFAULT_SQL_STEPS else: all_sql_database_summary = state.get("all_sql_database_summary") steps_for_prompt = state.get("recommended_steps") or DEFAULT_SQL_STEPS print(" * CREATE SQL QUERY CODE") # Prompt to get the SQL code from the LLM sql_query_code_prompt = PromptTemplate( template=""" You are a SQL Database Coding Expert. Given the following information about the SQL database, write the SQL code to collect the data and process it according to user instructions. The code should be tailored to the SQL database characteristics and should take into account user instructions, recommended steps, database and table characteristics. IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: - Do not use a LIMIT clause unless a user specifies a limit to be returned. - Return SQL in ```sql ``` format. - Only return a single query if possible. - Pay attention to use only the column names you can see in the tables below. Be careful to not query for columns that do not exist. Also, pay attention to which column is in which table. - Pay attention to the SQL dialect from the database summary metadata. Write the SQL code according to the dialect specified. - IMPORTANT: Pay attention to the table names and column names in the database. Make sure to use the correct table and column names in the SQL code. If a space is present in the table name or column name, make sure to account for it. User instructions / Question: {user_instructions} Recommended Steps: {recommended_steps} Below are summaries of the database metadata and the SQL tables: {all_sql_database_summary} Return: - The SQL code in ```sql ``` format to collect the data and process it according to the user instructions. Avoid these: - Do not include steps to save files. - Do not include steps to modify existing tables, create new tables or modify the database schema. - Make sure not to alter the existing data in the database. - Make sure not to include unsafe code that could cause data loss or corruption. """, input_variables=[ "user_instructions", "recommended_steps", "all_sql_database_summary", ], ) sql_query_code_agent = sql_query_code_prompt | llm | SQLOutputParser() sql_query_code = sql_query_code_agent.invoke( { "user_instructions": state.get("user_instructions"), "recommended_steps": steps_for_prompt, "all_sql_database_summary": all_sql_database_summary, } ) validation_error = _validate_sql(sql_query_code, safe_mode=safe_mode) if validation_error: return { "sql_query_code": sql_query_code, "sql_database_error": validation_error, "all_sql_database_summary": all_sql_database_summary, "recommended_steps": steps_for_prompt, } print(" * CREATE PYTHON FUNCTION TO RUN SQL CODE") response = f"""def {function_name}(connection): import pandas as pd import sqlalchemy as sql # Create a connection if needed is_engine = isinstance(connection, sql.engine.base.Engine) sql_query = ''' {sql_query_code} '''.strip() if is_engine: with connection.connect() as conn: return pd.read_sql(sql_query, conn) return pd.read_sql(sql_query, connection) """ response = add_comments_to_top(response, AGENT_NAME) # For logging: store the code generated file_path, file_name_2 = log_ai_function( response=response, file_name=file_name, log=log, log_path=log_path, overwrite=overwrite, ) return { "sql_query_code": sql_query_code, "sql_database_function": response, "sql_database_function_path": file_path, "sql_database_function_file_name": file_name_2, "sql_database_function_name": function_name, "all_sql_database_summary": all_sql_database_summary, "recommended_steps": steps_for_prompt, } # Human Review prompt_text_human_review = "Are the following SQL agent instructions correct? (Answer 'yes' or provide modifications)\n{steps}" if not bypass_explain_code: def human_review( state: GraphState, ) -> Command[Literal["recommend_sql_steps", "report_agent_outputs"]]: return node_func_human_review( state=state, prompt_text=prompt_text_human_review, yes_goto="report_agent_outputs", no_goto="recommend_sql_steps", user_instructions_key="user_instructions", recommended_steps_key="recommended_steps", code_snippet_key="sql_database_function", ) else: def human_review( state: GraphState, ) -> Command[Literal["recommend_sql_steps", "__end__"]]: return node_func_human_review( state=state, prompt_text=prompt_text_human_review, yes_goto="__end__", no_goto="recommend_sql_steps", user_instructions_key="user_instructions", recommended_steps_key="recommended_steps", code_snippet_key="sql_database_function", ) def execute_sql_database_code(state: GraphState): # If validation failed earlier, short-circuit and log if state.get("sql_database_error"): error_prefixed = state.get("sql_database_error") error_log_path = None if log: error_log_path = log_ai_error( error_message=error_prefixed, file_name=f"{file_name}_errors.log", log=log, log_path=log_path if log_path is not None else LOG_PATH, overwrite=False, ) if error_log_path: print(f" Error logged to: {error_log_path}") return { "data_sql": None, "sql_database_error": error_prefixed, "sql_database_error_log_path": error_log_path, } is_engine = isinstance(connection, sql.engine.base.Engine) conn = connection.connect() if is_engine else connection result = node_func_execute_agent_from_sql_connection( state=state, connection=conn, result_key="data_sql", error_key="sql_database_error", code_snippet_key="sql_database_function", agent_function_name=state.get("sql_database_function_name"), post_processing=lambda df: df.to_dict() if isinstance(df, pd.DataFrame) else df, error_message_prefix="An error occurred during executing the sql database pipeline: ", ) error_prefixed = result.get("sql_database_error") error_log_path = None if error_prefixed and log: error_log_path = log_ai_error( error_message=error_prefixed, file_name=f"{file_name}_errors.log", log=log, log_path=log_path if log_path is not None else LOG_PATH, overwrite=False, ) if error_log_path: print(f" Error logged to: {error_log_path}") result["sql_database_error_log_path"] = error_log_path return result def fix_sql_database_code(state: GraphState): prompt = """ You are a SQL Database Agent code fixer. Your job is to create a {function_name}(connection) function that can be run on a sql connection. The function is currently broken and needs to be fixed. Make sure to only return the function definition for {function_name}(). Return Python code in ```python``` format with a single function definition, {function_name}(connection), that includes all imports inside the function. The connection object is a SQLAlchemy connection object. Don't specify the class of the connection object, just use it as an argument to the function. This is the broken code (please fix): {code_snippet} Last Known Error: {error} """ return node_func_fix_agent_code( state=state, code_snippet_key="sql_database_function", error_key="sql_database_error", llm=llm, prompt_template=prompt, agent_name=AGENT_NAME, log=log, file_path=state.get("sql_database_function_path", None), function_name=state.get("sql_database_function_name"), ) # Final reporting node def report_agent_outputs(state: GraphState): return node_func_report_agent_outputs( state=state, keys_to_include=[ "recommended_steps", "sql_database_function", "sql_database_function_path", "sql_database_function_name", "sql_query_code", "sql_database_error", "sql_database_error_log_path", ], result_key="messages", role=AGENT_NAME, custom_title="SQL Database Agent Outputs", ) # Create the graph node_functions = { "recommend_sql_steps": recommend_sql_steps, "human_review": human_review, "create_sql_query_code": create_sql_query_code, "execute_sql_database_code": execute_sql_database_code, "fix_sql_database_code": fix_sql_database_code, "report_agent_outputs": report_agent_outputs, } app = create_coding_agent_graph( GraphState=GraphState, node_functions=node_functions, recommended_steps_node_name="recommend_sql_steps", create_code_node_name="create_sql_query_code", execute_code_node_name="execute_sql_database_code", fix_code_node_name="fix_sql_database_code", explain_code_node_name="report_agent_outputs", error_key="sql_database_error", human_in_the_loop=human_in_the_loop, human_review_node_name="human_review", checkpointer=checkpointer, bypass_recommended_steps=bypass_recommended_steps, bypass_explain_code=bypass_explain_code, agent_name=AGENT_NAME, ) return appdef smart_schema_filter( llm, user_instructions, all_sql_database_summary, smart_filtering=True): """ This function filters the tables and columns based on the user instructions and the recommended steps. """ # Smart schema filtering if smart_filtering: print(" * SMART FILTER SCHEMA") filter_schema_prompt = PromptTemplate( template=""" You are a highly skilled data engineer. The user question is: "{user_instructions}" You have the full database metadata in JSON format below: {all_sql_database_summary} Please return ONLY the subset of this metadata that is relevant to answering the user’s question. - Preserve the same JSON structure for "schemas" -> "tables" -> "columns". - If any schemas/tables are irrelevant, omit them entirely. - If some columns in a relevant table are not needed, you can still keep them if you aren't sure. - However, try to keep only the minimum amount of data required to answer the user’s question. Return a valid JSON object. Do not include any additional explanation or text outside of the JSON. """, input_variables=["user_instructions", "all_sql_database_summary"], ) filter_schema_agent = filter_schema_prompt | llm | JsonOutputParser() try: response = filter_schema_agent.invoke( { "user_instructions": user_instructions, "all_sql_database_summary": all_sql_database_summary, } ) return response except Exception: return all_sql_database_summary else: return all_sql_database_summarydef _truncate_metadata(metadata: str) -> str: """Truncate metadata text to avoid overruns.""" if metadata is None: return "" if len(metadata) <= MAX_SCHEMA_CHARS: return metadata return metadata[:MAX_SCHEMA_CHARS] + "\n\n[truncated]"def _validate_sql(sql_text: str, safe_mode: bool = True): """ Basic safety checks to keep execution read-only. Returns an error message string if unsafe, else None. """ if not sql_text: return "SQL generation failed: empty query." if not safe_mode: return None lowered = sql_text.strip().lower() if not lowered.startswith("select"): return "Only read-only SELECT queries are allowed (safe_mode=True)." unsafe_keywords = ["insert", "update", "delete", "drop", "alter", "truncate", "create", "replace"] if any(kw in lowered for kw in unsafe_keywords): return "Write operations are not allowed; ensure the query is read-only (safe_mode=True)." return NoneThere are data_cleaning_agent, data_loader_tools_agent, data_visualization_agent, data_wrangling_agent, feature_engineering_agent, workflow_planner_agent. reference ai-data-science-team/ai_data_science_team/agents/data_cleaning_agent.py at master · business-science/ai-data-science-team