Lie Bracket is the Derivative of Conjugation, Hence Measuring How Rotation Fails to Commute! To illustrate this point, I’d like to start from the definition of Lie Algebra and Lie Bracket.
A Lie algebra is a vector space closed under lie bracket. Its elements represent infinitesimal motions, and whose bracket measures how these motions fail to commute — and this bracket is closed in the space.
Mathematically, A Lie algebra is:
A vector space equipped with a bilinear operation called the Lie bracket that satisfies specific axioms.

Another math definition of Lie Algebra is that it is the derivative of conjugation.
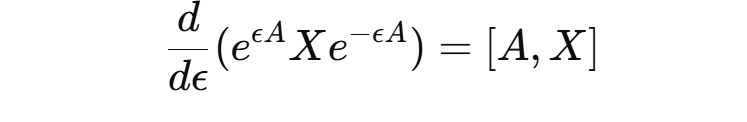
We also write it as
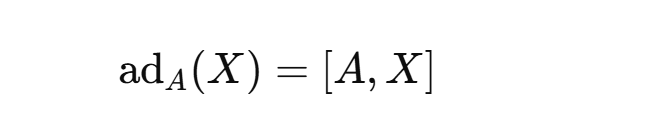
which means The adjoint action of on is the Lie bracket or The infinitesimal adjoint action generated by A sends X to their commutator.
Note the difference below: Ad = conjugation ; ad = infinitesimal conjugation

adjoint originates from French Mathematicians, means the self-representation.
To understand how this commutator or lie bracket measure the “motions fail to commute”, let’s use a concrete example.
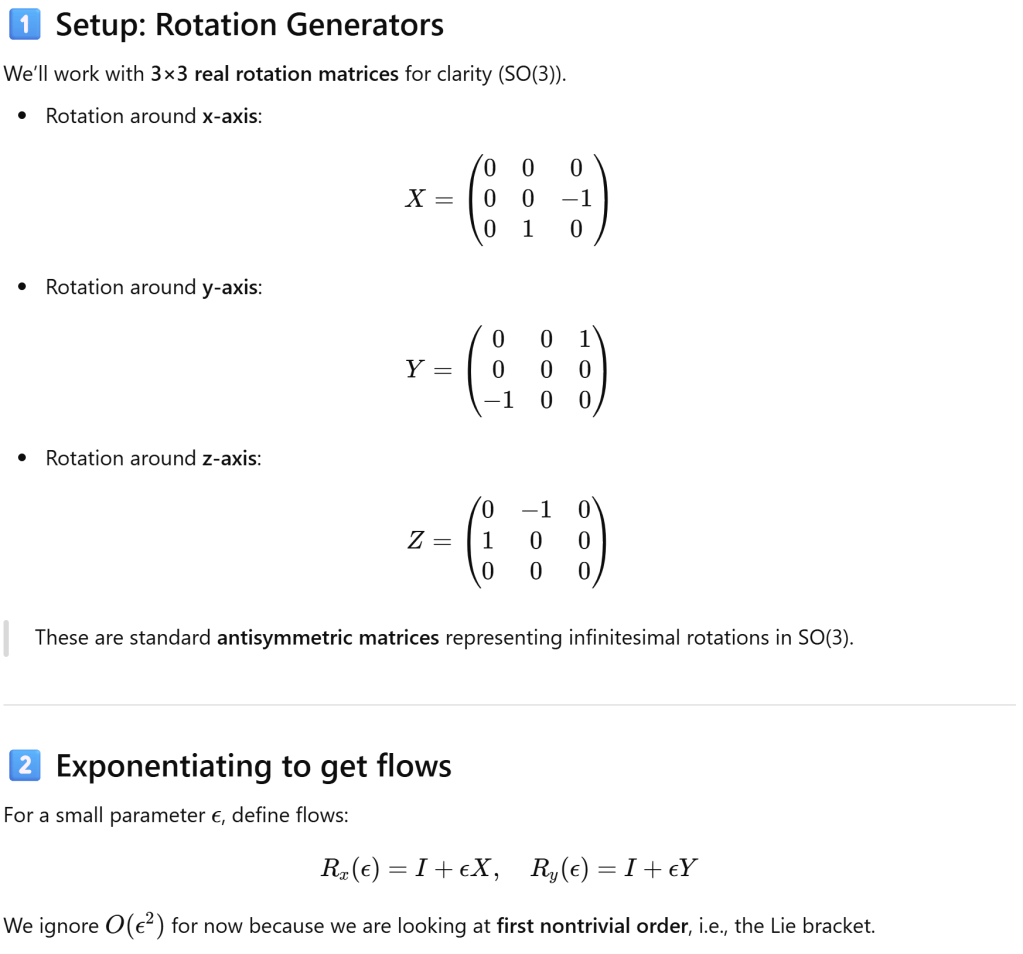

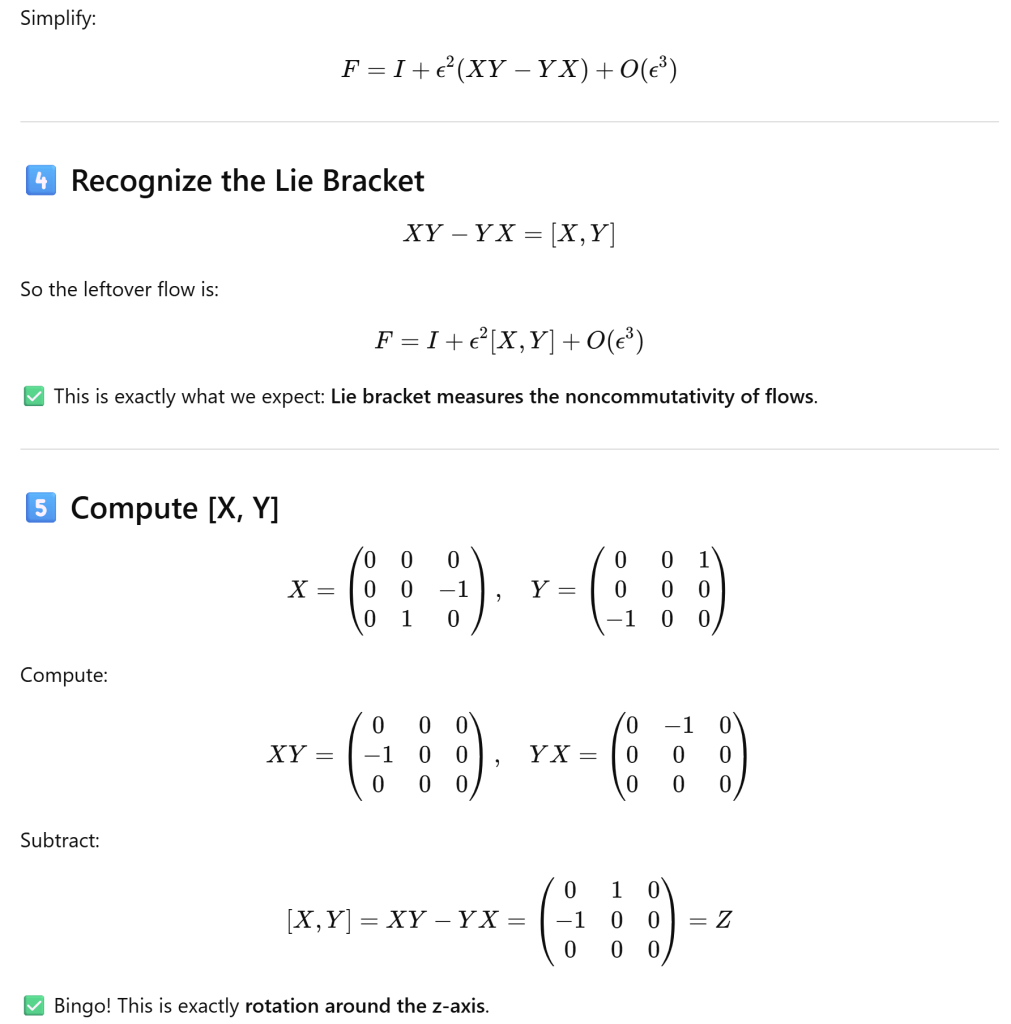
The measurement is NOT a real or complex value, it’s a structure represented or indicated by lie algebra element, closed!